Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord
... • lower motor neuron cell bodies are located in the anterior horns (grey matter), for each segment, their axons form an anterior spinal root, and project to groups of muscles (the myotome) • sensory neurons in a dorsal root enter the spinal cord (the territory of skin innervated by a segment = a der ...
... • lower motor neuron cell bodies are located in the anterior horns (grey matter), for each segment, their axons form an anterior spinal root, and project to groups of muscles (the myotome) • sensory neurons in a dorsal root enter the spinal cord (the territory of skin innervated by a segment = a der ...
Neuronal-Derived Nitric Oxide and Somatodendritically Released
... The classical model of neurovascular coupling (NVC) implies that activity-dependent axonal glutamate release at synapses evokes the production and release of vasoactive signals from both neurons and astrocytes, which dilate arterioles, increasing in turn cerebral blood flow (CBF) to areas with incre ...
... The classical model of neurovascular coupling (NVC) implies that activity-dependent axonal glutamate release at synapses evokes the production and release of vasoactive signals from both neurons and astrocytes, which dilate arterioles, increasing in turn cerebral blood flow (CBF) to areas with incre ...
The amygdala - University of Puget Sound
... inhibitory intercalated cells by the lateral and basal amygdala may inhibit the central amygdala output cells, thus disinhibiting their targets and leading to the expression of responses. The flow of information through amygdala circuits is modulated by a variety of neurotransmitter systems. Thus, n ...
... inhibitory intercalated cells by the lateral and basal amygdala may inhibit the central amygdala output cells, thus disinhibiting their targets and leading to the expression of responses. The flow of information through amygdala circuits is modulated by a variety of neurotransmitter systems. Thus, n ...
The Nervous System
... iv. Nyctalopia (night blindness) or the inability to see in dim light is caused by retinal degeneration or lack of vitamin A v. Macular degeneration: progressive degeneration of central part of retina; leading cause of permanent blindness in the elderly vi. Red-green color blindness: an X linked gen ...
... iv. Nyctalopia (night blindness) or the inability to see in dim light is caused by retinal degeneration or lack of vitamin A v. Macular degeneration: progressive degeneration of central part of retina; leading cause of permanent blindness in the elderly vi. Red-green color blindness: an X linked gen ...
MS word - University of Kentucky
... phase-out their response when the source of the stimulus (i.e. the CNS) continues the stimulation in an unchanged manner. Thus, they may fire a burst of signals initially, but quickly decrease their signals over time until no further signals are sent. In contrast, tonic-type neurons adapt slowly (if ...
... phase-out their response when the source of the stimulus (i.e. the CNS) continues the stimulation in an unchanged manner. Thus, they may fire a burst of signals initially, but quickly decrease their signals over time until no further signals are sent. In contrast, tonic-type neurons adapt slowly (if ...
exuberance in the development of cortical
... differentiated neurons that are generated early31, many of which are fated to die. This population is larger and more highly developed in phylogenetically more advanced species, although it can be identified even in rodents32. These neurons form a rich network of connections with both cortical and s ...
... differentiated neurons that are generated early31, many of which are fated to die. This population is larger and more highly developed in phylogenetically more advanced species, although it can be identified even in rodents32. These neurons form a rich network of connections with both cortical and s ...
Principles of Neural Science
... impulses, and (3) a response to this signal in the form of a perception or conscious experience of sensation. Their findings gave rise to the fields of psychophysics and sensory physiology. Psychophysics focused on the relationship between the physical characteristics of a stimulus and the attribute ...
... impulses, and (3) a response to this signal in the form of a perception or conscious experience of sensation. Their findings gave rise to the fields of psychophysics and sensory physiology. Psychophysics focused on the relationship between the physical characteristics of a stimulus and the attribute ...
LESSON 3.4 WORKBOOK
... whether the limb was in pain prior to amputation. If the real limb was in pain prior to amputation, then there is a high chance that the phantom limb will be painful too, presumably because the brain is still expecting that pain activation. Many patients experience pain because the phantom limb seem ...
... whether the limb was in pain prior to amputation. If the real limb was in pain prior to amputation, then there is a high chance that the phantom limb will be painful too, presumably because the brain is still expecting that pain activation. Many patients experience pain because the phantom limb seem ...
