Neuro Objectives 22 - U
... Medial longitudinal fasciculus: medial throughout brainstem, ventral to the ventricular system Oculomotor nuclei: rostral midbrain, medial, multiple nuclei ventral to periaqueductal gray Trochlear nuclei: caudal midbrain, medial, dorsal to MLF, only cranial nerve that leaves both dorsally and crosse ...
... Medial longitudinal fasciculus: medial throughout brainstem, ventral to the ventricular system Oculomotor nuclei: rostral midbrain, medial, multiple nuclei ventral to periaqueductal gray Trochlear nuclei: caudal midbrain, medial, dorsal to MLF, only cranial nerve that leaves both dorsally and crosse ...
Chapter 3 Two parts of nucleus prepositus hypoglossi project to two
... other parts of the PAG with respect to its neurochemistry. For example, NADPH-d (fig. 1) and cholecystokinin (Liu et al., 1994) are specifically present in PAGdl, while cytochrome oxidase (Conti et al., 1988) is found in almost all parts of the PAG, except PAGdl. Functionally, PAGdl has been associate ...
... other parts of the PAG with respect to its neurochemistry. For example, NADPH-d (fig. 1) and cholecystokinin (Liu et al., 1994) are specifically present in PAGdl, while cytochrome oxidase (Conti et al., 1988) is found in almost all parts of the PAG, except PAGdl. Functionally, PAGdl has been associate ...
mastering-the-world-of-psychology-4th-edition-wood
... A) Neural communication occurs every time an individual moves or has a thought. B) The synapse is the site where the pre-synaptic neuron communicates with the post-synaptic neuron. Incorrect. The neuron before the synapse is called pre-synaptic and the neuron after the synapse is called post-synapti ...
... A) Neural communication occurs every time an individual moves or has a thought. B) The synapse is the site where the pre-synaptic neuron communicates with the post-synaptic neuron. Incorrect. The neuron before the synapse is called pre-synaptic and the neuron after the synapse is called post-synapti ...
Caudal Medulla
... • composed of primary sensory fibers that enter the brain mainly in the trigeminal nerve. • This tract also receives fibers that originate from cranial nerves VII, IX, and X. (5,7,9,10) • terminate on the spinal trigeminal nucleus, which, in turn, projects to the contralateral thalamus as the ventra ...
... • composed of primary sensory fibers that enter the brain mainly in the trigeminal nerve. • This tract also receives fibers that originate from cranial nerves VII, IX, and X. (5,7,9,10) • terminate on the spinal trigeminal nucleus, which, in turn, projects to the contralateral thalamus as the ventra ...
22 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Motor System in Humans
... The behavioral repertoire of humans is broad, extending from simple behaviors such as sensory perception to more complex cognitive behaviors like language or creativity. Interestingly, no matter how simple or complex are these behaviors, they share without exception the common feature that their exp ...
... The behavioral repertoire of humans is broad, extending from simple behaviors such as sensory perception to more complex cognitive behaviors like language or creativity. Interestingly, no matter how simple or complex are these behaviors, they share without exception the common feature that their exp ...
Behavioral consequences of abnormal cortical development
... In the process of reviewing the relevant literature and analyzing our own recent data, it has become clear that developmental regulation of cortical morphogenesis and behavior differs between the sexes, probably due to perinatal steroid hormones. This hormonal influence likely explains why many aspe ...
... In the process of reviewing the relevant literature and analyzing our own recent data, it has become clear that developmental regulation of cortical morphogenesis and behavior differs between the sexes, probably due to perinatal steroid hormones. This hormonal influence likely explains why many aspe ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Is Important for the Manifestations ofα
... can lead to endoplasmic reticulum stress/unfolded protein response (ERS/UPR), chronic ERS could contribute to neurodegeneration in ␣-synucleinopathy. Using the A53T mutant human ␣S transgenic (A53T␣S Tg) mouse model of ␣-synucleinopathy, we show that disease onset in the ␣S Tg model is coincident wi ...
... can lead to endoplasmic reticulum stress/unfolded protein response (ERS/UPR), chronic ERS could contribute to neurodegeneration in ␣-synucleinopathy. Using the A53T mutant human ␣S transgenic (A53T␣S Tg) mouse model of ␣-synucleinopathy, we show that disease onset in the ␣S Tg model is coincident wi ...
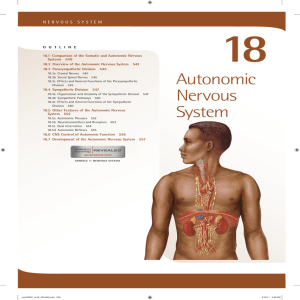
Autonomic Nervous System
... The sympathetic (sim-pa -̆ thet ́ ik) division is primarily concerned with preparing the body for emergencies. It is often referred to as the “fight-or-flight” division because increased sympathetic activity results in the increased alertness and metabolic activity needed in stressful or frighteni ...
