Nervous System
... Most stimuli are received by receptors located on the membrane of nerve cells. ...
... Most stimuli are received by receptors located on the membrane of nerve cells. ...
Document
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
click - Uplift Education
... 15) When a neuron is at resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the interstitial fluid (outside the cell)? When a neuron is a resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the cytosol (inside the cell)? What processes position the ions in these locations? 16 ...
... 15) When a neuron is at resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the interstitial fluid (outside the cell)? When a neuron is a resting membrane potential, which ions are more concentrated in the cytosol (inside the cell)? What processes position the ions in these locations? 16 ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... Excitatory Transmission Neurotransmitter causes depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron by opening postsynaptic ion channels Na+ rushes in causing depolarization and an action potential Inhibitory Transmission Neurotransmitter causes hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic neuron (-75 mV to -9 ...
... Excitatory Transmission Neurotransmitter causes depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron by opening postsynaptic ion channels Na+ rushes in causing depolarization and an action potential Inhibitory Transmission Neurotransmitter causes hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic neuron (-75 mV to -9 ...
Document
... __A__3. Which of the following is true about a motor neuron? a. Dendrites carry information toward the cell body. b. Dendrites carry information away from the cell body. c. Axons carry information toward the cell body. d. None of the above __C__4. Neurons that have repolarized will have a high conce ...
... __A__3. Which of the following is true about a motor neuron? a. Dendrites carry information toward the cell body. b. Dendrites carry information away from the cell body. c. Axons carry information toward the cell body. d. None of the above __C__4. Neurons that have repolarized will have a high conce ...
17-01-05 1 Golgi - stained neurons Neuronal function
... - relatively constant diameter in any neuron - always have specialized areas that release neurotransmitter -- terminal or en passant ...
... - relatively constant diameter in any neuron - always have specialized areas that release neurotransmitter -- terminal or en passant ...
The Scientific Method - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
Review Sheet 1 scientific method and neurobiology
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
... Neurotransmissions and the nervous systems: (neurotransmission is often nicknamed the “all-or-nothing response” to explain the electrical firing of neurons and the chemical release of neurotransmitters) o Axons, dendrites, synaptic gap and myelin sheath o Specific neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine, e ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
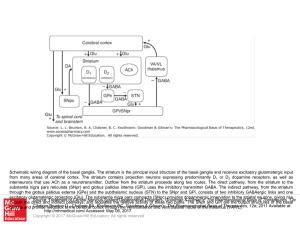
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. Neurons 1. Ne ...
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. Neurons 1. Ne ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... In Greek, dendrites mean branches, hence, they are like extensive tree branches. The more branches, the more information a neuron can receive. ...
... In Greek, dendrites mean branches, hence, they are like extensive tree branches. The more branches, the more information a neuron can receive. ...
A2.2.2.SecretSignals - jj-sct
... We also know that all body functions depend on these messages to keep us at homeostasis both physiologically and psychologically. We know a lot, but many mysteries of the brain still have to be solved before we can effectively help people with serious nervous system injuries or diseases. Electrical ...
... We also know that all body functions depend on these messages to keep us at homeostasis both physiologically and psychologically. We know a lot, but many mysteries of the brain still have to be solved before we can effectively help people with serious nervous system injuries or diseases. Electrical ...
Ling 8700: Lecture Notes 1 A Model of Neural Activation
... Mental states for concepts are distributed over the cortex in different brain areas: • visual cortex (posterior) • auditory cortex (medial, bilateral) • motor cortex (medial, dorsal) Mental states therefore have various features: visual, auditory, proprioceptive, ... • features may be encoded by sev ...
... Mental states for concepts are distributed over the cortex in different brain areas: • visual cortex (posterior) • auditory cortex (medial, bilateral) • motor cortex (medial, dorsal) Mental states therefore have various features: visual, auditory, proprioceptive, ... • features may be encoded by sev ...
Powerpoint - Center Grove Community School
... – transplants of fetal dopamine-producing substantia nigra cells – adrenal gland transplants – electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors ...
... – transplants of fetal dopamine-producing substantia nigra cells – adrenal gland transplants – electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors ...
THE NEURON (Slides 4 to 14) • Based on the PowerPoint attached
... A neuron is resting when its membrane forms a partial barrier between the inside and outside of the neuron. The solution contains electrically charged particles called ions. When the neuron is at rest, there are more negative ions on the outside which is called the resting potential. A resting neuro ...
... A neuron is resting when its membrane forms a partial barrier between the inside and outside of the neuron. The solution contains electrically charged particles called ions. When the neuron is at rest, there are more negative ions on the outside which is called the resting potential. A resting neuro ...
Artificial Intelligence Methods
... Neurons in a McCulloch-Pitts network are connected by directed, weighted paths A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the ...
... Neurons in a McCulloch-Pitts network are connected by directed, weighted paths A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the ...
Chapter 3
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
Slide ()
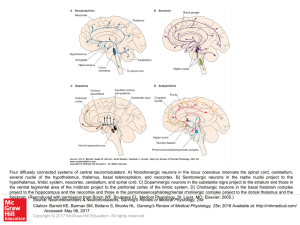
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.