Cystatin C prevents degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons
... Destruction of nigrostriatal dopaminergic (DA) pathway triggers various persistent responses, such as inflammation and increased synthesis of neural growth factors, both in striatum and in substantia nigra. The pathological processes involved in such responses are poorly characterized and could cont ...
... Destruction of nigrostriatal dopaminergic (DA) pathway triggers various persistent responses, such as inflammation and increased synthesis of neural growth factors, both in striatum and in substantia nigra. The pathological processes involved in such responses are poorly characterized and could cont ...
Extraction of Sensory Parameters from a Neural Map by Primary
... Figure 1. Functional organization of the cricket cercal sensory system. A, Schematic diagram of the common house cricket, Acheta domestica, showing the location of the abdominal nerve cord. The cerci are two abdominal appendages projecting from the rear of the animal’s body. Both cerci are covered w ...
... Figure 1. Functional organization of the cricket cercal sensory system. A, Schematic diagram of the common house cricket, Acheta domestica, showing the location of the abdominal nerve cord. The cerci are two abdominal appendages projecting from the rear of the animal’s body. Both cerci are covered w ...
The Reorganization of Primary Auditory Cortex by Invasion of
... remaining afferents to the deafferented brain area is a way to compensate for the loss of excitatory drive. Sprouting can come from the perilesional area, ipsilateral subcortical or cortical areas, and/or contralateral areas. Chronic peripheral nerve injuries can cause central somatosensory neurons ...
... remaining afferents to the deafferented brain area is a way to compensate for the loss of excitatory drive. Sprouting can come from the perilesional area, ipsilateral subcortical or cortical areas, and/or contralateral areas. Chronic peripheral nerve injuries can cause central somatosensory neurons ...
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Right
... Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive technique for directly stimulating cortical neurons. Electrical energy crosses the brain almost painlessly, without causing convulsions or cognitive impairment but causing a depolarization of neurons (13) with cortical changes in monoamines (1 ...
... Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive technique for directly stimulating cortical neurons. Electrical energy crosses the brain almost painlessly, without causing convulsions or cognitive impairment but causing a depolarization of neurons (13) with cortical changes in monoamines (1 ...
04 narc John neuron
... (A) Photomicrograph showing histamine-immunostained cells located above the level of the fornix (A1), at the level of the fornix (A2), and adjacent to the base of the brain (A3). The location of the electrode track within the histamine cell group is shown (A4). Arrows indicate the histamine-immunore ...
... (A) Photomicrograph showing histamine-immunostained cells located above the level of the fornix (A1), at the level of the fornix (A2), and adjacent to the base of the brain (A3). The location of the electrode track within the histamine cell group is shown (A4). Arrows indicate the histamine-immunore ...
Neuregulin-1/ErbB4 signaling regulates Kv4.2-mediated - AJP-Cell
... factors that is required for the differentiation, migration, and development of neurons. NRG-1 signaling is thought to contribute to both neuronal development and the neuropathology of schizophrenia, which is believed to be a neurodevelopmental disorder. However, few studies have investigated the ro ...
... factors that is required for the differentiation, migration, and development of neurons. NRG-1 signaling is thought to contribute to both neuronal development and the neuropathology of schizophrenia, which is believed to be a neurodevelopmental disorder. However, few studies have investigated the ro ...
Neuronal control of leech behavior - Emory Biology
... middle panel) have provided intracellular and extracellular recordings during each of the behaviors, thereby revealing the underlying motor neuronal firing patterns. The isolated nervous system (bottom panel), in its entirety or in pieces, produces motor patterns that are distinguishable as the neur ...
... middle panel) have provided intracellular and extracellular recordings during each of the behaviors, thereby revealing the underlying motor neuronal firing patterns. The isolated nervous system (bottom panel), in its entirety or in pieces, produces motor patterns that are distinguishable as the neur ...
Neuronal and microglial cathepsins in aging and age
... Besides functions inside the endosomal/lysosomal system, there is evidence that some members of cathepsins are also involved in extracellular proteolysis resulting in pathological conditions. Leakage of cathepsins into the cytoplasm is often achieved by the endocytosis of oxidizable substrates that ...
... Besides functions inside the endosomal/lysosomal system, there is evidence that some members of cathepsins are also involved in extracellular proteolysis resulting in pathological conditions. Leakage of cathepsins into the cytoplasm is often achieved by the endocytosis of oxidizable substrates that ...
