Neurons & the Nervous System
... – Uses energy reserves to cope with stress or emergency – Adrenaline! ...
... – Uses energy reserves to cope with stress or emergency – Adrenaline! ...
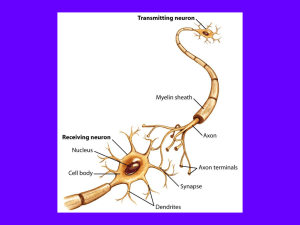
Intro-The neuron
... Transmission within Neurons Transmission is Electrical: • When sufficiently stimulated, cell "fires“ • Positive charge transmitted down axon ...
... Transmission within Neurons Transmission is Electrical: • When sufficiently stimulated, cell "fires“ • Positive charge transmitted down axon ...
Sample Questions for Evaluation #1 – General
... 5. For no apparent reason, Adam has recently begun to feel so tense and anxious that he frequently stays home from work. It would be most beneficial for Adam to contact a(n) ________ psychologist. a) personality b) biological c) clinical d) industrial/organizational 6. The scientific attitude requir ...
... 5. For no apparent reason, Adam has recently begun to feel so tense and anxious that he frequently stays home from work. It would be most beneficial for Adam to contact a(n) ________ psychologist. a) personality b) biological c) clinical d) industrial/organizational 6. The scientific attitude requir ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
Time Zones
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
Key Stage 4 – Nervous models Pupil worksheet
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
KS4_nervous_models_Pupil_Sheets
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
Types of neurons
... Information collectors Receive inputs from neighboring neurons Inputs may number in thousands If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
... Information collectors Receive inputs from neighboring neurons Inputs may number in thousands If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
Quiz 6 study guide
... b. The postsynaptic neuron might still reach threshold via temporal summation of repeated inputs from the presynaptic neuron. c. The postsynaptic neuron might still reach threshold via spatial summation of inputs of multiple presynaptic neurons. d. Both B and C are possible. N23. If, in a lab experi ...
... b. The postsynaptic neuron might still reach threshold via temporal summation of repeated inputs from the presynaptic neuron. c. The postsynaptic neuron might still reach threshold via spatial summation of inputs of multiple presynaptic neurons. d. Both B and C are possible. N23. If, in a lab experi ...
BOX 2.1 THE NEURON DOCTRINE The cell theory, which states
... known as the neurondoctrine. This great concept in essence states that the cell theory applies to the nervous system: each neuron is an individual entity, the basic unit of neural circuitry (Fig. 2.2B). The acrimonious debate between reticularists and proponents of the neuron doctrine raged for deca ...
... known as the neurondoctrine. This great concept in essence states that the cell theory applies to the nervous system: each neuron is an individual entity, the basic unit of neural circuitry (Fig. 2.2B). The acrimonious debate between reticularists and proponents of the neuron doctrine raged for deca ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - In this presentation, we’ll take a look at some different parts of our brain and examine what they do. - Limbic System - Borders the brainstem and the cerebral hemispheres - Amygdala - two almond-shaped neural clusters that influence aggression and fear. - Lesioning this part of the brain decreas ...
... - In this presentation, we’ll take a look at some different parts of our brain and examine what they do. - Limbic System - Borders the brainstem and the cerebral hemispheres - Amygdala - two almond-shaped neural clusters that influence aggression and fear. - Lesioning this part of the brain decreas ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... Billions of neurons are packed into the cortex, where they receive, process and store the memory of sensory information as well as originate ideas. ...
... Billions of neurons are packed into the cortex, where they receive, process and store the memory of sensory information as well as originate ideas. ...
Neural Pathways
... 2. when stimulated, Na+ channels open temporarily becomes + and and Na+ rushes in -inside outside 3. channels then automatically close very quickly, but this causes the neighboring channels to open 4. it proceeds like a wave along the membrane to the tip of the axon 5. then it arrives at the synapse ...
... 2. when stimulated, Na+ channels open temporarily becomes + and and Na+ rushes in -inside outside 3. channels then automatically close very quickly, but this causes the neighboring channels to open 4. it proceeds like a wave along the membrane to the tip of the axon 5. then it arrives at the synapse ...
Candy Neurons
... Draw a picture of the neuron (with direction of a signal indicated) below: (must have candy neuron checked by me BEFORE DRAWING) ...
... Draw a picture of the neuron (with direction of a signal indicated) below: (must have candy neuron checked by me BEFORE DRAWING) ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... 2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich 2.2.a How does communication happen within the body? Electrical Signals Nervous System ...
... 2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich 2.2.a How does communication happen within the body? Electrical Signals Nervous System ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... 5. For no apparent reason, Adam has recently begun to feel so tense and anxious that he frequently stays home from work. It would be most beneficial for Adam to contact a(n) ________ psychologist. a) personality b) biological c) clinical d) industrial/organizational 6. The scientific attitude requir ...
... 5. For no apparent reason, Adam has recently begun to feel so tense and anxious that he frequently stays home from work. It would be most beneficial for Adam to contact a(n) ________ psychologist. a) personality b) biological c) clinical d) industrial/organizational 6. The scientific attitude requir ...
Candy Neurons Activity
... Students work in pairs of two to create their candy neurons. They must be labeled and contain all key parts. Once they are done they must link of their diagram with another two groups. When you have a group of 6 come by for some direct instruction showing that neurons fire DAT way. Dendrites t ...
... Students work in pairs of two to create their candy neurons. They must be labeled and contain all key parts. Once they are done they must link of their diagram with another two groups. When you have a group of 6 come by for some direct instruction showing that neurons fire DAT way. Dendrites t ...
The Synaptic Cleft or Synapse
... The axon terminal at a synapse contains tiny vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. If a nerve impulse takes place, vesicles fuse and release the neurotransmitter. A common neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. ...
... The axon terminal at a synapse contains tiny vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. If a nerve impulse takes place, vesicles fuse and release the neurotransmitter. A common neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. ...
The Brain and Behavior
... from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One a ...
... from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One a ...
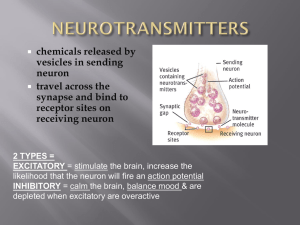
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... • Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells • Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells • Types of neurotransmitters: – Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane – Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of p ...
... • Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells • Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells • Types of neurotransmitters: – Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane – Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of p ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.