Depression
... • Depression is currently the FOURTH most significant cause of suffering and disability worldwide • and, sadly, It will be the SECOND most debilitating human condition by the year 2020. ...
... • Depression is currently the FOURTH most significant cause of suffering and disability worldwide • and, sadly, It will be the SECOND most debilitating human condition by the year 2020. ...
M 3 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... • All movements require the brain to send appropriate messages to the muscles and coordinate incoming messages from sensory organs and glands etc. • Such messages - movement, feelings, thinking – are communicated through specialized cells called neurons. ...
... • All movements require the brain to send appropriate messages to the muscles and coordinate incoming messages from sensory organs and glands etc. • Such messages - movement, feelings, thinking – are communicated through specialized cells called neurons. ...
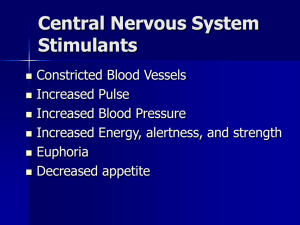
Sympathomimetics
... and the vasoconstriction induced in many vascular beds ( receptors). Epinephrine also activates 2 receptors in some vessels (eg, skeletal muscle vessels), leading vasodilation. Consequently, total peripheral resistance may actually fall, explaining the fall in diastolic pressure that is sometimes se ...
... and the vasoconstriction induced in many vascular beds ( receptors). Epinephrine also activates 2 receptors in some vessels (eg, skeletal muscle vessels), leading vasodilation. Consequently, total peripheral resistance may actually fall, explaining the fall in diastolic pressure that is sometimes se ...
Drug Use, Misuse, Abuse
... responses for stress. -3- Most communication via neurotransmitters- may be stimulatory or inhibitory. The effect depends upon the receptor type of the receiving cells. Drugs may be neurotransmitter mimetics or blocking agents. Neurotransmitters include epinephrine, norepinephrine- both sympathetic; ...
... responses for stress. -3- Most communication via neurotransmitters- may be stimulatory or inhibitory. The effect depends upon the receptor type of the receiving cells. Drugs may be neurotransmitter mimetics or blocking agents. Neurotransmitters include epinephrine, norepinephrine- both sympathetic; ...
Anatomy Research Project
... stress, therefore norepinephrine increases the heart rate as well as blood pressure. It also increases the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver, increases the conversion of fats to fatty acids, and relaxes the bronchial smooth muscle to open up the air passage to the lungs. ...
... stress, therefore norepinephrine increases the heart rate as well as blood pressure. It also increases the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver, increases the conversion of fats to fatty acids, and relaxes the bronchial smooth muscle to open up the air passage to the lungs. ...
PowerPoint - Pitt Honors Human Physiology
... • These drugs are fairly selective for PDE5, but there are limited actions on other enzymes. For example, Sildenafil is only about 10-fold as potent for PDE5 compared to PDE6, an enzyme found in the retina; this cross reactivity is thought to be the basis for abnormalities related to color vision o ...
... • These drugs are fairly selective for PDE5, but there are limited actions on other enzymes. For example, Sildenafil is only about 10-fold as potent for PDE5 compared to PDE6, an enzyme found in the retina; this cross reactivity is thought to be the basis for abnormalities related to color vision o ...
Week Three Slides
... increase number of action potentials Also binds to receptors on axon terminals in nucleus accumbens to release more dopamine with each action potential ...
... increase number of action potentials Also binds to receptors on axon terminals in nucleus accumbens to release more dopamine with each action potential ...
Psychopharmacology
... • MAO – the presynaptic enzyme that destroys recently reabsorbed serotonin, nor/epinephrine, dopamine • Inhibitors stop the enzyme from destroying the neurotransmitters, increasing their supply in the synapse • MAO also works in the liver to break down tyramine, a chemical in food that tells your bl ...
... • MAO – the presynaptic enzyme that destroys recently reabsorbed serotonin, nor/epinephrine, dopamine • Inhibitors stop the enzyme from destroying the neurotransmitters, increasing their supply in the synapse • MAO also works in the liver to break down tyramine, a chemical in food that tells your bl ...
Sympathetic Nervous System
... neurons realease ACh. The ACh binds to and activates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. • In response to the stimulus, the postganglionic neurons release norepinephrine. • This prolonged activation releases adrenaline from the adrenal medulla. • Once released the adrenaline and norepinephrine bind t ...
... neurons realease ACh. The ACh binds to and activates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. • In response to the stimulus, the postganglionic neurons release norepinephrine. • This prolonged activation releases adrenaline from the adrenal medulla. • Once released the adrenaline and norepinephrine bind t ...
