First-in-first-out item replacement in a model of
... are reactivated repeatedly by the combination of ADP and positive theta modulation of membrane potential at a rate that matches the frequency of theta oscillation. A pattern of spikes that represents a stimulus input is maintained by this persistent spiking without any prerequisite synaptic connecti ...
... are reactivated repeatedly by the combination of ADP and positive theta modulation of membrane potential at a rate that matches the frequency of theta oscillation. A pattern of spikes that represents a stimulus input is maintained by this persistent spiking without any prerequisite synaptic connecti ...
LFP Power Spectra in V1 Cortex: The Graded Effect of Stimulus
... Hz) frequency bands of the LFP as a function of stimulus contrast indicates that the LFP power gradually increases with stimulus strength across a wide band in a manner roughly comparable to the increase in the simultaneously recorded spike activity. However, the low-frequency band power remains app ...
... Hz) frequency bands of the LFP as a function of stimulus contrast indicates that the LFP power gradually increases with stimulus strength across a wide band in a manner roughly comparable to the increase in the simultaneously recorded spike activity. However, the low-frequency band power remains app ...
Neuronal LRP1 Knockout in Adult Mice Leads to Impaired Brain
... (Mahley, 1988; Bu, 2009). Brain apoE/lipoprotein particles, produced primarily by astrocytes, deliver cholesterol and other lipids to neurons via apoE receptors, which belong to the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family (Herz and Bock, 2002; Herz and Chen, 2006; Bu, 2009). The LDL receptor-r ...
... (Mahley, 1988; Bu, 2009). Brain apoE/lipoprotein particles, produced primarily by astrocytes, deliver cholesterol and other lipids to neurons via apoE receptors, which belong to the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family (Herz and Bock, 2002; Herz and Chen, 2006; Bu, 2009). The LDL receptor-r ...
Program
and
Abstracts
from
the
Fifth
Annual
Canadian
Neuroscience
Meeting
May
29
–
June
1
2011
Quebec
City
Convention
Center
... Abstract: Objective: Pallial regions of teleost fish are associated with learning about social signal discrimination, spatial learning and emotional conditioning. We recently showed that neurons in the dorsal central part of the apteronotid pallium (DC) have similar features to neocortical neuron ...
... Abstract: Objective: Pallial regions of teleost fish are associated with learning about social signal discrimination, spatial learning and emotional conditioning. We recently showed that neurons in the dorsal central part of the apteronotid pallium (DC) have similar features to neocortical neuron ...
full program with abstracts
... Hexanucleotide (G4C2) repeat expansions in a noncoding region of C9ORF72 are the major cause of familial ALS (~40%) and FTD (~20%). The C9ORF72 repeat expansion undergoes RAN translation, resulting in expression of five dipeptide repeat proteins (DRPs). Whilst it remains unclear how mutations in C9O ...
... Hexanucleotide (G4C2) repeat expansions in a noncoding region of C9ORF72 are the major cause of familial ALS (~40%) and FTD (~20%). The C9ORF72 repeat expansion undergoes RAN translation, resulting in expression of five dipeptide repeat proteins (DRPs). Whilst it remains unclear how mutations in C9O ...
download file
... zone et al. 1992a,b). In all of these cases, experience-dependent plasticity is specific to the stimuli that were attended to during behavior and passive exposure does not cause enduring changes in neuronal responses (Recanzone et al. 1993; Weinberger 1998; Weinberger and Bakin 1998). These results ...
... zone et al. 1992a,b). In all of these cases, experience-dependent plasticity is specific to the stimuli that were attended to during behavior and passive exposure does not cause enduring changes in neuronal responses (Recanzone et al. 1993; Weinberger 1998; Weinberger and Bakin 1998). These results ...
Whole-Brain Serial-Section Electron Microscopy In Larval Zebrafish
... handling data for relatively large volumes at nanoscale resolution has thus restricted all studies in vertebrates to neuron fragments, thereby hindering investigations of complete circuits. These efforts were transformed by recent advances in computing, sample handling, and imaging techniques1, but ...
... handling data for relatively large volumes at nanoscale resolution has thus restricted all studies in vertebrates to neuron fragments, thereby hindering investigations of complete circuits. These efforts were transformed by recent advances in computing, sample handling, and imaging techniques1, but ...
The role of the basal ganglia in reinforcement learning
... in their firing rate when the situation is better than expected (positive surprise). This signal is in accordance with a reinforcement error signal. However, the low tonic discharge rate of the dopaminergic neurons suggests that their capability to encode negative events by suppressing firing rate i ...
