Al Tmimi - Cardiovascular active medications tekst
... Adrenergic agonists can be simply classified according to their sensitivity to α or β receptors, for example phenylephrine has a α1 agonist effect with very minimally effect on β-adrenergic receptors, while isoproterenol activate only the β-adrenergic receptors. Other medications like epinephrine, n ...
... Adrenergic agonists can be simply classified according to their sensitivity to α or β receptors, for example phenylephrine has a α1 agonist effect with very minimally effect on β-adrenergic receptors, while isoproterenol activate only the β-adrenergic receptors. Other medications like epinephrine, n ...
sympathetic nervous system
... Nervous system of the digestive tract Composed of 100 million neurons found in the walls of the digestive tract (no components found in CNS) ...
... Nervous system of the digestive tract Composed of 100 million neurons found in the walls of the digestive tract (no components found in CNS) ...
New Psychoactive Substances NPS
... or 4-methylephedrone: Releasing dopamine/norepinephrine Dopamine transporter inhibitor Stimulant effects Teeth grinding, cardiovascular problems, behavioural undercontrol Bath salts containing substituted cathinones White crystals often resemble legal bathing products cathinone ...
... or 4-methylephedrone: Releasing dopamine/norepinephrine Dopamine transporter inhibitor Stimulant effects Teeth grinding, cardiovascular problems, behavioural undercontrol Bath salts containing substituted cathinones White crystals often resemble legal bathing products cathinone ...
Drug acting on autonomic and central nervous systems
... response and prolongating ”on time”. Moclobemide inhibits MAO-A, thus preventing degradation of norepinephrine and serotonin. Selegeline inhibits MAO-B, thus delaying metabolic degradation of dopamine. 2. The answer is d. Neostigmine is used orally or by injection as a stimulant of the smooth muscle ...
... response and prolongating ”on time”. Moclobemide inhibits MAO-A, thus preventing degradation of norepinephrine and serotonin. Selegeline inhibits MAO-B, thus delaying metabolic degradation of dopamine. 2. The answer is d. Neostigmine is used orally or by injection as a stimulant of the smooth muscle ...
Chapter 17 Antipsychotic Agents
... Tricyclics antidepressants block the amine (norepinephrine or serotonin) reuptake pumps. Such an action presumably permits a longer sojourn逗留 of neurotransmitter at the receptor site. (The pathogenesis of depression- the Amine-Hypothesis) ...
... Tricyclics antidepressants block the amine (norepinephrine or serotonin) reuptake pumps. Such an action presumably permits a longer sojourn逗留 of neurotransmitter at the receptor site. (The pathogenesis of depression- the Amine-Hypothesis) ...
Extensive Neurotransmitter Profile
... well as hormones. They are produced by noradrenergic and adrenergic neurons respectively, as well as by the adrenal medulla. They are most well known for their involvement in the ‘fight and flight’ response, in which they increase heart rate, trigger the release of glucose from energy stores and inc ...
... well as hormones. They are produced by noradrenergic and adrenergic neurons respectively, as well as by the adrenal medulla. They are most well known for their involvement in the ‘fight and flight’ response, in which they increase heart rate, trigger the release of glucose from energy stores and inc ...
HYPERTENSIN PHL315
... because it can cause reflex stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. since the vasodilatation causes sever transient drop in blood pressure. This reflex stimulation causes increased heart rate and contractility, and also rennin release (causes marked fluid retention and edema). • In order for ...
... because it can cause reflex stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. since the vasodilatation causes sever transient drop in blood pressure. This reflex stimulation causes increased heart rate and contractility, and also rennin release (causes marked fluid retention and edema). • In order for ...
Adrenergic Agonists
... These receptors are not affected by α or β-blocking drugs. Therefore, dopamine is clinically useful in the treatment of shock, in which significant increases in sympathetic activity might compromise renal function. [Note: Similar dopamine receptors are found in the autonomic ganglia and in the CNS.] ...
... These receptors are not affected by α or β-blocking drugs. Therefore, dopamine is clinically useful in the treatment of shock, in which significant increases in sympathetic activity might compromise renal function. [Note: Similar dopamine receptors are found in the autonomic ganglia and in the CNS.] ...
