Additional Nervous System Notes
... Important neurotransmitters – “classical” neurotransmitters that have been recognized for many years: 1. Acetylcholine – secreted at neuromuscular junctions, by autonomic nervous system, and central nervous system – only neurotransmitter released at synapses between neurons and muscles (always excit ...
... Important neurotransmitters – “classical” neurotransmitters that have been recognized for many years: 1. Acetylcholine – secreted at neuromuscular junctions, by autonomic nervous system, and central nervous system – only neurotransmitter released at synapses between neurons and muscles (always excit ...
Neurotransmitter Notes
... and Autism. Norepinephrine also known as noradrenaline is a excitatory neurotransmitter that is produced by the adrenal medulla or made from dopamine. High levels of norepinephrine are linked to anxiety, stress, high blood pressure, and hyperactivity. Low levels are linked to lack of energy, focus, ...
... and Autism. Norepinephrine also known as noradrenaline is a excitatory neurotransmitter that is produced by the adrenal medulla or made from dopamine. High levels of norepinephrine are linked to anxiety, stress, high blood pressure, and hyperactivity. Low levels are linked to lack of energy, focus, ...
Antipsychotic/Neuroleptic Agents and Lithium
... Less Extrapyramidal symptoms Low potency More Histaminic side effects ...
... Less Extrapyramidal symptoms Low potency More Histaminic side effects ...
Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System
... D. Synthesis and Metabolism of Catecholamines Tyrosine in the bloodstream is taken up into nerves and converted into catecholamine. The five main enzymes whose functions are critical to the formation of catecholamines are discussed below (Figure 6). Tyrosine hydroxylase (tyrosine to dopa) is the rat ...
... D. Synthesis and Metabolism of Catecholamines Tyrosine in the bloodstream is taken up into nerves and converted into catecholamine. The five main enzymes whose functions are critical to the formation of catecholamines are discussed below (Figure 6). Tyrosine hydroxylase (tyrosine to dopa) is the rat ...
CHAPTER 20 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
... = pelvic splanchnic nerves distal ½ lg intestine and rectum urinary bladder , ureters reproductive organs ...
... = pelvic splanchnic nerves distal ½ lg intestine and rectum urinary bladder , ureters reproductive organs ...
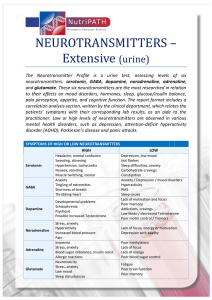
NEUROTRANSMITTERS – Extensive (urine)
... well as hormones. They are produced by noradrenergic and adrenergic neurons respectively, as well as by the adrenal medulla. They are most well known for their involvement in the ‘fight and flight’ response, in which they increase heart rate, trigger the release of glucose from energy stores and inc ...
... well as hormones. They are produced by noradrenergic and adrenergic neurons respectively, as well as by the adrenal medulla. They are most well known for their involvement in the ‘fight and flight’ response, in which they increase heart rate, trigger the release of glucose from energy stores and inc ...
ADRENAL GLAND Medulla
... Normal plasma level of free norepinephrine is about 300 pg/mL (1.8 nmol/L). On standing, the level increases 50-100%. free epinephrine level, is normally about 30 pg/mL (0.16 nmol/L). ...
... Normal plasma level of free norepinephrine is about 300 pg/mL (1.8 nmol/L). On standing, the level increases 50-100%. free epinephrine level, is normally about 30 pg/mL (0.16 nmol/L). ...
The Four Major Neurotransmitters
... Tourette's. High levels also contribute to Depression, OCD, and Autism. Norepinephrine also known as noradrenaline is a excitatory neurotransmitter that is produced by the adrenal medulla or made from dopamine. High levels of norepinephrine are linked to anxiety, stress, high blood pressure, and hyp ...
... Tourette's. High levels also contribute to Depression, OCD, and Autism. Norepinephrine also known as noradrenaline is a excitatory neurotransmitter that is produced by the adrenal medulla or made from dopamine. High levels of norepinephrine are linked to anxiety, stress, high blood pressure, and hyp ...
body and behavior
... branching out from cell body; receive impulses from other neurons 3) Axon: long fiber that carries impulses from cell body Myelin sheath: white, fatty substance that insulates axons Axon terminals: branch out from end of axon; send msgs to next neuron ...
... branching out from cell body; receive impulses from other neurons 3) Axon: long fiber that carries impulses from cell body Myelin sheath: white, fatty substance that insulates axons Axon terminals: branch out from end of axon; send msgs to next neuron ...
Psychotropic Meds - nursing-
... Inhibits MAO, thus interfering with breakdown of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin ...
... Inhibits MAO, thus interfering with breakdown of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin ...