... in their firing rate when the situation is better than expected (positive surprise). This signal is in accordance with a reinforcement error signal. However, the low tonic discharge rate of the dopaminergic neurons suggests that their capability to encode negative events by suppressing firing rate i ...
Full Text - Anesth Pain Med
... can trigger CH attacks similar to spontaneous attacks, suggesting a role for NO in nociceptive processes (53). There is an obvious link between CGRP, vasodilatation and pain but its exact role during an attack is not yet very clear. While CGRP has a vasodilatory effect, SP and neurokinin A (NKA) inc ...
... can trigger CH attacks similar to spontaneous attacks, suggesting a role for NO in nociceptive processes (53). There is an obvious link between CGRP, vasodilatation and pain but its exact role during an attack is not yet very clear. While CGRP has a vasodilatory effect, SP and neurokinin A (NKA) inc ...
Axon Initiation and Growth Cone Turning on Bound Protein Gradients Cellular/Molecular Junyu Mai,
... wafer was plasma treated to remove photoresist layer and then vapor-coated in a vacuum bowl for 10 h with [tridecafluoro-1,1,2,2tetrahydrooctyl]-1-trichlorosilane (United Chemical Technologies) to make the surface hydrophobic, a necessary step to ensure a smooth gradient and easy removal of the agar ...
... wafer was plasma treated to remove photoresist layer and then vapor-coated in a vacuum bowl for 10 h with [tridecafluoro-1,1,2,2tetrahydrooctyl]-1-trichlorosilane (United Chemical Technologies) to make the surface hydrophobic, a necessary step to ensure a smooth gradient and easy removal of the agar ...
Raven Ch
... B. Answer b is incorrect. Hyperpolarizing the presynaptic membrane will not prevent an action potential in the postsynaptic cell, which is the function of inhibitory neurotransmitters. The correct answer is a— C. Answer c is incorrect. Depolarizing the postsynaptic cell will make an action potentia ...
... B. Answer b is incorrect. Hyperpolarizing the presynaptic membrane will not prevent an action potential in the postsynaptic cell, which is the function of inhibitory neurotransmitters. The correct answer is a— C. Answer c is incorrect. Depolarizing the postsynaptic cell will make an action potentia ...
Time course of the development of motor behaviors in the zebrafish
... rats (Kudo and Yamada, 1987), and zebrafish (Kimmel et al., 1974). However, the earliest events, including the genesis of motor functions, their maturation during embryonic development, and the nature of the neural networks, are less well characterized. Previous studies of the zebrafish looked at ge ...
... rats (Kudo and Yamada, 1987), and zebrafish (Kimmel et al., 1974). However, the earliest events, including the genesis of motor functions, their maturation during embryonic development, and the nature of the neural networks, are less well characterized. Previous studies of the zebrafish looked at ge ...
FREE Sample Here
... MOD: Module 2-1 Neurons: The Body’s Wiring OBJ: 2.3 KEY: Evaluate/Explain NOT: www Which of the following is NOT true of action potentials? A) They are generated according to an all-or-none principle. B) They all travel at the same speed. C) They are electrical charges that shoot down the axon. D) T ...
... MOD: Module 2-1 Neurons: The Body’s Wiring OBJ: 2.3 KEY: Evaluate/Explain NOT: www Which of the following is NOT true of action potentials? A) They are generated according to an all-or-none principle. B) They all travel at the same speed. C) They are electrical charges that shoot down the axon. D) T ...
facing page
... It is well-established that the presence of addictive drugs to abusers provokes the activation of brain regions that are involved in both addictive and learning processes (Belujon & Grace, 2011; Fowler et al., 2014; Van den Oever et al,. 2013). Based on such studies, it was suggested that addiction, ...
... It is well-established that the presence of addictive drugs to abusers provokes the activation of brain regions that are involved in both addictive and learning processes (Belujon & Grace, 2011; Fowler et al., 2014; Van den Oever et al,. 2013). Based on such studies, it was suggested that addiction, ...
The amygdala: securing pleasure and avoiding pain
... the amygdala, nor the impact that processing in this structure has on the motivational limbic corticostriatal circuitry of which it is an important structure. Here we discuss the interactions between different amygdala nuclei with cortical and striatal regions involved in motivation; interconnection ...
... the amygdala, nor the impact that processing in this structure has on the motivational limbic corticostriatal circuitry of which it is an important structure. Here we discuss the interactions between different amygdala nuclei with cortical and striatal regions involved in motivation; interconnection ...
Chapter 9- Nervous System Lecture 9.1
... The process by which the impulse in the presynaptic neuron is transmitted across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic neuron is called synaptic transmission. ...
... The process by which the impulse in the presynaptic neuron is transmitted across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic neuron is called synaptic transmission. ...
