Autonomic Nervous System
... activity. – increases heart rate, BP, airflow, blood glucose levels and other functions 2. Parasympathetic Division has calming affect on many body functions and assists in maintenance and repair of tissues. – increases digestion and waste elimination • The two divisions may innervate the same targe ...
... activity. – increases heart rate, BP, airflow, blood glucose levels and other functions 2. Parasympathetic Division has calming affect on many body functions and assists in maintenance and repair of tissues. – increases digestion and waste elimination • The two divisions may innervate the same targe ...
Neural Communication Summary Notes
... neuron, muscle, or gland. 4. Myelin Sheath: layer of fatty tissue also known as Schwann cells that help speed up impulses by insulating the axon and providing Nodes of Ranvier (gaps between the cells) that allow for quick node to node hopping. Glial cells guide neural connections and provide nutrien ...
... neuron, muscle, or gland. 4. Myelin Sheath: layer of fatty tissue also known as Schwann cells that help speed up impulses by insulating the axon and providing Nodes of Ranvier (gaps between the cells) that allow for quick node to node hopping. Glial cells guide neural connections and provide nutrien ...
Chapter 2: The Physiology of Stress
... The ANS regulates visceral activities and vital organs, including: ...
... The ANS regulates visceral activities and vital organs, including: ...
Effects of Drugs on the Nervous System
... ingredient that acts in the brain and produces addiction is nicotine. More recent research has shown that the addiction produced by nicotine is extremely powerful and is at least as strong as addictions to other drugs such as heroin and cocaine. Some of the effects of nicotine include changes in res ...
... ingredient that acts in the brain and produces addiction is nicotine. More recent research has shown that the addiction produced by nicotine is extremely powerful and is at least as strong as addictions to other drugs such as heroin and cocaine. Some of the effects of nicotine include changes in res ...
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
... symptoms. It is therefore recommended to slowly taper down the dose under the supervision of a psychopharmacologist when discontinuing SNRIs. Antidepressants including SNRIs have some dependence producing effects, most notably a withdrawal syndrome. However, their dependence producing properties are ...
... symptoms. It is therefore recommended to slowly taper down the dose under the supervision of a psychopharmacologist when discontinuing SNRIs. Antidepressants including SNRIs have some dependence producing effects, most notably a withdrawal syndrome. However, their dependence producing properties are ...
Guidelines and Treatment Updates in the Diagnosis and
... Bupropion (Wellbutrin) • NDRI (Norepinephrine Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor) – Boosts dopamine and norepinephrine ...
... Bupropion (Wellbutrin) • NDRI (Norepinephrine Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor) – Boosts dopamine and norepinephrine ...
F.Neuroleptics
... component of neuroleptanesthesia, promethazine is not a good antipsychotic drug, but the agent is used in pruritus because of its antihistaminic properties. Adverse Effects: 1. Parkinsonian effects due to excess of cholinergic influence may be normalized by anticholinergics but often the symptoms pe ...
... component of neuroleptanesthesia, promethazine is not a good antipsychotic drug, but the agent is used in pruritus because of its antihistaminic properties. Adverse Effects: 1. Parkinsonian effects due to excess of cholinergic influence may be normalized by anticholinergics but often the symptoms pe ...
Lecture 4
... are not suitable for long-term pain management as they cause complete numbness and can have serious side-effects over time. • Opioid painkillers such as morphine are highly effective at reducing pain, but longterm use can lead to dependence and tolerance. As the body becomes used to the drug it beco ...
... are not suitable for long-term pain management as they cause complete numbness and can have serious side-effects over time. • Opioid painkillers such as morphine are highly effective at reducing pain, but longterm use can lead to dependence and tolerance. As the body becomes used to the drug it beco ...
Biology 30 Notes October 9, 2014 (DID NOT FINISH CONITNUE ON
... system carry a signal from the hypothalamus directly to the adrenal medulla. It is neurons not other hormones that stimulate this gland. The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. Effects – increase breathing rate, heart rate, blood pressure, blood flow to the heart and muscles, an ...
... system carry a signal from the hypothalamus directly to the adrenal medulla. It is neurons not other hormones that stimulate this gland. The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. Effects – increase breathing rate, heart rate, blood pressure, blood flow to the heart and muscles, an ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... 5-HT1 group (CNS, blood vessels) (cAMP) 5-HT2 group (CNS, blood vessels) (IP3/DAG) 5-HT3 group (peripheral nervous system) 5-HT4 group (enteric nervous system) – Main functions: • Intestine: increases motility • Blood vessel: constriction (large vessels) dilation (arterioles) • Nerve ending: trigg ...
... 5-HT1 group (CNS, blood vessels) (cAMP) 5-HT2 group (CNS, blood vessels) (IP3/DAG) 5-HT3 group (peripheral nervous system) 5-HT4 group (enteric nervous system) – Main functions: • Intestine: increases motility • Blood vessel: constriction (large vessels) dilation (arterioles) • Nerve ending: trigg ...
Drugs on the brain
... All drugs have side effects but new drugs aim to provide beneficial effects with minimal side effects ...
... All drugs have side effects but new drugs aim to provide beneficial effects with minimal side effects ...
Lecture 7 - Antidepressants new 11-12
... Restore the levels of NE & 5HT in the synaptic cleft by binding to NET & SERT Has mild antimuscarinic effect Short t1/2 ...
... Restore the levels of NE & 5HT in the synaptic cleft by binding to NET & SERT Has mild antimuscarinic effect Short t1/2 ...