Development and aging of cortical thickness correspond to genetic
... processes that could lead to early postnatal thickness increase, such as proliferation of dendrites, dendritic spines, axonal sprouting, and vascular development, and also processes that would lead to apparent thinning, such as synaptic pruning and intracortical myelination (13– 15, 50, 51). The lat ...
... processes that could lead to early postnatal thickness increase, such as proliferation of dendrites, dendritic spines, axonal sprouting, and vascular development, and also processes that would lead to apparent thinning, such as synaptic pruning and intracortical myelination (13– 15, 50, 51). The lat ...
Wnt/Planar Cell Polarity Signaling Controls the Anterior–Posterior
... and the trajectory of the initial axon segment projections (arrows). Fzd3⫺/⫺ mice form very short axons within the descending region, many of which project into inappropriate lateral just proximal to the TH-positive cell body. andanteriordirections(E).G,Lp/Lpmiceformaxonswithinthedescendingregiontha ...
... and the trajectory of the initial axon segment projections (arrows). Fzd3⫺/⫺ mice form very short axons within the descending region, many of which project into inappropriate lateral just proximal to the TH-positive cell body. andanteriordirections(E).G,Lp/Lpmiceformaxonswithinthedescendingregiontha ...
PDF - Journal of Neuroscience
... ms before one of the two directional lights (left or right) illuminated for 100 ms. The cue-light disclosed the response direction in which the animal could retrieve fluid reward. On 20% of all trials, simultaneous with port exit, the light opposite the first illuminated to instruct the rat to inhib ...
... ms before one of the two directional lights (left or right) illuminated for 100 ms. The cue-light disclosed the response direction in which the animal could retrieve fluid reward. On 20% of all trials, simultaneous with port exit, the light opposite the first illuminated to instruct the rat to inhib ...
Dissertation 20161009 Text Citations
... perception system, including the occipital and fusiform face areas and the posterior superior temporal sulcus. In fMRI studies, the fusiform face area (FFA) and, more generally, the fusiform gyri, were found to have bilaterally greater responses to untrustworthy and trustworthy faces (Said et al., 2 ...
... perception system, including the occipital and fusiform face areas and the posterior superior temporal sulcus. In fMRI studies, the fusiform face area (FFA) and, more generally, the fusiform gyri, were found to have bilaterally greater responses to untrustworthy and trustworthy faces (Said et al., 2 ...
Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus activation contributes to
... Heart failure (HF) is a serious cardiovascular disease and is characterized by exaggerated sympathetic activity. In this paper, we review these limited studies, with particular emphasis on examining the role of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) in the neurohumoral excitation in HF. The PVN is an imp ...
... Heart failure (HF) is a serious cardiovascular disease and is characterized by exaggerated sympathetic activity. In this paper, we review these limited studies, with particular emphasis on examining the role of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) in the neurohumoral excitation in HF. The PVN is an imp ...
Response Properties of Neighboring Neurons in the
... anatomical arrangement such as the layered structure of the neocortex, the complex circuitry of the cerebellum, or the laminar structure of the cochlear nucleus (Kandel et al., 2000), the ability to investigate whether responses are grouped in any functional arrangement spatially offers the opportun ...
... anatomical arrangement such as the layered structure of the neocortex, the complex circuitry of the cerebellum, or the laminar structure of the cochlear nucleus (Kandel et al., 2000), the ability to investigate whether responses are grouped in any functional arrangement spatially offers the opportun ...
Effect of Lesions of the Ventrolateral Preoptic Nucleus on NREM and
... major role in causing sleep. Steininger et al. (1997) and Yang and Hatton (1997) have shown that electrical stimulation in the VLPO region causes GABAA receptor-mediated hyperpolarization and inhibition of TMN neurons in brain slices. These results suggest that the VLPO may play an important role in ...
... major role in causing sleep. Steininger et al. (1997) and Yang and Hatton (1997) have shown that electrical stimulation in the VLPO region causes GABAA receptor-mediated hyperpolarization and inhibition of TMN neurons in brain slices. These results suggest that the VLPO may play an important role in ...
The medial geniculate, not the amygdala, as the root of auditory fear
... thalamus, including the medial division of the medial geniculate body (MGm) and the posterior intralaminar nucleus (PIN). While MGv only projects to primary auditory cortex, MGm/PIN projects to both primary and association areas of auditory cortex, as well as to the lateral nucleus of the amygdala ( ...