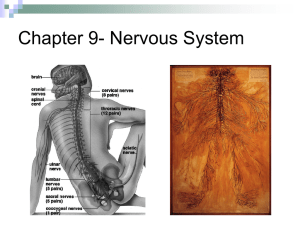
Chapter 9
... If a nerve fiber responds at all to a stimulus, it responds completely by conducting an impulse (all-ornone response). ...
... If a nerve fiber responds at all to a stimulus, it responds completely by conducting an impulse (all-ornone response). ...
Previous studies have shown that there are a large variety of
... in the rat visual cortex, contrasting sharply with layer 6 neurons in the primate visual cortex. These observations provide insight into differences in function between cortical projections to first order versus higher order thalamic nuclei and also show that these circuits can be organized differen ...
... in the rat visual cortex, contrasting sharply with layer 6 neurons in the primate visual cortex. These observations provide insight into differences in function between cortical projections to first order versus higher order thalamic nuclei and also show that these circuits can be organized differen ...
Drosophila as a Model Organism for the Study of
... structures. While our understanding of the mushroom body circuitry is still developing, targeted genetic manipulations suggest that punishment and reward are signaled by innervation of the presynaptic compartment of mushroom body neurons by dopaminergic and octopaminergic neurons, respectively (Schw ...
... structures. While our understanding of the mushroom body circuitry is still developing, targeted genetic manipulations suggest that punishment and reward are signaled by innervation of the presynaptic compartment of mushroom body neurons by dopaminergic and octopaminergic neurons, respectively (Schw ...
Orexins and fear: implications for the treatment of - e
... anxiety, such as benzodiazepines and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, offer transient symptom relief and are associated with negative side effects. In addition, a significant proportion of patients do not respond to treatment or relapse after treatment remission [55]. Combining cognitive-beh ...
... anxiety, such as benzodiazepines and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, offer transient symptom relief and are associated with negative side effects. In addition, a significant proportion of patients do not respond to treatment or relapse after treatment remission [55]. Combining cognitive-beh ...
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in Inflammatory and Degenerative Brain
... mental retardation, defective development of cortical neurons, and abnormalities of dendritic branching—the laminar pattern of cortical COX-2 immunoreactivity is disrupted, in that COX-2-positive neurons are decreased in number and randomly distributed (18). Rats subjected to selective destruction o ...
... mental retardation, defective development of cortical neurons, and abnormalities of dendritic branching—the laminar pattern of cortical COX-2 immunoreactivity is disrupted, in that COX-2-positive neurons are decreased in number and randomly distributed (18). Rats subjected to selective destruction o ...
Stochastic Model of Central Synapses: Slow Diffusion of Transmitter
... interactions with transporter molecules are assumed to affect the transmitter motion. We estimate the transporter density to be 5170 to 8900 mm − 2 in the synaptic cleft and its vicinity, using the experimentally observed time constant of glutamate. Furthermore a theoretical model of synaptic transm ...
... interactions with transporter molecules are assumed to affect the transmitter motion. We estimate the transporter density to be 5170 to 8900 mm − 2 in the synaptic cleft and its vicinity, using the experimentally observed time constant of glutamate. Furthermore a theoretical model of synaptic transm ...
BZA BCI Projects
... What is a BCI? BCIs may be: • Non-invasive (usually EEG) • Invasive • ECoG (surface of cortex) • depth recording (in brain) ...
... What is a BCI? BCIs may be: • Non-invasive (usually EEG) • Invasive • ECoG (surface of cortex) • depth recording (in brain) ...
The Olfactory Sensory Map in Drosophila
... vertebrates8 and labial palps of insects.6,9 It is still unclear in the field whether these taste qualities re‑ main segregated into stimulus‑specific labeled lines from the periphery to higher brain centers,8,10,11 or whether distributed coding across groups of sensory and central brain neurons all ...
... vertebrates8 and labial palps of insects.6,9 It is still unclear in the field whether these taste qualities re‑ main segregated into stimulus‑specific labeled lines from the periphery to higher brain centers,8,10,11 or whether distributed coding across groups of sensory and central brain neurons all ...
Human Feature Extraction – The Role of the Articulatory Rhythm
... The functionality of a single neuron, i.e. the relation between its input and output, is well modelled by the physical relations based on the flow of ions [30]. Due to the electrical potential within a neuron, generated by the ion flow, a neuron can be set to a ‘state’, where it emits a train of ele ...
... The functionality of a single neuron, i.e. the relation between its input and output, is well modelled by the physical relations based on the flow of ions [30]. Due to the electrical potential within a neuron, generated by the ion flow, a neuron can be set to a ‘state’, where it emits a train of ele ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.