Learning Modules PowerPoint
... from talking – if the child does not talk again, then they have been punished – however, if the child was seeking attention, they will talk again to get the teacher’s attention ...
... from talking – if the child does not talk again, then they have been punished – however, if the child was seeking attention, they will talk again to get the teacher’s attention ...
HSP3M Chapter 3 Homework Questions
... Human perception is so unique because we can detect the smallest stimulus and decide quickly on what it means to us. Each individual perceives things differently depending on several factors such as ...
... Human perception is so unique because we can detect the smallest stimulus and decide quickly on what it means to us. Each individual perceives things differently depending on several factors such as ...
cognitive learning
... depends on remembering the actions of model, when model is no longer available. Motor Reproduction Process: Watching must be converted into doing. ...
... depends on remembering the actions of model, when model is no longer available. Motor Reproduction Process: Watching must be converted into doing. ...
Learning Practice Questions
... 18. Jack finally takes out the garbage so that his father will stop pestering him. Jack’s behavior is influenced by a. positive reinforcement b. negative reinforcement c. positive punishment d. negative punishment 19. A pigeon can easily be taught to flap its wings to avoid shock but not for food re ...
... 18. Jack finally takes out the garbage so that his father will stop pestering him. Jack’s behavior is influenced by a. positive reinforcement b. negative reinforcement c. positive punishment d. negative punishment 19. A pigeon can easily be taught to flap its wings to avoid shock but not for food re ...
Brittney Carroll
... punishment would be a child is caught cheating on a test. The teacher takes the test away and gives the child a zero and yells at the child. The child never cheated again. This is punishment because the child received a bad grade and got yelled at. Operant conditioning is used practically everyday a ...
... punishment would be a child is caught cheating on a test. The teacher takes the test away and gives the child a zero and yells at the child. The child never cheated again. This is punishment because the child received a bad grade and got yelled at. Operant conditioning is used practically everyday a ...
HND – 2. Individual Behavior
... Positive Reinforcement Following a response with something pleasant. Negative Reinforcement Following a response by the termination or withdrawal of something unpleasant. Punishment attempts to decrease the probability of specific behaviours being exhibited (eliminate undesirable behavior.) ...
... Positive Reinforcement Following a response with something pleasant. Negative Reinforcement Following a response by the termination or withdrawal of something unpleasant. Punishment attempts to decrease the probability of specific behaviours being exhibited (eliminate undesirable behavior.) ...
Copy Notes
... after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned response acquisition: in classical conditioning, the initial stage when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response; in operant ...
... after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned response acquisition: in classical conditioning, the initial stage when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response; in operant ...
Ch.6 Learning Power Point Notes
... (ex. Stephan and Cody were two mentally disabled boys who seldom smiled at other people. Dr. Hopkins used a procedure in which he would take them for walks, and if they smiled at passers by, he would give them some pieces of M & M's candy. This procedure caused Stephan and Cody to smile much more of ...
... (ex. Stephan and Cody were two mentally disabled boys who seldom smiled at other people. Dr. Hopkins used a procedure in which he would take them for walks, and if they smiled at passers by, he would give them some pieces of M & M's candy. This procedure caused Stephan and Cody to smile much more of ...
LEArniNG
... Positive contingency :behavior leads to aversive stimulus. Negative contingency : behavior prevents an appetitive stimulus (omission training). Reinforcement produces GOOD outcomes. Punishment produces BAD outcomes. These principles can be implicated for child rearing. The temporal relationship betw ...
... Positive contingency :behavior leads to aversive stimulus. Negative contingency : behavior prevents an appetitive stimulus (omission training). Reinforcement produces GOOD outcomes. Punishment produces BAD outcomes. These principles can be implicated for child rearing. The temporal relationship betw ...
Lecture 4
... All six apes vainly endeavored to reach the fruit by leaping up from the ground. Sultan soon relinquished this attempt, paced restlessly up and down, suddenly stood still in front of the box, seized it, tipped it hastily straight towards the objective, but began to climb upon it at a (horizontal) di ...
... All six apes vainly endeavored to reach the fruit by leaping up from the ground. Sultan soon relinquished this attempt, paced restlessly up and down, suddenly stood still in front of the box, seized it, tipped it hastily straight towards the objective, but began to climb upon it at a (horizontal) di ...
