Cell Body - Cloudfront.net
... sensory for balance and hearing IX Glossopharyngeal nerve – sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx X Vagus nerves – sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera ...
... sensory for balance and hearing IX Glossopharyngeal nerve – sensory for taste; motor fibers to the pharynx X Vagus nerves – sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera ...
The Number of Cortical Neurons Used to See
... exhibitory region surrounded by a rectangular inhibitory region. Thus simple cells have distinct exhibitory and inhibitory regions, and respond to temporal modulation of grating patterns, at the same frequency (Tao et. al., 2003). Thus they have a greater sensitivity to location, orientation and sp ...
... exhibitory region surrounded by a rectangular inhibitory region. Thus simple cells have distinct exhibitory and inhibitory regions, and respond to temporal modulation of grating patterns, at the same frequency (Tao et. al., 2003). Thus they have a greater sensitivity to location, orientation and sp ...
Sensory Areas
... Body is represented spatially in the primary motor cortex Motor Areas—Frontal Eye Field ...
... Body is represented spatially in the primary motor cortex Motor Areas—Frontal Eye Field ...
Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
... The imaging findings make sense because the brain areas that are reduced in size in children with ADHD are the very ones that regulate attention. The right prefrontal cortex, for example, is involved in “editing” one’s behavior, resisting distractions and developing an awareness of self and time. Th ...
... The imaging findings make sense because the brain areas that are reduced in size in children with ADHD are the very ones that regulate attention. The right prefrontal cortex, for example, is involved in “editing” one’s behavior, resisting distractions and developing an awareness of self and time. Th ...
Self-images in the video monitor coded by monkey intraparietal
... use rake-shaped tools to extend their reaching distance, and found in the intraparietal cortex a group of bimodal (somatosensory and visual) neurons which seemed to represent the image of the hand into which the tool was incorporated as its extension (Iriki et al., 1996). That is, around the somatos ...
... use rake-shaped tools to extend their reaching distance, and found in the intraparietal cortex a group of bimodal (somatosensory and visual) neurons which seemed to represent the image of the hand into which the tool was incorporated as its extension (Iriki et al., 1996). That is, around the somatos ...
Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders
... the aetiology of sALS (sporadic ALS) has remained unknown, 20% of fALS cases are associated with a dominantly inherited mutation in this particular gene. Till now, more than 100 different mutations in SOD1 have been described [32]. Surprisingly, most of these mutant SODs retain full enzymatic activi ...
... the aetiology of sALS (sporadic ALS) has remained unknown, 20% of fALS cases are associated with a dominantly inherited mutation in this particular gene. Till now, more than 100 different mutations in SOD1 have been described [32]. Surprisingly, most of these mutant SODs retain full enzymatic activi ...
The Neurons of the Medial Geniculate Body in the Mustached Bat
... JEFFERY A. WINER AND JEFFREY J. WENSTRUP Division of Neurobiology, Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California at Berkeley, Berkeley, California 94720-3200 ...
... JEFFERY A. WINER AND JEFFREY J. WENSTRUP Division of Neurobiology, Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California at Berkeley, Berkeley, California 94720-3200 ...
The Nucleus Basalis of Meynert
... term storage and long-term retrieval in normal male volunteers.22 Perry and others23 compared mental test scores, cholinergic activity and neuropathological changes in 28 demented patients with appropriate controls (normals). CAT and AChE activity decreased as mean senile plaque count rose, and thes ...
... term storage and long-term retrieval in normal male volunteers.22 Perry and others23 compared mental test scores, cholinergic activity and neuropathological changes in 28 demented patients with appropriate controls (normals). CAT and AChE activity decreased as mean senile plaque count rose, and thes ...
The Neuronal Correlate of Consciousness
... highly susceptible to excitatory input and capable of emitting action potentials. In the subsequent trough of the cycle the membrane potential is hyperpolarized and membrane conductance is high because of strong GABAergic inhibition generated by the rhythmically active inhibitory interneurons. Durin ...