... thalamus, including the medial division of the medial geniculate body (MGm) and the posterior intralaminar nucleus (PIN). While MGv only projects to primary auditory cortex, MGm/PIN projects to both primary and association areas of auditory cortex, as well as to the lateral nucleus of the amygdala ( ...
mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotic drugs
... DA neurons in the substantia nigra, which project to the dorsal striatum, sparing those of the A10 ventral tegmentum, which project to the cortex and mesolimbic systems (12). The subsequent evidence that clozapine, compared to neuroleptic drugs such as haloperidol, had at least six advantages in add ...
... DA neurons in the substantia nigra, which project to the dorsal striatum, sparing those of the A10 ventral tegmentum, which project to the cortex and mesolimbic systems (12). The subsequent evidence that clozapine, compared to neuroleptic drugs such as haloperidol, had at least six advantages in add ...
The effect of lithium on the adrenoceptor
... Objective: Lithium remains the most widely used treatment for bipolar disorder; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying its therapeutic actions have not been fully elucidated. We studied the in-vivo effect of lithium on the density of α-adrenoceptor (α-AR) and β-AR subtypes and linked second me ...
... Objective: Lithium remains the most widely used treatment for bipolar disorder; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying its therapeutic actions have not been fully elucidated. We studied the in-vivo effect of lithium on the density of α-adrenoceptor (α-AR) and β-AR subtypes and linked second me ...
An implantable neural probe with monolithically integrated dielectric
... network functions and behavior. This goal cannot be achieved effectively by electrical stimulation since it indiscriminately stimulates neuronal processes, including somata, dendrites and axons in a complex manner [2]. Recent advances in optogenetics provide a new approach to neural circuit analysis ...
... network functions and behavior. This goal cannot be achieved effectively by electrical stimulation since it indiscriminately stimulates neuronal processes, including somata, dendrites and axons in a complex manner [2]. Recent advances in optogenetics provide a new approach to neural circuit analysis ...
Wide field-of-view, twin-region two-photon imaging across extended
... revealing activity correlations and population dynamics within an individual cortical area. However, many conventional two-photon imaging systems maintain cellular resolution only over a field of view (FOV) ~500 µm wide. This FOV precludes the simultaneous visualization of multiple cortical areas, w ...
... revealing activity correlations and population dynamics within an individual cortical area. However, many conventional two-photon imaging systems maintain cellular resolution only over a field of view (FOV) ~500 µm wide. This FOV precludes the simultaneous visualization of multiple cortical areas, w ...
Neural correlates of stimulus–response and response–outcome
... same block were averaged together. In this way, free- and forcedchoice trials were matched for direction, outcome and position in block. To represent population activity, we first binned the firing rate of each neuron, from the beginning of each trial to the end of each trial. Then we subtracted the ...
... same block were averaged together. In this way, free- and forcedchoice trials were matched for direction, outcome and position in block. To represent population activity, we first binned the firing rate of each neuron, from the beginning of each trial to the end of each trial. Then we subtracted the ...
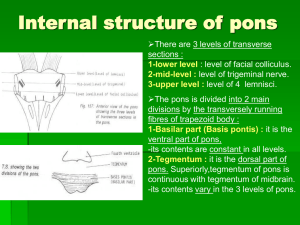
07-pons + midbrain2009-03-24 08:441.9 MB
... sleep, particularly REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. 2-acts as an attention center, (functional deficiency resulting in depression). ...
... sleep, particularly REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. 2-acts as an attention center, (functional deficiency resulting in depression). ...
Sònia Najas Sales Role of DYRK1A in the development of Syndrome
... syndrome (DS), which is caused by an extra copy of human chromosome (HSA) 21. The analysis of brain tissue from foetuses and children with DS and from trisomic mice that model the syndrome indicated that intellectual disability in DS is caused, at least in part, by alterations in the cytoarchitectur ...
... syndrome (DS), which is caused by an extra copy of human chromosome (HSA) 21. The analysis of brain tissue from foetuses and children with DS and from trisomic mice that model the syndrome indicated that intellectual disability in DS is caused, at least in part, by alterations in the cytoarchitectur ...
HLH-14 is a C. elegans Achaete-Scute protein that
... characteristics. Yet HLH-14 does not have a strictly proneural role; it appears to act in neuronal differentiation as well. Additionally, genetic data suggest that hlh-14 and hlh-2 act together in neurogenesis. Surprisingly, we find that loss of hlh-14 function causes an asymmetric cell division def ...
... characteristics. Yet HLH-14 does not have a strictly proneural role; it appears to act in neuronal differentiation as well. Additionally, genetic data suggest that hlh-14 and hlh-2 act together in neurogenesis. Surprisingly, we find that loss of hlh-14 function causes an asymmetric cell division def ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.