Antidepressants and Sedatives David G. Standaert, MD, Ph.D
... Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI’s) Bupropion Nonselective MAO inhibitors Non-pharmacological therapy ECT Psychotherapy ...
... Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI’s) Bupropion Nonselective MAO inhibitors Non-pharmacological therapy ECT Psychotherapy ...
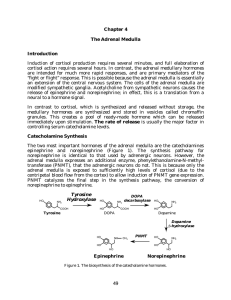
Chapter 4 The Adrenal Medulla Introduction - Rose
... The biosynthesis pathway begins with the amino acid tyrosine. The first step in the pathway is the committed step for catecholamine synthesis. Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the rate limiting step for the production of epinephrine and norepinephrine, the conversion of tyrosine to dihydroxyphenylalan ...
... The biosynthesis pathway begins with the amino acid tyrosine. The first step in the pathway is the committed step for catecholamine synthesis. Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the rate limiting step for the production of epinephrine and norepinephrine, the conversion of tyrosine to dihydroxyphenylalan ...
Many Types of Xanthenes Theophylline Theobromine Caffeine
... Receptors Four types A1 inhibits excitatory neurons – Dopamine, glutamate, and ACh secreting neurons – Reduces production of cAMP – Slows the activity of the cAMP Protein Kinase – Reduces occurrence of the action potential ...
... Receptors Four types A1 inhibits excitatory neurons – Dopamine, glutamate, and ACh secreting neurons – Reduces production of cAMP – Slows the activity of the cAMP Protein Kinase – Reduces occurrence of the action potential ...
Stimulants - Littleton High School
... normally controlled by neurotransmitters are elicited. Because it is not metabolized as rapidly as adrenaline, noradrenaline, and dopamine (these are all polar where amphetamine is nonpolar), it remains active in the body longer and effects can still be felt four to six hours after oral ingestion of ...
... normally controlled by neurotransmitters are elicited. Because it is not metabolized as rapidly as adrenaline, noradrenaline, and dopamine (these are all polar where amphetamine is nonpolar), it remains active in the body longer and effects can still be felt four to six hours after oral ingestion of ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... The sphincter muscle of the iris and the ciliary muscle are innervated by cholinergic nerve fibers. The sphincter muscle is not able to contract normally, the radial muscle causes the pupil to dilate. The patient is unable to focus (accommodate). Anticholinergics block cholinergic pathways and recep ...
... The sphincter muscle of the iris and the ciliary muscle are innervated by cholinergic nerve fibers. The sphincter muscle is not able to contract normally, the radial muscle causes the pupil to dilate. The patient is unable to focus (accommodate). Anticholinergics block cholinergic pathways and recep ...
indiv_drugs_f14
... Acute effect: any smoke can interfere with oxygen binding to red blood cells Acute: marijuana can disrupt coordination, balance, reaction time Acute: increase heart rate and blood pressure Acute: stored THC in fat could be released into bloodstream during exercise Chronic: depends on how frequently ...
... Acute effect: any smoke can interfere with oxygen binding to red blood cells Acute: marijuana can disrupt coordination, balance, reaction time Acute: increase heart rate and blood pressure Acute: stored THC in fat could be released into bloodstream during exercise Chronic: depends on how frequently ...
Direct cholinergic agonists
... The indirect-acting sympathomimetic agents act by releasing previously stored norepinephrine. Amphetamine and its relative, methylphenidate, are central nervous ,stem stimulants used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children. Amphetamine and others of its relatives are indirect-a ...
... The indirect-acting sympathomimetic agents act by releasing previously stored norepinephrine. Amphetamine and its relative, methylphenidate, are central nervous ,stem stimulants used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children. Amphetamine and others of its relatives are indirect-a ...
Lecture 3 – intro to ANS drugs – cholinergic
... axon terminal Synthesized from acetyl-CoA + choline (via enzyme choline acetyltransferase or ChAT) ▪ Acetyl CoA comes from the mitochondria (Krebs) ▪ Choline is absorbed by the nerve cell from outside thru a transporter called choline transporter (CHT) ▪ Blocked by a research drug called Hemicholi ...