... highly susceptible to excitatory input and capable of emitting action potentials. In the subsequent trough of the cycle the membrane potential is hyperpolarized and membrane conductance is high because of strong GABAergic inhibition generated by the rhythmically active inhibitory interneurons. Durin ...
growth hormone releasing hormone
... Hypothalamus is protected from these influences by blood brain barrier (BBB). BBB is a complex mechanism regulating exchange of mediators between blood and CNS. It functions as protection from harmful stimuli (toxins) and also as transport system (for example glucose) into brain. BBB represented by ...
... Hypothalamus is protected from these influences by blood brain barrier (BBB). BBB is a complex mechanism regulating exchange of mediators between blood and CNS. It functions as protection from harmful stimuli (toxins) and also as transport system (for example glucose) into brain. BBB represented by ...
MSc Thesis Template Document
... brain’s activity is not yet fully defined and remains a huge research area. This project attempts to approach and understand the diversifications of brain’s responses while interfering with different situations. The aim is to observe and notice brain’s reactions to an external stimulus. Neural activ ...
... brain’s activity is not yet fully defined and remains a huge research area. This project attempts to approach and understand the diversifications of brain’s responses while interfering with different situations. The aim is to observe and notice brain’s reactions to an external stimulus. Neural activ ...
text of chapter 2
... diagonally across the picture (in a northwest/southeast direction), will cause more neural impulses than the darker parts of the image (Parkhurst, Law & Niebur, 2002). The lower panel illustrates a pattern that might be encoded by our neurons of the scene. Figure 2.6 about here -- Parkhurst et al. 2 ...
... diagonally across the picture (in a northwest/southeast direction), will cause more neural impulses than the darker parts of the image (Parkhurst, Law & Niebur, 2002). The lower panel illustrates a pattern that might be encoded by our neurons of the scene. Figure 2.6 about here -- Parkhurst et al. 2 ...
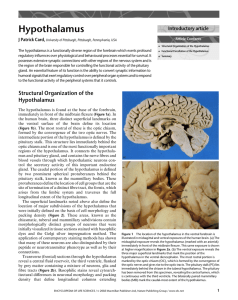
Hypothalamus
... However, the parvocellular neurons release their secretory products into fenestrated capillaries that drain into the long portal vessels that drain into the anterior lobe. The magnocellular neurons secrete either vasopressin or oxytocin, and are largely concentrated in the supraoptic (SON) and parav ...
... However, the parvocellular neurons release their secretory products into fenestrated capillaries that drain into the long portal vessels that drain into the anterior lobe. The magnocellular neurons secrete either vasopressin or oxytocin, and are largely concentrated in the supraoptic (SON) and parav ...
Development of Subcellular mRNA Compartmentation in
... of particular mRNAs into dendrites, which together create the capacity for local synthesis of particular proteins, play a key role in establishing the molecular domains that allow dendrites to function as they do. Given the fact that RNA sorting and transport mechanisms are such prominent features o ...
... of particular mRNAs into dendrites, which together create the capacity for local synthesis of particular proteins, play a key role in establishing the molecular domains that allow dendrites to function as they do. Given the fact that RNA sorting and transport mechanisms are such prominent features o ...
Mechanisms for Sensing Fat in Food in the Mouth
... the brain, and the information reaches the orbitofrontal cortex (which is secondary taste cortex) via the primary taste cortex in the insula (Verhagen and others 2004; Rolls 2011b). Figure 1 shows an example of a fat-responsive neuron in the orbitofrontal cortex where the evoked neuronal firing rate ...
... the brain, and the information reaches the orbitofrontal cortex (which is secondary taste cortex) via the primary taste cortex in the insula (Verhagen and others 2004; Rolls 2011b). Figure 1 shows an example of a fat-responsive neuron in the orbitofrontal cortex where the evoked neuronal firing rate ...
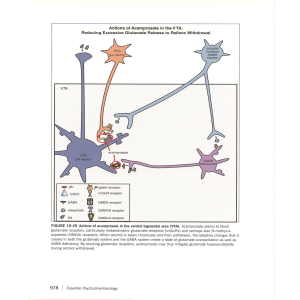
Stahl_3rd_ch19_Part2..
... since injection of the combination of buprenorphine plus naloxone results in no high and may even precipitate withdrawal. L-alpha-acetylmethodol acetate (LAAM) is a long-acting orally active opiate with pharmacological properties similar to those of methadone, but it is rarely used because of concer ...