Spanish scientists discover a new function of the dopamine in the
... melatonin, which is produced and released at night and which acts in different parts of the body regulating the metabolic activity. Norepinephrine is a hormone involved in regulating melatonin synthesis and release in the pineal gland. The functions of norepinephrine are carried out via the binding ...
... melatonin, which is produced and released at night and which acts in different parts of the body regulating the metabolic activity. Norepinephrine is a hormone involved in regulating melatonin synthesis and release in the pineal gland. The functions of norepinephrine are carried out via the binding ...
Session 16 Worksheet
... turn receives signals from sympathetic ________________________________ fibers. The first structure consists of a special neuron type called ________________________________ cells. In general, neural stimulation results in the the release of ________________________________ and _____________________ ...
... turn receives signals from sympathetic ________________________________ fibers. The first structure consists of a special neuron type called ________________________________ cells. In general, neural stimulation results in the the release of ________________________________ and _____________________ ...
Norepinephrine - Rice CAAM Department
... Differences in the norepinephrine system are implicated in depression. Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are antidepressants that treat depression by increasing the amount of serotonin and norepinephrine available to postsynaptic cells in the brain. There is some recent evidence implying ...
... Differences in the norepinephrine system are implicated in depression. Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are antidepressants that treat depression by increasing the amount of serotonin and norepinephrine available to postsynaptic cells in the brain. There is some recent evidence implying ...
CNSDrugs - shabeelpn
... becomes tachycardic (SVT). You want to give her adenosine. Is there an interaction you should be aware of? How should you ...
... becomes tachycardic (SVT). You want to give her adenosine. Is there an interaction you should be aware of? How should you ...
20.b) SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM, ALFA AND BETA
... or by blocking the action of norepinephrine and epinephrine. Other drugs act indirectly by altering the release of norepinephrine by the adrenergic neuron. ...
... or by blocking the action of norepinephrine and epinephrine. Other drugs act indirectly by altering the release of norepinephrine by the adrenergic neuron. ...
16 Antidepressants
... Classically depression was attributed to a deficiency in the neurotransmitters serotonin Classically, depression was attributed to a deficiency in the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine (“monoamines”). Prolonging the presence of NT in synaptic cleft was thought to be responsi ...
... Classically depression was attributed to a deficiency in the neurotransmitters serotonin Classically, depression was attributed to a deficiency in the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine (“monoamines”). Prolonging the presence of NT in synaptic cleft was thought to be responsi ...
FUN2: 11:00-12:00 Scribe: Taylor Nelson Wednesday, December
... i. The use of the term indirect is the same as the use for the term Cholinergic stimulus ii. These compounds produce their effects by releasing NE from the nerve terminals iii. They do not inhibit an enzyme iv. The best example, with a major indirect mechanism of action is amphetamine and its variou ...
... i. The use of the term indirect is the same as the use for the term Cholinergic stimulus ii. These compounds produce their effects by releasing NE from the nerve terminals iii. They do not inhibit an enzyme iv. The best example, with a major indirect mechanism of action is amphetamine and its variou ...
Document
... Gamma-amniobutyric acid Primary inhibitory transmitter in the brain Signals other cells to subdue them Examples: Phenobarbital (Luminal), Diazepam (Valium) ...
... Gamma-amniobutyric acid Primary inhibitory transmitter in the brain Signals other cells to subdue them Examples: Phenobarbital (Luminal), Diazepam (Valium) ...
Tyrosine-Derived Neurotransmitters
... S-transferase. The conjugates formed are usually excreted from the cell and, in the case of the liver they are excreted in the bile. Several mechanisms exist for the transport of amino acids across cell membranes. Many are symport or antiport mechanisms that couple amino acid transport to sodium tr ...
... S-transferase. The conjugates formed are usually excreted from the cell and, in the case of the liver they are excreted in the bile. Several mechanisms exist for the transport of amino acids across cell membranes. Many are symport or antiport mechanisms that couple amino acid transport to sodium tr ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... learn to do well in school, or are they born good at it?” In the past, one way to study genes and heredity was by studying twins. This is still used today to conduct research. Look on page 73. ...
... learn to do well in school, or are they born good at it?” In the past, one way to study genes and heredity was by studying twins. This is still used today to conduct research. Look on page 73. ...
Chapter 2
... Types of Neurons (specialized cell that responds to and sends signals) • Sensory neurons: carry messages from sense receptors towards the CNS (afferent – approach CNS) • Motor neurons: carry messages from CNS toward muscles and glands (efferent – exit CNS) • Interneurons: carry messages between nerv ...
... Types of Neurons (specialized cell that responds to and sends signals) • Sensory neurons: carry messages from sense receptors towards the CNS (afferent – approach CNS) • Motor neurons: carry messages from CNS toward muscles and glands (efferent – exit CNS) • Interneurons: carry messages between nerv ...
Endocrine System Hormones
... • Helps maintain blood glucose levels by increasing gluconeogenesis..from amino acids and conversion to glucose of fatty acids from adipose tissue… • Plays and essential part in maintaining blood pressure..make it possible for epinephrine and norepinephrine to maintain a normal level of vasoconstric ...
... • Helps maintain blood glucose levels by increasing gluconeogenesis..from amino acids and conversion to glucose of fatty acids from adipose tissue… • Plays and essential part in maintaining blood pressure..make it possible for epinephrine and norepinephrine to maintain a normal level of vasoconstric ...
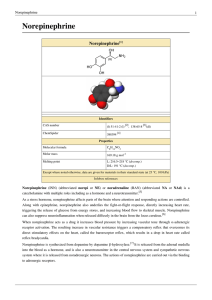
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.