... axon terminal Synthesized from acetyl-CoA + choline (via enzyme choline acetyltransferase or ChAT) ▪ Acetyl CoA comes from the mitochondria (Krebs) ▪ Choline is absorbed by the nerve cell from outside thru a transporter called choline transporter (CHT) ▪ Blocked by a research drug called Hemicholi ...
Introduction to Autonomic Drugs: Cholinergic agents
... axon terminal Synthesized from acetyl-CoA + choline (via enzyme choline acetyltransferase or ChAT) ▪ Acetyl CoA comes from the mitochondria (Krebs) ▪ Choline is absorbed by the nerve cell from outside thru a transporter called choline transporter (CHT) ▪ Blocked by a research drug called Hemicholi ...
... axon terminal Synthesized from acetyl-CoA + choline (via enzyme choline acetyltransferase or ChAT) ▪ Acetyl CoA comes from the mitochondria (Krebs) ▪ Choline is absorbed by the nerve cell from outside thru a transporter called choline transporter (CHT) ▪ Blocked by a research drug called Hemicholi ...
Action - جامعة الكوفة
... agents have increased the safety of anesthesia, because less anesthetic is required to produce muscle relaxation. Mechanism of action: a- At low doses: these drugs intract with the nicotinic receptos to prevent the binding of acetylcholine, prevent depolarization of the muscle cell membrane and inhi ...
... agents have increased the safety of anesthesia, because less anesthetic is required to produce muscle relaxation. Mechanism of action: a- At low doses: these drugs intract with the nicotinic receptos to prevent the binding of acetylcholine, prevent depolarization of the muscle cell membrane and inhi ...
Chapter 13 Study Questions Key
... different from norepinephrine? Epinephrine is secreted from the adrenal medulla when an arousing event occurs. It binds to receptors in the liver, causing the release of glucose into the blood to support the flight-or-flight response, but in the brain the glucose helps to maintain transcription and ...
... different from norepinephrine? Epinephrine is secreted from the adrenal medulla when an arousing event occurs. It binds to receptors in the liver, causing the release of glucose into the blood to support the flight-or-flight response, but in the brain the glucose helps to maintain transcription and ...
Topic 14
... contribute to development of goiter. Here we see a few of the many thyroidpituitary interactions that can result in hyperthyoid or hypothyroidism. ...
... contribute to development of goiter. Here we see a few of the many thyroidpituitary interactions that can result in hyperthyoid or hypothyroidism. ...
Adrenergic Drugs - Nursing Pharmacology
... Also called cardioselective sympathomimetics Used to support the heart during cardiac failure or ...
... Also called cardioselective sympathomimetics Used to support the heart during cardiac failure or ...
Psychoactive Drugs
... 3. Intravenous (injected in liquid form through a needle into the skin) 4. Inhaled through the lungs (as gases, vapors, or particles) 5. Through skin (patches on skin) 6. Through mucous membranes (snorting or sniffing; under tongue) ...
... 3. Intravenous (injected in liquid form through a needle into the skin) 4. Inhaled through the lungs (as gases, vapors, or particles) 5. Through skin (patches on skin) 6. Through mucous membranes (snorting or sniffing; under tongue) ...
DUCURS poster 26
... We successfully developed and employed an HPLC assay to mouse brain catecholamines in a PD study. However, our curre findings do not indicate a significant PD interaction between bup and sertraline, and further studies are needed to fully investigate ...
... We successfully developed and employed an HPLC assay to mouse brain catecholamines in a PD study. However, our curre findings do not indicate a significant PD interaction between bup and sertraline, and further studies are needed to fully investigate ...
Drugs used to treat Hypertension
... Incorporate lifestyle changes, even if medication brings BP within nl. Limits Check BP on regular basis and report significant variations (and pulse) Get out of bed slowly ...
... Incorporate lifestyle changes, even if medication brings BP within nl. Limits Check BP on regular basis and report significant variations (and pulse) Get out of bed slowly ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.