... since injection of the combination of buprenorphine plus naloxone results in no high and may even precipitate withdrawal. L-alpha-acetylmethodol acetate (LAAM) is a long-acting orally active opiate with pharmacological properties similar to those of methadone, but it is rarely used because of concer ...
Role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the control
... anxiogenic stimuli. We will focus here on the function of BST in brain reward circuitry, particularly in terms of its connectivity with the mesolimbic DA system, and the major role it plays in modulating DA neuronal activity. We refer also to an excellent review for studies on the role of BST in the ...
... anxiogenic stimuli. We will focus here on the function of BST in brain reward circuitry, particularly in terms of its connectivity with the mesolimbic DA system, and the major role it plays in modulating DA neuronal activity. We refer also to an excellent review for studies on the role of BST in the ...
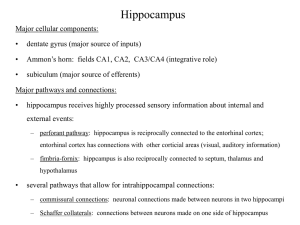
Critical Periods:
... plays an important role in learning and in the formation of short-term memory (working memory) – however, the ability of H.M. to remember early events in his life indicates that the hippocampus is not the location where long-term memories are stored ...
... plays an important role in learning and in the formation of short-term memory (working memory) – however, the ability of H.M. to remember early events in his life indicates that the hippocampus is not the location where long-term memories are stored ...
Central nervous system control of food intake and body
... signal nutrient abundance, the enzyme AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a sensor of nutrient insufficiency. When cells experience a critical drop of fuel availability (as reflected by an increased AMP/ATP ratio), AMPK activation increases substrate oxidation to replenish depleted ATP levels. In ...
... signal nutrient abundance, the enzyme AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a sensor of nutrient insufficiency. When cells experience a critical drop of fuel availability (as reflected by an increased AMP/ATP ratio), AMPK activation increases substrate oxidation to replenish depleted ATP levels. In ...
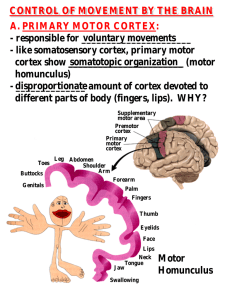
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR
... -caudate and putamen neurons then send their axons to ____________________; internal globus pallidus - in turn, GP axons contact the ________________, thalamus (VA/VL) which feedback onto cortex to modulate movement force. ...
... -caudate and putamen neurons then send their axons to ____________________; internal globus pallidus - in turn, GP axons contact the ________________, thalamus (VA/VL) which feedback onto cortex to modulate movement force. ...
Sensory Regeneration in Arthropods: Implications of Homoeosis
... and because regenerated parts generally successively add increasing numbers of get to function appropriately, they must sensory cells, each growing to the CNS and have regenerated appropriate neural con- making new synapses. Sensory regeneranections, be they sensory, motor, or both. tion recapitulat ...
... and because regenerated parts generally successively add increasing numbers of get to function appropriately, they must sensory cells, each growing to the CNS and have regenerated appropriate neural con- making new synapses. Sensory regeneranections, be they sensory, motor, or both. tion recapitulat ...
INFORMATION PROCESSING WITH POPULATION CODES
... done over s (such as computing the probable time and position of impact of a rapidly approaching object), it is best to preserve the probability density and to do the computations over it in its entirety (as is common in Bayesian settings10,11). Often, however, we need a single value or estimate of ...
... done over s (such as computing the probable time and position of impact of a rapidly approaching object), it is best to preserve the probability density and to do the computations over it in its entirety (as is common in Bayesian settings10,11). Often, however, we need a single value or estimate of ...
Autistic-Spectrum-Disorders-Current
... • Inversion of the pattern of hemispheric activation was found in autistic children • ↑ cortical activity RT hemisphere posteriorly, including the centro-parietal and temporo-occipital sites ...
... • Inversion of the pattern of hemispheric activation was found in autistic children • ↑ cortical activity RT hemisphere posteriorly, including the centro-parietal and temporo-occipital sites ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.