View PDF - MRC Brain Network Dynamics Unit
... 2010; Threlfell et al., 2012) evidence suggests that a major source of this synaptic excitation are the projections from the intralaminar thalamic nuclei (ITN). Indeed, thalamic input appears necessary for the pause response of TANs in nonhuman primates (Matsumoto et al., 2001). In vivo, electrical ...
... 2010; Threlfell et al., 2012) evidence suggests that a major source of this synaptic excitation are the projections from the intralaminar thalamic nuclei (ITN). Indeed, thalamic input appears necessary for the pause response of TANs in nonhuman primates (Matsumoto et al., 2001). In vivo, electrical ...
A Feedback Model of Visual Attention
... to multiplicatively modulate the synaptic strengths of inter-regional connections so that attended information can be selectively routed to higher cortical regions. Equivalent results can be achieved by using top-down signals to modulate the activity of neurons rather than weights of synapses (Salin ...
... to multiplicatively modulate the synaptic strengths of inter-regional connections so that attended information can be selectively routed to higher cortical regions. Equivalent results can be achieved by using top-down signals to modulate the activity of neurons rather than weights of synapses (Salin ...
5211: Session 1 Hypothalamus and its regulation of anterior and
... Introduction to the Pituitary and Hypothalamus Pituitary and hypothalamus utilize synaptic communication as well as hormonal communication to regulate target cells. Pituitary and hypothalamus are the link between the nervous system and the endocrine system. Hypothalamus is also major regulator of b ...
... Introduction to the Pituitary and Hypothalamus Pituitary and hypothalamus utilize synaptic communication as well as hormonal communication to regulate target cells. Pituitary and hypothalamus are the link between the nervous system and the endocrine system. Hypothalamus is also major regulator of b ...
The functional role of GABA and glycine in monaural and binaural
... Summary. The functional role of GABA and glycine in monaural and binaural signal analysis was studied in single unit recordings from the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus (IC) of horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus rouxi) employing microiontophoresis of the putative neurotransmitters and their anta ...
... Summary. The functional role of GABA and glycine in monaural and binaural signal analysis was studied in single unit recordings from the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus (IC) of horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus rouxi) employing microiontophoresis of the putative neurotransmitters and their anta ...
Contributions to the Understanding of the Neural Bases of
... So, consciousness is a function of numerous interacting systems. Certainly, without higher brain stem and diencephalic integration it cannot exist. In fact, consciousness is not a single process but a collection of many processes, such as those associated with language, thinking, memory, emotion, fe ...
... So, consciousness is a function of numerous interacting systems. Certainly, without higher brain stem and diencephalic integration it cannot exist. In fact, consciousness is not a single process but a collection of many processes, such as those associated with language, thinking, memory, emotion, fe ...
PDF
... shown in the lower panel. In the spinal cord (SC), one branch of the afferents enters the ascending dorsal column pathway to terminate in the ipsilateral cuneate nucleus (violet line). The other branch terminates in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Second-order neurons activated in the dorsal hor ...
... shown in the lower panel. In the spinal cord (SC), one branch of the afferents enters the ascending dorsal column pathway to terminate in the ipsilateral cuneate nucleus (violet line). The other branch terminates in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Second-order neurons activated in the dorsal hor ...
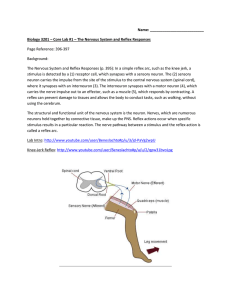
Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
... stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which ...
... stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which ...
Discovery of a Proneurogenic, Neuroprotective
... (IP) injection daily with the thymidine analog bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU, 50 mg/kg) to score birth and survival of proliferating hippocampal neural precursor cells. Because social interaction and voluntary exercise stimulate hippocampal neurogenesis, mice were housed individually without access to run ...
... (IP) injection daily with the thymidine analog bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU, 50 mg/kg) to score birth and survival of proliferating hippocampal neural precursor cells. Because social interaction and voluntary exercise stimulate hippocampal neurogenesis, mice were housed individually without access to run ...
Imitation, mirror neurons and autism
... abnormalities such as epilepsy, mental handicap and various brain pathologies. There is also evidence that autism is part of a broader phenotype [9] and sub-syndromal symptoms are often found in population surveys [1]. As such, it may be best conceptualised as a dimensional rather than a categorical ...