... The sympathetic (sim-pa -̆ thet ́ ik) division is primarily concerned with preparing the body for emergencies. It is often referred to as the “fight-or-flight” division because increased sympathetic activity results in the increased alertness and metabolic activity needed in stressful or frighteni ...
Neurally Plausible Model of Robot Reaching Inspired by Infant
... encouraging, and funny husband, Lonnie Yu, who supported me in every possible way while I was writing this dissertation. Finally, I would like to thank my beautiful, fluffy cat, Ling Ling, whose presence in my life provides me with an enormous amount of hope and joy. ...
... encouraging, and funny husband, Lonnie Yu, who supported me in every possible way while I was writing this dissertation. Finally, I would like to thank my beautiful, fluffy cat, Ling Ling, whose presence in my life provides me with an enormous amount of hope and joy. ...
Are cortical spikes conveyed to contralateral
... method referenced to cortical spike discharges. The waveform of CCAP was characterized by a slow-rising negative potential change that preceded the cortical spike discharge and continued to increase after it occurred (Fig. 2). As shown in Fig. 4, the following common features among all 20 patients w ...
... method referenced to cortical spike discharges. The waveform of CCAP was characterized by a slow-rising negative potential change that preceded the cortical spike discharge and continued to increase after it occurred (Fig. 2). As shown in Fig. 4, the following common features among all 20 patients w ...
The Perirhinal, Entorhinal, and Parahippocampal Cortices and
... modal sensory systems, the orbitofrontal cortex, insula, and cingulate cortex (Suzuki and Amaral 1994a). Tracing studies have also demonstrated a rich network of intrinsic associational connections within the PRc, which presumably bind this multimodal information together (Lavenex et al. 2004). In l ...
... modal sensory systems, the orbitofrontal cortex, insula, and cingulate cortex (Suzuki and Amaral 1994a). Tracing studies have also demonstrated a rich network of intrinsic associational connections within the PRc, which presumably bind this multimodal information together (Lavenex et al. 2004). In l ...
connect_review_20150316 - Royal Holloway, University of London
... associated with the ventral stream, including the well-studied fusiform face area (FFA) in the fusiform gyrus (Kanwisher et al., 1997). FFA responds more to faces than non-face objects, as do areas in the ventral occipital lobe (OFA) and posterior superior temporal sulcus (STS). An influential netwo ...
... associated with the ventral stream, including the well-studied fusiform face area (FFA) in the fusiform gyrus (Kanwisher et al., 1997). FFA responds more to faces than non-face objects, as do areas in the ventral occipital lobe (OFA) and posterior superior temporal sulcus (STS). An influential netwo ...
Sources of the Scalp-Recorded Amplitude
... hemisphere where the electrical, mechanical, or chemical (KCI) stimulation is applied and is marked by the absence of the electroencephalogram . It creates a deep, reversible inhibition of all cortical functions (Leao, 1944 ; Bures et al, 1974). It is long lasting (2-3 hours) and does not appear to ...
... hemisphere where the electrical, mechanical, or chemical (KCI) stimulation is applied and is marked by the absence of the electroencephalogram . It creates a deep, reversible inhibition of all cortical functions (Leao, 1944 ; Bures et al, 1974). It is long lasting (2-3 hours) and does not appear to ...
Local Connections to Specific Types of Layer 6
... identified the sublaminar organization of corticothalamic projection neurons, there have been few studies that have analyzed the detailed morphologies of these cells, particularly comparing the cells in the upper and lower sublayers to find quantifiable differences. As a result, the intracortical ci ...
... identified the sublaminar organization of corticothalamic projection neurons, there have been few studies that have analyzed the detailed morphologies of these cells, particularly comparing the cells in the upper and lower sublayers to find quantifiable differences. As a result, the intracortical ci ...
functional classes of neurons in primary auditory cortex of the cat
... of units might vary along the dimension where binaural interactions previously have been shown to vary. Using simple criteria based on characteristics of sensitivity to sound location, we could distinguish three classesof units in AI, two of which had sharply defined spatial receptive fields. These ...
... of units might vary along the dimension where binaural interactions previously have been shown to vary. Using simple criteria based on characteristics of sensitivity to sound location, we could distinguish three classesof units in AI, two of which had sharply defined spatial receptive fields. These ...
Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and
... skipping (21, 25, 26) as well as a scaffold for nuclear bodies through interactions with survival motor neuron protein (27). TDP-43 is normally localized primarily to the nucleus, but our data indicate that, under pathological conditions in FTLD-U, TDP-43 is eliminated from nuclei of UBI-bearing neu ...
