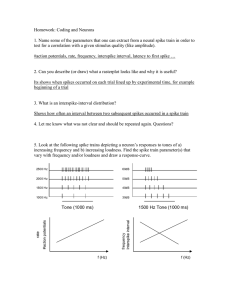
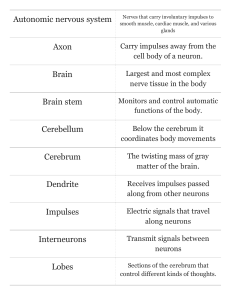
Document
... •Interneuron connect neurons within specific regions of the central nervous system. •Parts of the Neuron •Axon carries synapse away from the cell body. •Dendrite receive synaptic information and it travels toward the cell body. •Cell Body (Soma) where information is integrated into the neuron. http: ...
... •Interneuron connect neurons within specific regions of the central nervous system. •Parts of the Neuron •Axon carries synapse away from the cell body. •Dendrite receive synaptic information and it travels toward the cell body. •Cell Body (Soma) where information is integrated into the neuron. http: ...
Mind Is Matter
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
Etiopathogenesis of Alzem - Nursing Powerpoint Presentations
... hence the disease cannot be cured. There is no effective drug for relieving symptoms, and no prospect of one in the near ...
... hence the disease cannot be cured. There is no effective drug for relieving symptoms, and no prospect of one in the near ...
Name
... pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS _____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and mo ...
... pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS _____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and mo ...
Syllabus
... Required textbook: Kandel et al., Principles of Neural Science, 5th Ed. One chapter will be assigned for each lecture. ...
... Required textbook: Kandel et al., Principles of Neural Science, 5th Ed. One chapter will be assigned for each lecture. ...
Brain Organization or, why everyone should have some
... Temporal Occipital In general they have function but remember this is in general ...
... Temporal Occipital In general they have function but remember this is in general ...
chapter_8_powerpoint_le07
... The brain carries out calculations at synapses, the sites at which neurons interact. While hundreds of neurotransmitters and receptors have been identified, they can be functionally classified into two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the ...
... The brain carries out calculations at synapses, the sites at which neurons interact. While hundreds of neurotransmitters and receptors have been identified, they can be functionally classified into two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the ...
Document
... Action potential is a digital one-way electrical pulse from axon initial segment to axon terminus Neurons can fire action potentials repetitively at frequencies up to 200 pulses/sec There are 10 billion neurons in the human nervous system ...
... Action potential is a digital one-way electrical pulse from axon initial segment to axon terminus Neurons can fire action potentials repetitively at frequencies up to 200 pulses/sec There are 10 billion neurons in the human nervous system ...
myers Chapter 02 review game
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
Slide 1
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
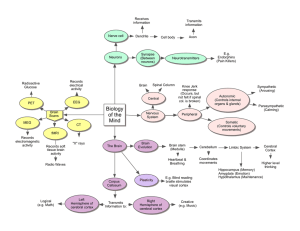
The Biology of Mind
... the links between biology and behavior ◦ Some biological psychologists call ...
... the links between biology and behavior ◦ Some biological psychologists call ...
Powerpoint slides are here
... Summary so far Role of basal ganglia is to combine with cortex to produce movement Next: role of cerebellum ...
... Summary so far Role of basal ganglia is to combine with cortex to produce movement Next: role of cerebellum ...
Abstract View OPTICAL RECORDING OF THE TRITONIA SWIMMING CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR. ;
... during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interneurons were imaged, including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). ...
... during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interneurons were imaged, including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). ...
Key - Cornell
... 4. Which characteristics of real neurons can you think of that leaky integrate-and-fire neurons do not model? Non-linearities in summation, refractory period 5. If one does not want to explicitly model action potential generation using Na+ and K+ channels, what is a good alternative? How is a refrac ...
... 4. Which characteristics of real neurons can you think of that leaky integrate-and-fire neurons do not model? Non-linearities in summation, refractory period 5. If one does not want to explicitly model action potential generation using Na+ and K+ channels, what is a good alternative? How is a refrac ...
Neuron Anatomy Activity - Ask a Biologist
... The parts of the neuron have been labeled. Your challenge is to write the correct name for each part and explain what it does. If you need some help, visit the web article listed below. ...
... The parts of the neuron have been labeled. Your challenge is to write the correct name for each part and explain what it does. If you need some help, visit the web article listed below. ...
107B exam 1 test yourself
... **KNOW THIS** Overlay of egocentric maps – FOUR maps in Vision 1. retinotopic map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 2. ocular dominance columns (projects to layer ______ of V1) 3. orientation tuning map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 4. koniocellular input (to layers ______ of V1) Organized in hor ...
... **KNOW THIS** Overlay of egocentric maps – FOUR maps in Vision 1. retinotopic map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 2. ocular dominance columns (projects to layer ______ of V1) 3. orientation tuning map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 4. koniocellular input (to layers ______ of V1) Organized in hor ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
Print › Nervous System | Quizlet
... Transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles making them ...
... Transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles making them ...
Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of
... B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmitter molecules. E) primarily electrical rather than chemical. 9. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles located on knoblike terminals at the end of the A) dendrites. B) cell body. C) axon. D) myelin sh ...
... B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmitter molecules. E) primarily electrical rather than chemical. 9. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles located on knoblike terminals at the end of the A) dendrites. B) cell body. C) axon. D) myelin sh ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.