Organization of the Nervous System and the Neuron
... No contact between neurons except at electrical synapses (escape reflexes, retina, heart) Axonal terminals release neurotransmitters which cause depolarization of next neuron Neurotransmitter is removed from synapse by reuptake at axonal terminal or enzymatic breakdown ...
... No contact between neurons except at electrical synapses (escape reflexes, retina, heart) Axonal terminals release neurotransmitters which cause depolarization of next neuron Neurotransmitter is removed from synapse by reuptake at axonal terminal or enzymatic breakdown ...
Neurons - World of Teaching
... Sodium ions (Na+) rush into the axon. This neutralizes the negative ions inside. The inside of the axon becomes temporarily (+) while the outside becomes temporarily (-). The reversal of charge is known as “depolarization” Nearby Sodium (Na+) channels open to continue the ...
... Sodium ions (Na+) rush into the axon. This neutralizes the negative ions inside. The inside of the axon becomes temporarily (+) while the outside becomes temporarily (-). The reversal of charge is known as “depolarization” Nearby Sodium (Na+) channels open to continue the ...
Nervous
... through Na+ gated channels. Gated Ion Channels are open or close in response to membrane stretch, the binding of a specific ligand, or a change in the membrane potential. Direct Synaptic Transmission The neurotransmitter binds to ligand–gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, producing an e ...
... through Na+ gated channels. Gated Ion Channels are open or close in response to membrane stretch, the binding of a specific ligand, or a change in the membrane potential. Direct Synaptic Transmission The neurotransmitter binds to ligand–gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, producing an e ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Sodium ions (Na+) rush into the axon. This neutralizes the negative ions inside. The inside of the axon becomes temporarily (+) while the outside becomes temporarily (-). The reversal of charge is known as “depolarization” Nearby Sodium (Na+) channels open to continue the ...
... Sodium ions (Na+) rush into the axon. This neutralizes the negative ions inside. The inside of the axon becomes temporarily (+) while the outside becomes temporarily (-). The reversal of charge is known as “depolarization” Nearby Sodium (Na+) channels open to continue the ...
Neurotransmitters
... transmission at these synapses. Acetylcholine also operates in many regions of the brain, but using different types of receptors. Dopamine has a number of important functions in the brain. It plays a critical role in the reward system, but dysfunction of the dopamine system is also implicated in Par ...
... transmission at these synapses. Acetylcholine also operates in many regions of the brain, but using different types of receptors. Dopamine has a number of important functions in the brain. It plays a critical role in the reward system, but dysfunction of the dopamine system is also implicated in Par ...
Unit 2 Review
... 6. A neuron either fires or it doesn’t. There is no in between. This phenomenon is called _______________________________. 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
... 6. A neuron either fires or it doesn’t. There is no in between. This phenomenon is called _______________________________. 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
Neurons and the Brain
... It’s the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system. It acts on basic autonomic and muscular functions Plays an important role in arousal and attention ...
... It’s the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system. It acts on basic autonomic and muscular functions Plays an important role in arousal and attention ...
Slideshow
... serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
... serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
Chapter 4
... Brain’s Four Lobes Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Brain Lateralization ...
... Brain’s Four Lobes Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Brain Lateralization ...
Slide ()
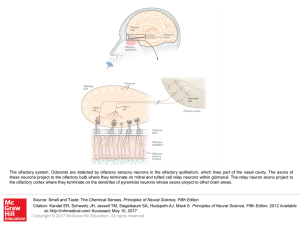
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
KC Kajander GJ Giesler, Jr. KJ Gingrich JH Byrne YS Chan J
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
... S. Warren, H. A. Hamalainen, and E. P. Gardner, “Objective classification of motion- and directionsensitive neurons in primary somatosensory cortex of awake monkeys.” It was incorrectly stated that Orban and co-workers (J. iVeurophysioZ. 45: 1059-1073, 198 1) attributed direction selectivity to cort ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Visual Cortical Dynamics Charles Gilbert The Rockefeller University
... learning, working memory and motor commands. At the level of brain circuitry this process involves an interaction between long range and intrinsic cortical connections and causes neurons to act as adaptive processors that are able to assume different functional states according to the task being exe ...
... learning, working memory and motor commands. At the level of brain circuitry this process involves an interaction between long range and intrinsic cortical connections and causes neurons to act as adaptive processors that are able to assume different functional states according to the task being exe ...
Brain Questions
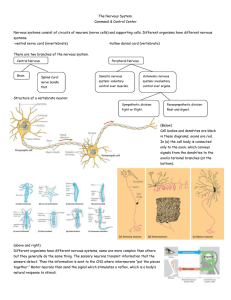
... 1- State three functions of the nervous system 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripher ...
... 1- State three functions of the nervous system 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripher ...
What is the Nervous System?
... (+) and (–) charged ions flow back & forth across cell membrane – but at DIFFERENT rates Leads to higher concentration of negatively charged ions in cell ...
... (+) and (–) charged ions flow back & forth across cell membrane – but at DIFFERENT rates Leads to higher concentration of negatively charged ions in cell ...
Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level
... enzyme cholinesterase which breaks down acetylcholine, allowing the sodium channels to close, and repolarization to take place. Why is this important to neuron function? ...
... enzyme cholinesterase which breaks down acetylcholine, allowing the sodium channels to close, and repolarization to take place. Why is this important to neuron function? ...
Data/hora: 28/03/2017 12:03:40 Provedor de dados: 17 País: United
... Resumo: The neuron, when considered as a signal processing device, itsinputs are the frequency of pulses received at the synapses, and its output is the frequency of action potentials generated- in essence, a neuron is a pulse frequency signal processing device. In comparison, electrical devices use ...
... Resumo: The neuron, when considered as a signal processing device, itsinputs are the frequency of pulses received at the synapses, and its output is the frequency of action potentials generated- in essence, a neuron is a pulse frequency signal processing device. In comparison, electrical devices use ...
(Early Period) - Connectionism
... A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impulses down their lengthy projections (axons) towards junctions with other neurons (synapses) or are inactive. ● Hebb’s rule: D ...
... A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impulses down their lengthy projections (axons) towards junctions with other neurons (synapses) or are inactive. ● Hebb’s rule: D ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... Block chemical locks in the heart and cause it to decrease in rate Transmitters communicate between nerves and body organs (muscles/ ...
... Block chemical locks in the heart and cause it to decrease in rate Transmitters communicate between nerves and body organs (muscles/ ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
nn2new-02
... Single neuron activity •If you measure the membrane potential of a neuron and print it out on the screen, it looks like (from time 0 to 60 minutes) ...
... Single neuron activity •If you measure the membrane potential of a neuron and print it out on the screen, it looks like (from time 0 to 60 minutes) ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.