4. Regulation- The Endocrine System
... Nervous System • Neurons fall into 3 Categories: 1. Sensory neurons- from body to spinal cord and brain 2. Interneurons- brain and spinal cord. Processes impulses and respond by sending impulses onto ...
... Nervous System • Neurons fall into 3 Categories: 1. Sensory neurons- from body to spinal cord and brain 2. Interneurons- brain and spinal cord. Processes impulses and respond by sending impulses onto ...
Self governing- serves internal organs and glands
... Problem in processing meaning language People can see the object but can’t name it ...
... Problem in processing meaning language People can see the object but can’t name it ...
Basic Neuroanatomy
... Leads to profound reduction in the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and a threefold increase in norepinephrine Symptoms of withdrawal are the opposite of the pharmacologic effects Magnitude of the withdrawal symptoms is directly related to the dose and frequency of the opiate taken Withd ...
... Leads to profound reduction in the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and a threefold increase in norepinephrine Symptoms of withdrawal are the opposite of the pharmacologic effects Magnitude of the withdrawal symptoms is directly related to the dose and frequency of the opiate taken Withd ...
Drugs Unit 2 - Cat`s TCM Notes
... Chronic muscular disease caused by a defect in neuromuscular transmission Autoimmune disease; patients make antibodies to ACh receptors, causing gradual destruction of them ...
... Chronic muscular disease caused by a defect in neuromuscular transmission Autoimmune disease; patients make antibodies to ACh receptors, causing gradual destruction of them ...
Adrenal Glands
... In response to a __________________, neurons of the ______________ nervous system carry a signal from the __________________ directly to the __________________ __________________. These neurons (rather than __________________) stimulate the adrenal medulla to secrete __________________ and a small a ...
... In response to a __________________, neurons of the ______________ nervous system carry a signal from the __________________ directly to the __________________ __________________. These neurons (rather than __________________) stimulate the adrenal medulla to secrete __________________ and a small a ...
Organization of the Brain - Mr. Van Frachen's Web Page
... isn’t receiving information the brain will divert the neurons to work on some other part. (This includes damage to the brain itself) ...
... isn’t receiving information the brain will divert the neurons to work on some other part. (This includes damage to the brain itself) ...
Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology
... • Nicotinic receptors are found on: – Motor end plates (somatic targets) – All ganglionic neurons of both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions – The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla ...
... • Nicotinic receptors are found on: – Motor end plates (somatic targets) – All ganglionic neurons of both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions – The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla ...
Pharmacology 6 – SNS Antagonists
... 5. Describe the actions of the false transmitter methyldopa and what are its clinical uses and side effects. 6. How can SNS antagonist drugs be used to treat arrhythmias and angina. 7. What is glaucoma and how is the aqueous humor formed in the eye. 8. Describe how SNS agonists and antagonists can b ...
... 5. Describe the actions of the false transmitter methyldopa and what are its clinical uses and side effects. 6. How can SNS antagonist drugs be used to treat arrhythmias and angina. 7. What is glaucoma and how is the aqueous humor formed in the eye. 8. Describe how SNS agonists and antagonists can b ...
NT Notes
... while you do your WS. This is a class set so please do not take them with you. It is also available on the webpage along with this powerpoint. ...
... while you do your WS. This is a class set so please do not take them with you. It is also available on the webpage along with this powerpoint. ...
Snímka 1 - TOP Recommended Websites
... • Minimal muscle relaxing and anticonvulsant effect. • Rapidly metabolized by liver enzymes into inactive metabolites. • Dosage should be reduced in patients with hepatic dysfunction, the elderly and patients taking cimetidine. ...
... • Minimal muscle relaxing and anticonvulsant effect. • Rapidly metabolized by liver enzymes into inactive metabolites. • Dosage should be reduced in patients with hepatic dysfunction, the elderly and patients taking cimetidine. ...
Sympathetic Nervous System
... Divisions of the ANS • Two divisions that innervate the same target organs • Two divisions may have cooperative or contrasting effects • Sympathetic division prepares body for physical activity (‘fight or flight’ response) ...
... Divisions of the ANS • Two divisions that innervate the same target organs • Two divisions may have cooperative or contrasting effects • Sympathetic division prepares body for physical activity (‘fight or flight’ response) ...
TOXICOLOGY – TEST 1 STUDY GUIDE
... - These agents remain attached to receptors for long periods of time providing constant stimulation. Produce short lasting muscle fasciculation followed by paralysis. 23. Synthesis of Norepinephrine - NE is an adrenergic agent. It is synthesized from the AA tyrosine. It is then hydroxylated to DOPA ...
... - These agents remain attached to receptors for long periods of time providing constant stimulation. Produce short lasting muscle fasciculation followed by paralysis. 23. Synthesis of Norepinephrine - NE is an adrenergic agent. It is synthesized from the AA tyrosine. It is then hydroxylated to DOPA ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.