... skipping (21, 25, 26) as well as a scaffold for nuclear bodies through interactions with survival motor neuron protein (27). TDP-43 is normally localized primarily to the nucleus, but our data indicate that, under pathological conditions in FTLD-U, TDP-43 is eliminated from nuclei of UBI-bearing neu ...
Mirror Neuron System in Monkey: A Computational Modeling
... this memory to correspond to the grasp that is actually executed. 3. F5 is hypothesized as first being responsible for integrating task constraints with the set of grasps that are afforded by the attended object in order to select a single grasp. After selection of a single grasp, F5 unfolds this re ...
... this memory to correspond to the grasp that is actually executed. 3. F5 is hypothesized as first being responsible for integrating task constraints with the set of grasps that are afforded by the attended object in order to select a single grasp. After selection of a single grasp, F5 unfolds this re ...
NEURAL NETWORKS
... cell, which is one of the most common types of cortical neurons. Like many other types of neurons, it receives most of its inputs through dendritic spines. The pyramidal cell can receive 10,000 or more synaptic contacts and it can project onto thousands of target cells. ...
... cell, which is one of the most common types of cortical neurons. Like many other types of neurons, it receives most of its inputs through dendritic spines. The pyramidal cell can receive 10,000 or more synaptic contacts and it can project onto thousands of target cells. ...
Serotonin in Affective Control
... interactions (thus straddling the boundary between classical neurotransmission and neuromodulation). They can also operate from afar, via axonal connections or volume transmission. These ...
... interactions (thus straddling the boundary between classical neurotransmission and neuromodulation). They can also operate from afar, via axonal connections or volume transmission. These ...
Immunohistochemical Study of Spinal Motor Neurons Following
... techniques in peripheral nerve surgery. However, their efficiency can be highly limited depending on the type of lesion and the gap between two nerve stumps and because of deficient proper nerve donors. So much interest has been focused on the development of alternative instruments for bridging the ...
... techniques in peripheral nerve surgery. However, their efficiency can be highly limited depending on the type of lesion and the gap between two nerve stumps and because of deficient proper nerve donors. So much interest has been focused on the development of alternative instruments for bridging the ...
Integration of Visual and Auditory Information by Superior Temporal
... auditory signals on the visual response. Effect of Sound on Visual Responses Auditory signals had a significant effect on the visual response in 22 (23%) of the 95 cells with visual responses. The visual response was significantly augmented in 8 of 95 cells and significantly attenuated in 8 of 95 ce ...
... auditory signals on the visual response. Effect of Sound on Visual Responses Auditory signals had a significant effect on the visual response in 22 (23%) of the 95 cells with visual responses. The visual response was significantly augmented in 8 of 95 cells and significantly attenuated in 8 of 95 ce ...
The rat ponto-medullary network responsible for paradoxical
... In the middle of the last century, a series of historical observations lead to the discovery of a vigilance state in humans and other mammals paradoxically characterized by cortical activation and rapid eye movements, but associated with a complete disappearance of the muscle tone (Aserinsky and Kle ...
... In the middle of the last century, a series of historical observations lead to the discovery of a vigilance state in humans and other mammals paradoxically characterized by cortical activation and rapid eye movements, but associated with a complete disappearance of the muscle tone (Aserinsky and Kle ...
Structure and dynamics of the corticothalamic driver pathway in the
... along the processing chain, the stimulus specificity of responses as well as the input-output transformations at each station. An interesting model system for investigating these dynamical processes is the rodent whisker system. Rodents can solve highly complicated tasks with their whiskers alone, d ...
... along the processing chain, the stimulus specificity of responses as well as the input-output transformations at each station. An interesting model system for investigating these dynamical processes is the rodent whisker system. Rodents can solve highly complicated tasks with their whiskers alone, d ...
Molecular and functional analysis of Drosophila single
... a role in controlling axonogenesis of mammillary body axons (Marion et al., 2005). The results from mammals indicate that sim can function in axonogenesis, and this is also a potential role for sim in central brain development given the sim disorganized neuropil phenotype. In this paper, we further ...
... a role in controlling axonogenesis of mammillary body axons (Marion et al., 2005). The results from mammals indicate that sim can function in axonogenesis, and this is also a potential role for sim in central brain development given the sim disorganized neuropil phenotype. In this paper, we further ...
Lester-Lect to CaltechAssociates-Nov
... reports that they think better when they smoke; this anecdotal observation is confirmed by data that smokers who smoke nicotine cigarettes (but not nicotine-free cigarettes) display several cognitive enhancements. In the rodent context, rats show more contextual fear conditioning if, one day after w ...
... reports that they think better when they smoke; this anecdotal observation is confirmed by data that smokers who smoke nicotine cigarettes (but not nicotine-free cigarettes) display several cognitive enhancements. In the rodent context, rats show more contextual fear conditioning if, one day after w ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.