... abnormalities such as epilepsy, mental handicap and various brain pathologies. There is also evidence that autism is part of a broader phenotype [9] and sub-syndromal symptoms are often found in population surveys [1]. As such, it may be best conceptualised as a dimensional rather than a categorical ...
Stochastic neural network dynamics: synchronisation and control
... One common feature of all cells is the surrounding surface membrane that is differentially permeable; these membranes selectively exchange specific nutrients and gases between the cell’s interior and its surrounding fluid. Membranes encompass a nucleus within an intracellular fluid called the cytop ...
... One common feature of all cells is the surrounding surface membrane that is differentially permeable; these membranes selectively exchange specific nutrients and gases between the cell’s interior and its surrounding fluid. Membranes encompass a nucleus within an intracellular fluid called the cytop ...
Introduction
... event which is required for cytochrome c release in response to DNA damage in sympathetic neurons14, we anticipated that p53 deficient neurons might be resistant to apoptosis at multiple points in the apoptotic pathway. Consistent with this known premitochondrial function of p53 in neurons, while t ...
... event which is required for cytochrome c release in response to DNA damage in sympathetic neurons14, we anticipated that p53 deficient neurons might be resistant to apoptosis at multiple points in the apoptotic pathway. Consistent with this known premitochondrial function of p53 in neurons, while t ...
Three-dimensional auditory localization in the
... overall sound intensity [39,44], and in IC where a population of neurons involved in space coding show stable latencies across a range of sound amplitudes [39]. Studies of the auditory cortex of the big brown bat report that the frequency, amplitude, and spatial location of a sound source interact t ...
... overall sound intensity [39,44], and in IC where a population of neurons involved in space coding show stable latencies across a range of sound amplitudes [39]. Studies of the auditory cortex of the big brown bat report that the frequency, amplitude, and spatial location of a sound source interact t ...
Anatomical organization of the central olfactory
... implies the importance of chemosensation. Due to their well-developed sense of smell and easily accessible nervous system, moths have served as suitable model organisms for researchers exploring general principles underlying odor information processing. Like in other insects, moths perceive odorants ...
... implies the importance of chemosensation. Due to their well-developed sense of smell and easily accessible nervous system, moths have served as suitable model organisms for researchers exploring general principles underlying odor information processing. Like in other insects, moths perceive odorants ...
Neuronal Processing of Chemical Information in Crustaceans Chapter 7
... such as amino acids. The dichotomy in sensilla structure is reflected in the organization of the associated CNS pathways. Olfactory receptor neurons selectively innervate a synaptic region in the midbrain, the olfactory lobe, which is organized into dense substructures called glomeruli. As is typica ...
... such as amino acids. The dichotomy in sensilla structure is reflected in the organization of the associated CNS pathways. Olfactory receptor neurons selectively innervate a synaptic region in the midbrain, the olfactory lobe, which is organized into dense substructures called glomeruli. As is typica ...
Spinal Cord and reflexes lab
... • Complex reflex that consists of an ipsilateral withdrawal reflex and a contralateral extensor reflex • This keeps you from falling over, for example if you step on something painful. When you pull your foot back, the other leg responds to hold you up. ...
... • Complex reflex that consists of an ipsilateral withdrawal reflex and a contralateral extensor reflex • This keeps you from falling over, for example if you step on something painful. When you pull your foot back, the other leg responds to hold you up. ...
Abstract 1. Introduction Temporal dynamics of perception and the
... problem (Marr, Ullman & Poggio, 1979)—as well as selective pressures for animals to be able to rapidly initiate behavioral responses, even in the absence of perfect, or detailed, information. ...
... problem (Marr, Ullman & Poggio, 1979)—as well as selective pressures for animals to be able to rapidly initiate behavioral responses, even in the absence of perfect, or detailed, information. ...
Gene Expression and the Control of Food Intake by Hypothalamic
... membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It is then cleaved and trafficked as a secreted protein through the Golgi complex and eventually the secretory granules. During trafficking, the POMC protein undergoes a series of posttranslational modifications through the actions of PC1/3 and PC2. POMC ...
... membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It is then cleaved and trafficked as a secreted protein through the Golgi complex and eventually the secretory granules. During trafficking, the POMC protein undergoes a series of posttranslational modifications through the actions of PC1/3 and PC2. POMC ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.