Depression of Acetylcholinesterase Synthesis Following Transient
... enkephalin and tachykinins was markedly decreased (Chesselet et al 1990) These studies suggest that cholinergic neurons are more resistant to ischemia than other neurons In view of existing differences we decided to investigate the changes in AChE synthesis after cerebral ischemia Since a transient ...
... enkephalin and tachykinins was markedly decreased (Chesselet et al 1990) These studies suggest that cholinergic neurons are more resistant to ischemia than other neurons In view of existing differences we decided to investigate the changes in AChE synthesis after cerebral ischemia Since a transient ...
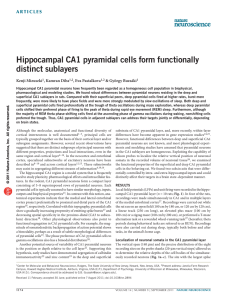
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally
... frequently, were more likely to have place fields and were more strongly modulated by slow oscillations of sleep. Both deep and superficial pyramidal cells fired preferentially at the trough of theta oscillations during maze exploration, whereas deep pyramidal cells shifted their preferred phase of ...
... frequently, were more likely to have place fields and were more strongly modulated by slow oscillations of sleep. Both deep and superficial pyramidal cells fired preferentially at the trough of theta oscillations during maze exploration, whereas deep pyramidal cells shifted their preferred phase of ...
Nerve Cells and Insect Behavior—Studies on Crickets1 This report
... FIG. 3. Visual and acoustical orientation of female Acheta domestica. A. Arrangement of the treadmill with a horizontal platform leaving an area of ca. 20 cm in diameter of the sphere open (dashed circle) for the cricket's movement. The pulsed-infrared scanning system is shown above this area. The v ...
... FIG. 3. Visual and acoustical orientation of female Acheta domestica. A. Arrangement of the treadmill with a horizontal platform leaving an area of ca. 20 cm in diameter of the sphere open (dashed circle) for the cricket's movement. The pulsed-infrared scanning system is shown above this area. The v ...
Temporal fate specification and neural progenitor competence
... called temporal patterning or temporal-identity specification (BOX 1). An understanding of temporal patterning mechanisms is important for multiple reasons: it will illuminate how spatial and temporal cues are integrated to generate specific cell types and how ageing progenitors change competence to ...
... called temporal patterning or temporal-identity specification (BOX 1). An understanding of temporal patterning mechanisms is important for multiple reasons: it will illuminate how spatial and temporal cues are integrated to generate specific cell types and how ageing progenitors change competence to ...
Ion Channels in Bursting Neurons
... that the conductances found in this axon are fewer and more simplified than those found in any other region of a typical neuron. The reason is that axons, in general, are highly customized neural structures. In the squid, the giant axon is solely responsible for assuring the rapid and regular conduc ...
... that the conductances found in this axon are fewer and more simplified than those found in any other region of a typical neuron. The reason is that axons, in general, are highly customized neural structures. In the squid, the giant axon is solely responsible for assuring the rapid and regular conduc ...
Article 5 - Graduate Program in Neuroscience | UBC
... two rewards appeared simultaneously at randomly alternating left and right target positions, allowing the animal to touch the lever of its choice following the trigger stimulus. Types of Task-related Activity Orbitofrontal neurons in area 11, rostral area 13 and lateral area 14 displayed only three ...
... two rewards appeared simultaneously at randomly alternating left and right target positions, allowing the animal to touch the lever of its choice following the trigger stimulus. Types of Task-related Activity Orbitofrontal neurons in area 11, rostral area 13 and lateral area 14 displayed only three ...
PDF file
... closed” throughout the lifetime. The “skull” of the network encapsulates the network from its external physical environment, leaving its sensory ends and its motor ends open to the external environment (other than the brain). Note that the body of the agent is also included in this external environm ...
... closed” throughout the lifetime. The “skull” of the network encapsulates the network from its external physical environment, leaving its sensory ends and its motor ends open to the external environment (other than the brain). Note that the body of the agent is also included in this external environm ...
Functional neuroanatomy of the primate isocortical motor system
... in layer V. However, these cells do not stop abruptly at the areal border. Instead, their density decreases gradually and there is considerable interindividual variability. If this criterion alone is used, the definition of the area 4/area 6 border becomes more or less arbitrary. This single criteri ...
... in layer V. However, these cells do not stop abruptly at the areal border. Instead, their density decreases gradually and there is considerable interindividual variability. If this criterion alone is used, the definition of the area 4/area 6 border becomes more or less arbitrary. This single criteri ...