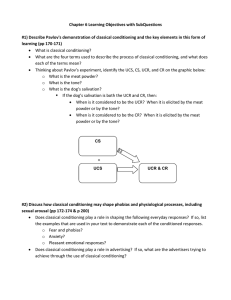
Chapter 6 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions #1) Describe
... #7) Explain how stimuli govern operant behavior and how generalization and discrimination occur in operant conditioning (pp 181‐182 + Table 6.1) ...
... #7) Explain how stimuli govern operant behavior and how generalization and discrimination occur in operant conditioning (pp 181‐182 + Table 6.1) ...
Learning: Principles and Applications
... Learning • Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior that results from experience. • Not all behaviors that we learn are acquired in the same way. • Furthermore, the same behavior can be learned in different ways. ...
... Learning • Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior that results from experience. • Not all behaviors that we learn are acquired in the same way. • Furthermore, the same behavior can be learned in different ways. ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
... explanation is known as operant conditioning. These two types of learning are exhibited in our everyday lives through our home, school, and school. Classical conditioning was discovered by Iran Petrovich Pavlov. He was originally a physiologist whose main focus was the digestive system (Gazzaniga 23 ...
... explanation is known as operant conditioning. These two types of learning are exhibited in our everyday lives through our home, school, and school. Classical conditioning was discovered by Iran Petrovich Pavlov. He was originally a physiologist whose main focus was the digestive system (Gazzaniga 23 ...
Notes: Classical Conditioning
... Learning- A relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs because of experience. ...
... Learning- A relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs because of experience. ...
Chapter 8 Review Notes
... conditioning are the following: In classical conditioning, the organism learns associations between events that it does not control, and responses are automatic. In operant conditioning, the organism learns associations between its behavior and resulting events; the organism operates on the environm ...
... conditioning are the following: In classical conditioning, the organism learns associations between events that it does not control, and responses are automatic. In operant conditioning, the organism learns associations between its behavior and resulting events; the organism operates on the environm ...
Topic4-Learning
... rather than being fixed Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... rather than being fixed Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Lecture: Classical Conditioning
... depends on the effects it has on the environment Responses that have satisfying effects are strengthened and more likely to occur again ...
... depends on the effects it has on the environment Responses that have satisfying effects are strengthened and more likely to occur again ...
IBPaperOne - Socialscientist.us
... not being allowed to touch the toys. Therefore the aggression they exhibited may not have been solely due to the video they observed. Also is unethical to manipulate children to be aggressive. There are possible long-term consequences for these children. Contributions – The social learning theory ...
... not being allowed to touch the toys. Therefore the aggression they exhibited may not have been solely due to the video they observed. Also is unethical to manipulate children to be aggressive. There are possible long-term consequences for these children. Contributions – The social learning theory ...
Name: For each of the examples below decide identify the
... For each of the examples below decide identify the unconditioned stimulus (US), unconditioned response (UR), conditioned stimulus (CS), and conditioned response (CR). Classical Conditioning Examples: 1. Every time someone flushes a toilet in the apartment building, the shower becomes very hot and ca ...
... For each of the examples below decide identify the unconditioned stimulus (US), unconditioned response (UR), conditioned stimulus (CS), and conditioned response (CR). Classical Conditioning Examples: 1. Every time someone flushes a toilet in the apartment building, the shower becomes very hot and ca ...
Innate/Learned Behavior Powerpoint
... Soon, the rat pressed the lever far more often than he would just by chance. But with each instance of lever pressing, the operant is reinforced by reward with food. The rat learns that pressing the lever is associated with food, and so he will increasingly press it. ...
... Soon, the rat pressed the lever far more often than he would just by chance. But with each instance of lever pressing, the operant is reinforced by reward with food. The rat learns that pressing the lever is associated with food, and so he will increasingly press it. ...
Learning
... shoe…causes you pain…removing the stone, relieves the pain. Putting on sunscreen before going to the beach. ...
... shoe…causes you pain…removing the stone, relieves the pain. Putting on sunscreen before going to the beach. ...
Learning and Conditioning
... the new stimulus is to the old, the more strongly the subject is likely to respond. ...
... the new stimulus is to the old, the more strongly the subject is likely to respond. ...
Ch 6 Test: Learning
... a. punished for what they do b. attractive, likeable, successful and high in status c. loners and independent thinkers d. around us a lot when we were children 15. In which of the following theories does the subject play the most passive role? a. observational learning b. classical conditioning c. o ...
... a. punished for what they do b. attractive, likeable, successful and high in status c. loners and independent thinkers d. around us a lot when we were children 15. In which of the following theories does the subject play the most passive role? a. observational learning b. classical conditioning c. o ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.