specimen jar craft - National Wildlife Federation
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
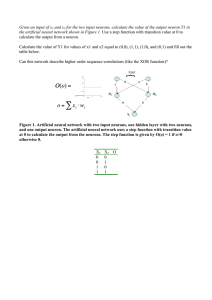
Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the
... Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the value of the output neuron Y1 in the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0 ...
... Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the value of the output neuron Y1 in the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0 ...
Name: Date: Period:
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
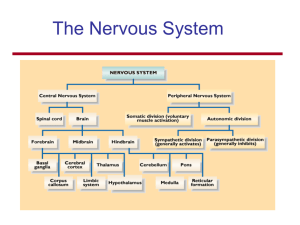
The Nervous System
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
neuron and nervous system
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
Slide ()
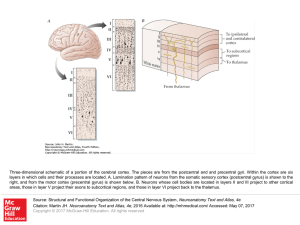
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
Human Body Systems - Whitehall District Schools
... Nerve Impulses • Electrical impulse due to a chemical change along the membrane of a neuron • Resting Potential: electrical potential of the neural membrane (70mV), created by Na/K pump, creates charge difference • Threshold: Minimum level of stimulus to activate a neuron, a neuron is an all or not ...
... Nerve Impulses • Electrical impulse due to a chemical change along the membrane of a neuron • Resting Potential: electrical potential of the neural membrane (70mV), created by Na/K pump, creates charge difference • Threshold: Minimum level of stimulus to activate a neuron, a neuron is an all or not ...
Chapter 3: The Nervous System
... •It also has a role in the control of eating, sleep and arousal. In addition, it can ...
... •It also has a role in the control of eating, sleep and arousal. In addition, it can ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... the fibers of many axons which allows faster transmission speeds in neurons. ...
... the fibers of many axons which allows faster transmission speeds in neurons. ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... The long projection that carries signals away from the cell body. The membrane voltage change from an incoming signal here triggers the opening of channels that allow ions (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels farther along the axon to open, creating a voltage ...
... The long projection that carries signals away from the cell body. The membrane voltage change from an incoming signal here triggers the opening of channels that allow ions (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels farther along the axon to open, creating a voltage ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... problem on both sides of my periphery. So, several more tests were run, and he thought I was either going blind from the Reyes’ Syndrome I had five years prior, I had a tumor somewhere in my brain. It turned out to be the latter. I had a pituitary adenoma. It seemed like a week later, I was rushed i ...
... problem on both sides of my periphery. So, several more tests were run, and he thought I was either going blind from the Reyes’ Syndrome I had five years prior, I had a tumor somewhere in my brain. It turned out to be the latter. I had a pituitary adenoma. It seemed like a week later, I was rushed i ...
Chapter 2: Brain Development
... More Cell Differentiation (Yes, this is important) • Signals help determine the specific neurotransmitters that can be used by a neuron • If neurons are cultured by themselves = norepinephrine • Cultured with cardiac tissue = acetylcholine • Based on different genes turning off and on ...
... More Cell Differentiation (Yes, this is important) • Signals help determine the specific neurotransmitters that can be used by a neuron • If neurons are cultured by themselves = norepinephrine • Cultured with cardiac tissue = acetylcholine • Based on different genes turning off and on ...
Pipecleaner Neuron Guide - spectrUM Discovery Area
... • Dendrite–dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons. • Myelin sheath–myelin is a special type of cell that wraps around axons to insulate the information that is being sent and helps deliver it fast ...
... • Dendrite–dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons. • Myelin sheath–myelin is a special type of cell that wraps around axons to insulate the information that is being sent and helps deliver it fast ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
synaptic transmission worksheet
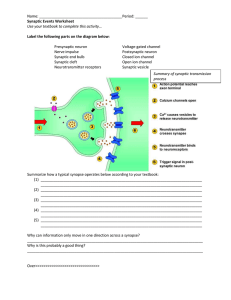
... Name: ________________________________________ Period: ______ Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
... Name: ________________________________________ Period: ______ Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
File
... There are different conditions in which a neuron can be found during an action potential: 1. Resting Potential – Na+ ions are in equilibrium with K+ ions across the axonal membrane, resulting in a net positive charge outside and a negative charge inside the neuron. 2. Depolarization – an active tran ...
... There are different conditions in which a neuron can be found during an action potential: 1. Resting Potential – Na+ ions are in equilibrium with K+ ions across the axonal membrane, resulting in a net positive charge outside and a negative charge inside the neuron. 2. Depolarization – an active tran ...
The Nervous System
... • If a portion is stimulated beyond its threshold, it briefly reverses polarity • This polarity reversal travels down the neuron • Neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminals ...
... • If a portion is stimulated beyond its threshold, it briefly reverses polarity • This polarity reversal travels down the neuron • Neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminals ...
The Zombie Diaries
... that carries signals between neurons as well as other cells in the body. These chemicals are released from the end of one neuron and cross the synapse to receptor sites in the next neuron. ...
... that carries signals between neurons as well as other cells in the body. These chemicals are released from the end of one neuron and cross the synapse to receptor sites in the next neuron. ...
Psychology`s biological roots: neurons and neural communication
... After weighing the input it receives from other neurons, a neuron can decide to send a message to another neuron It does so through an electro-chemical process called action potential or neuronal firing ...
... After weighing the input it receives from other neurons, a neuron can decide to send a message to another neuron It does so through an electro-chemical process called action potential or neuronal firing ...
Synapses
... transporters at the presynaptic membrane? • Therapeutic and Recreational Drug Effects ...
... transporters at the presynaptic membrane? • Therapeutic and Recreational Drug Effects ...
PPT
... • Motor Neurons: send messages from central nervous system to other areas • Interneurons: neurons that are neither sensory or motor neuron; can also describe CNS neurons whose axons do not leave the structure in which they reside ...
... • Motor Neurons: send messages from central nervous system to other areas • Interneurons: neurons that are neither sensory or motor neuron; can also describe CNS neurons whose axons do not leave the structure in which they reside ...
Message Transmission
... communicating neurons – It really is a gap (the synaptic cleft), the cells don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic neuron • Crossing the cleft is called synaptic transmission – One-way process handled by neurotransmitters ...
... communicating neurons – It really is a gap (the synaptic cleft), the cells don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic neuron • Crossing the cleft is called synaptic transmission – One-way process handled by neurotransmitters ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.