Caudal Topographic Nucleus Isthmi and the Rostra1
... large, sparsely branched dendritic fields overlapped by local axon collaterals while distally, their axons nontopographically innervate not only the deeper layers of the ipsilateral tectum but also ipsilateral Imc. Imr receives a nontopographic tectal input that contrasts with the topographic tectal ...
... large, sparsely branched dendritic fields overlapped by local axon collaterals while distally, their axons nontopographically innervate not only the deeper layers of the ipsilateral tectum but also ipsilateral Imc. Imr receives a nontopographic tectal input that contrasts with the topographic tectal ...
The Structure and Plasticity of the Proximal Axon of Hippocampal
... molecules, with the exception of Ankyrin-G (AnkG). However, multipolar neurons regulate their intrinsic excitability via plastic changes in AIS length and location. Notably, understanding how the AIS plasticity is regulated may help understand its importance in neuro-pathologies like epilepsy, bipol ...
... molecules, with the exception of Ankyrin-G (AnkG). However, multipolar neurons regulate their intrinsic excitability via plastic changes in AIS length and location. Notably, understanding how the AIS plasticity is regulated may help understand its importance in neuro-pathologies like epilepsy, bipol ...
Sensory5
... Note: greater representation for body parts with richer sensory innervation, such as the fingers. *the representation is not static, however. Rather, it is based on use. (if a body’s sensory paths are damaged from a particular area, its cortical representation atrophies (shrinks)). 3. Modality-speci ...
... Note: greater representation for body parts with richer sensory innervation, such as the fingers. *the representation is not static, however. Rather, it is based on use. (if a body’s sensory paths are damaged from a particular area, its cortical representation atrophies (shrinks)). 3. Modality-speci ...
Differential Characteristics of Face Neuron Responses Within the
... opposed to facial view), as well as showing significant interactions between facial views and facial identity, respectively. The 131 face neurons showing a significant effect in response to facial views were further analyzed. In this paper, we focused on neuronal responses to match stimuli. However, ...
... opposed to facial view), as well as showing significant interactions between facial views and facial identity, respectively. The 131 face neurons showing a significant effect in response to facial views were further analyzed. In this paper, we focused on neuronal responses to match stimuli. However, ...
Dynamic shaping of dopamine signals during probabilistic
... ramping in the firing rate of dopamine neurons that correlates with the variance of reward, with a maximum response to CSs that predict rewards with a probability of 0.5 (Fiorillo et al., 2003). A variance-correlated signal can also be found in the nucleus accumbens, a downstream target of these neur ...
... ramping in the firing rate of dopamine neurons that correlates with the variance of reward, with a maximum response to CSs that predict rewards with a probability of 0.5 (Fiorillo et al., 2003). A variance-correlated signal can also be found in the nucleus accumbens, a downstream target of these neur ...
Researchers inch closer to causes, cures for insomnia, narcolepsy
... no prompting signal — a condition called primary insomnia. Regardless of the trigger (or lack thereof ), temporary insomnia has a nasty way of becoming a habit. Poor sleep habits can become ingrained. When trouble sleeping persists for three or four nights a week over several months, insomnia is con ...
... no prompting signal — a condition called primary insomnia. Regardless of the trigger (or lack thereof ), temporary insomnia has a nasty way of becoming a habit. Poor sleep habits can become ingrained. When trouble sleeping persists for three or four nights a week over several months, insomnia is con ...
Full version (PDF file)
... typically respond to the presence of odorant with an increase in the frequency of firing of action potentials (Getchell 1986) are the key element of the olfactory pathway. The detection and discrimination of different odorant molecules are correlated with the electrophysiology of the olfactory recep ...
... typically respond to the presence of odorant with an increase in the frequency of firing of action potentials (Getchell 1986) are the key element of the olfactory pathway. The detection and discrimination of different odorant molecules are correlated with the electrophysiology of the olfactory recep ...
PDF
... running with MATLAB (Mathworks, USA). The anatomical T1 image and the functional images were manually reoriented to the anterior commissure–posterior commissure line. Slice-time correction was conducted to adjust for time differences due to multi-slice imaging acquisition. To correct for between-scan ...
... running with MATLAB (Mathworks, USA). The anatomical T1 image and the functional images were manually reoriented to the anterior commissure–posterior commissure line. Slice-time correction was conducted to adjust for time differences due to multi-slice imaging acquisition. To correct for between-scan ...
