Neurotransmisson Practice
... readiness to fire. 7. Excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed to the sending neuron in a process called _______________________. 8. Among the neurotransmitters that researchers have pinpointed is ________, which influences movement, learning, attention, and emotions and seems to play a role in schiz ...
... readiness to fire. 7. Excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed to the sending neuron in a process called _______________________. 8. Among the neurotransmitters that researchers have pinpointed is ________, which influences movement, learning, attention, and emotions and seems to play a role in schiz ...
Unit 3 Essential Vocabulary File - District 196 e
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
File
... neuron, sends out information Postsynaptic- neuron whose dendrites forms a synapse with the axon of the presynaptic neuron, receives information There is no physical structure connecting the two neurons. ...
... neuron, sends out information Postsynaptic- neuron whose dendrites forms a synapse with the axon of the presynaptic neuron, receives information There is no physical structure connecting the two neurons. ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
Nervous System II – Neurons
... Nervous System II – Neurons Neurons Information is transmitted through ...
... Nervous System II – Neurons Neurons Information is transmitted through ...
Slide ()
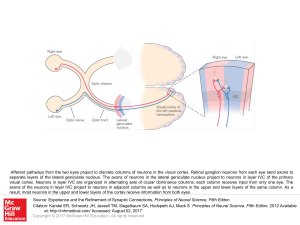
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
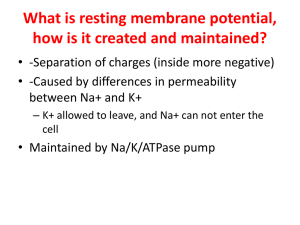
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... What is an action potential? Graph and describe different parts of process • --Conduction of electric current • 1. If above threshold, voltage gated channels open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
... What is an action potential? Graph and describe different parts of process • --Conduction of electric current • 1. If above threshold, voltage gated channels open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... coordination of many neurons. How does its structure suit it for these purposes? (p261) 37. What is an EEG? What does it reveal about brain activity during sleep? (11.9) 38. The limbic system of the brain affects our ___________________ and short-term _________________. The system is modulated by th ...
... coordination of many neurons. How does its structure suit it for these purposes? (p261) 37. What is an EEG? What does it reveal about brain activity during sleep? (11.9) 38. The limbic system of the brain affects our ___________________ and short-term _________________. The system is modulated by th ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... Once it’s more positive inside than outside the cell, the channel closes ...
... Once it’s more positive inside than outside the cell, the channel closes ...
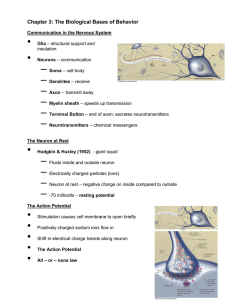
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... – Fluids inside and outside neuron – Electrically charged particles (ions) – Neuron at rest – negative charge on inside compared to outside – -70 millivolts – resting potential ...
... – Fluids inside and outside neuron – Electrically charged particles (ions) – Neuron at rest – negative charge on inside compared to outside – -70 millivolts – resting potential ...
Neuron_Exercises_HPsychAY10
... You will do this by engaging in a series of ten-minute projects with a partner. You will complete the following “stations” and/or projects in whatever order seems best to you: 1. Create a diagram of the structure of the neuron using construction paper and crayons or pencils. 2. Answer the following ...
... You will do this by engaging in a series of ten-minute projects with a partner. You will complete the following “stations” and/or projects in whatever order seems best to you: 1. Create a diagram of the structure of the neuron using construction paper and crayons or pencils. 2. Answer the following ...
Slide ()
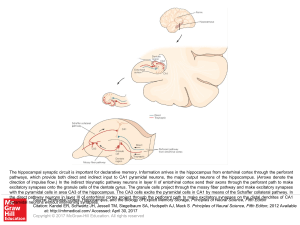
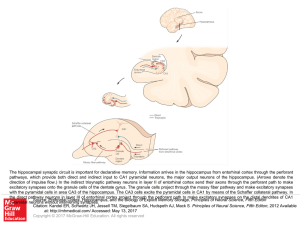
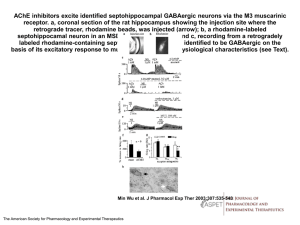
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
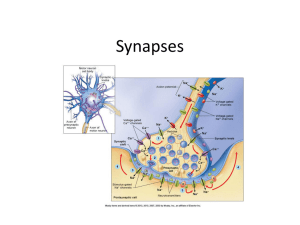
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
The Brain
... information much faster than other neurons Axon terminal – at the end of the neuron and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons (through synapses) ...
... information much faster than other neurons Axon terminal – at the end of the neuron and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons (through synapses) ...
Types of neurons - Brigham Young University
... Multiple Sclerosis is an autoimmune attack on myelin sheaths resulting in 100 times slower signal propagation along the axon ...
... Multiple Sclerosis is an autoimmune attack on myelin sheaths resulting in 100 times slower signal propagation along the axon ...
Lecture 6
... Neocortex: Cortex means bark in Greek, it lies as a bark over the rest of the brain with a surface of 2000cm^2. At the back is the occipital area important for visual processing (the later takes up 40% of the brain) very high visual resolution (& capability for associative and therefore creative ...
... Neocortex: Cortex means bark in Greek, it lies as a bark over the rest of the brain with a surface of 2000cm^2. At the back is the occipital area important for visual processing (the later takes up 40% of the brain) very high visual resolution (& capability for associative and therefore creative ...
Lectures on mathematical neuroscience
... • An action potential in the pre-synaptic neuron provides a current to the post-synaptic cell. • The effect may be either excitatory (naively thought to promote firing of post-synaptic neuron) or inhibitory (naively having the opposite effect). • Synapses have their own time scales for rise and deca ...
... • An action potential in the pre-synaptic neuron provides a current to the post-synaptic cell. • The effect may be either excitatory (naively thought to promote firing of post-synaptic neuron) or inhibitory (naively having the opposite effect). • Synapses have their own time scales for rise and deca ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... vesicles that contain dopamine. This triggers the vesicles to be released, even without an action potential. Combined, this causes a surge of dopamine to be present in the synaptic cleft, leading to overactivation of neurons and an extreme ‘high’. ...
... vesicles that contain dopamine. This triggers the vesicles to be released, even without an action potential. Combined, this causes a surge of dopamine to be present in the synaptic cleft, leading to overactivation of neurons and an extreme ‘high’. ...
Nervous Systems
... Resting potential: membrane potential at rest; polarized Na+ outside, K+ inside cell Voltage-gated Na+ channel = CLOSED Nerve impulse: stimulus causes a change in membrane potential Action potential: neuron membrane depolarizes All-or-nothing response ...
... Resting potential: membrane potential at rest; polarized Na+ outside, K+ inside cell Voltage-gated Na+ channel = CLOSED Nerve impulse: stimulus causes a change in membrane potential Action potential: neuron membrane depolarizes All-or-nothing response ...
neurons
... electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
48 Nervous System PowerPoint
... more negative inside by K+ moving out—does not cause an action potential ...
... more negative inside by K+ moving out—does not cause an action potential ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... which mix with negative ions (Chloride-Cl) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal ...
... which mix with negative ions (Chloride-Cl) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.