Oral Pharmacotherapy of Childhood Movement Disorders
... premotor and supplementary motor cortices, whereas caudate-originating fibers terminate in the prefrontal cortex. Pallidal output inhibits the excitatory thalamocortical loop. The pallidum, in turn, is inhibited by the neostriatum, thus disinihibiting thalamocortical activity. The key neurotransmitt ...
... premotor and supplementary motor cortices, whereas caudate-originating fibers terminate in the prefrontal cortex. Pallidal output inhibits the excitatory thalamocortical loop. The pallidum, in turn, is inhibited by the neostriatum, thus disinihibiting thalamocortical activity. The key neurotransmitt ...
FINE STRUCTURE OF NERVE FIBERS AND GROWTH CONES OF
... in tissue culture tc continually undergo changes in conformation and to foster numerous transitory slender extensions (filopodia) a n d / o r a veillike ruffling sheet. After explantation of l-day-old rat superior cervical ganglia (as pieces or as individual neurons), nerve fibers and tips were phot ...
... in tissue culture tc continually undergo changes in conformation and to foster numerous transitory slender extensions (filopodia) a n d / o r a veillike ruffling sheet. After explantation of l-day-old rat superior cervical ganglia (as pieces or as individual neurons), nerve fibers and tips were phot ...
Motif distribution, dynamical properties, and computational
... between excitatory and inhibitory neurons located in different layers, i.e. layer 2/3, 4 and 5, differ significantly for the functional and the potential microcircuit template (see Thomson and Lamy, 2007). In addition this dataset also includes neurons in layer 6. We investigate these two cortical mi ...
... between excitatory and inhibitory neurons located in different layers, i.e. layer 2/3, 4 and 5, differ significantly for the functional and the potential microcircuit template (see Thomson and Lamy, 2007). In addition this dataset also includes neurons in layer 6. We investigate these two cortical mi ...
Experience-dependent corticofugal adjustment
... at 5.0 kHz above the ASr frequency. The behavioral response to an electrical leg stimulation (ESl) was leg flexion and body movement. When ASt followed by ESl was delivered for 30 min, the animal showed the behavioral response to every ESl, and in addition, it showed the response to ASt in the last ...
... at 5.0 kHz above the ASr frequency. The behavioral response to an electrical leg stimulation (ESl) was leg flexion and body movement. When ASt followed by ESl was delivered for 30 min, the animal showed the behavioral response to every ESl, and in addition, it showed the response to ASt in the last ...
Pathfinding in Computer Games
... E – Edges: A set of connections between the vertices, which can be either directed or not ...
... E – Edges: A set of connections between the vertices, which can be either directed or not ...
adult rat spinal cord culture on an organosilane surface in
... self-assembled monolayer, which had previously been shown to support neuronal, endothelial, and cardiac cell growth (Kleinfeld et al., 1988; Stenger et al., 1992; Spargo et al., 1994; Schaffner et al., 1995; Ravenscroft et al., 1998; Das et al., 2003, 2004), and had also been used in creating high-r ...
... self-assembled monolayer, which had previously been shown to support neuronal, endothelial, and cardiac cell growth (Kleinfeld et al., 1988; Stenger et al., 1992; Spargo et al., 1994; Schaffner et al., 1995; Ravenscroft et al., 1998; Das et al., 2003, 2004), and had also been used in creating high-r ...
Chapter 4 monkey
... visuomotor neurons and 1 motor neuron. One of the two target discs was placed in the RF of the recorded neuron and the other disc at an angle of 90 or 135 deg at a similar eccentricity (ranging from 8 to 18°) (Fig. 1). The stimuli were chosen such that one of the discs (saccade endpoints) fell well ...
... visuomotor neurons and 1 motor neuron. One of the two target discs was placed in the RF of the recorded neuron and the other disc at an angle of 90 or 135 deg at a similar eccentricity (ranging from 8 to 18°) (Fig. 1). The stimuli were chosen such that one of the discs (saccade endpoints) fell well ...
Wirth et al., 2009, Neuron
... learning of novel object-place-response associations. Recordings were made throughout the full anterior-posterior extent of the hippocampus, and based on MRI reconstructions, they appeared to include neurons from all hippocampal subdivisions (Figure 1D). We did not attempt to select cells based on t ...
... learning of novel object-place-response associations. Recordings were made throughout the full anterior-posterior extent of the hippocampus, and based on MRI reconstructions, they appeared to include neurons from all hippocampal subdivisions (Figure 1D). We did not attempt to select cells based on t ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.