Adrenergic Drugs
... and β, with several subtypes. α receptors have the subtypes α1 and α2. β receptors have the subtypes β1, β2 and β3. ...
... and β, with several subtypes. α receptors have the subtypes α1 and α2. β receptors have the subtypes β1, β2 and β3. ...
Schizophrenia - Beauchamp College
... whose symptoms do not improve on haloperidol. A patient maintained on clozapine is less likely to show side effects related to involuntary movements (tardive dyskinesia). It tends not to block the receptors for dopamine in the striatum (could explain it’s lack of motor side effects). However it has ...
... whose symptoms do not improve on haloperidol. A patient maintained on clozapine is less likely to show side effects related to involuntary movements (tardive dyskinesia). It tends not to block the receptors for dopamine in the striatum (could explain it’s lack of motor side effects). However it has ...
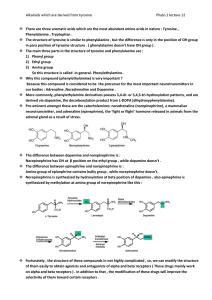
Norepinephrine
... To produce β blocker we must understand the agonist because the same receptor will bind to both the agonist and antagonist. From agonist, what should be available to be β selective? 1- Catechol. 2- Alkyl chain on amine. In agonist, as we increase the alkyl chain we make better binding and increase t ...
... To produce β blocker we must understand the agonist because the same receptor will bind to both the agonist and antagonist. From agonist, what should be available to be β selective? 1- Catechol. 2- Alkyl chain on amine. In agonist, as we increase the alkyl chain we make better binding and increase t ...
other nitrogen-containing compounds
... • Norepinephrine and epinephrine are released from storage vesicles in the adrenal medulla in response to fright, exercise, cold, and low levels of blood glucose. • They increase the degradation of glycogen and triacylglycerol, as well as increase blood pressure and the output of the heart. These ef ...
... • Norepinephrine and epinephrine are released from storage vesicles in the adrenal medulla in response to fright, exercise, cold, and low levels of blood glucose. • They increase the degradation of glycogen and triacylglycerol, as well as increase blood pressure and the output of the heart. These ef ...
SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) and SNRIs
... believed to have a key role in regulating mood, appetite, anxiety, sleep and may have an effect on memory and learning. Norepinephrine (or noradrenaline) is both a hormone and a brain neurotransmitter. Like Serotonin, it is thought to affect mood and anxiety. SSRIs and SNRIs increase concentrations ...
... believed to have a key role in regulating mood, appetite, anxiety, sleep and may have an effect on memory and learning. Norepinephrine (or noradrenaline) is both a hormone and a brain neurotransmitter. Like Serotonin, it is thought to affect mood and anxiety. SSRIs and SNRIs increase concentrations ...
Brain Packet
... 2. Explain the role of neurotransmitters in the neurons ability to generate its own action potential. 3. Specific neurotransmitters have specific effects on behavior and emotions. Please look at the following neurotransmitters and discuss their link to different psychiatric symptoms. Make sure to ad ...
... 2. Explain the role of neurotransmitters in the neurons ability to generate its own action potential. 3. Specific neurotransmitters have specific effects on behavior and emotions. Please look at the following neurotransmitters and discuss their link to different psychiatric symptoms. Make sure to ad ...
13th Lecture Updated
... The final product formed by the sequential action of MAO and COMT is partly conjugated to sulfate or glucuronide derivatives, which are excreted in the urine, but most of it is converted to vanillylmandelic acid and excreted in the urine in this form In the periphery, neither MAO nor COMT is pri ...
... The final product formed by the sequential action of MAO and COMT is partly conjugated to sulfate or glucuronide derivatives, which are excreted in the urine, but most of it is converted to vanillylmandelic acid and excreted in the urine in this form In the periphery, neither MAO nor COMT is pri ...
Neurotransmitters - Shifa College of Medicine
... channel themselves to produce their effects. Metabotrophic receptors: these activate second messenger system (cAMP, PIP3) to produce their effects. ...
... channel themselves to produce their effects. Metabotrophic receptors: these activate second messenger system (cAMP, PIP3) to produce their effects. ...
Document
... Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs), also known as noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (NARIs), are compounds that elevate the extracellular level of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine in the central nervous system by inhibiting its reuptake from the synaptic cleft into the presynaptic neuronal ...
... Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs), also known as noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (NARIs), are compounds that elevate the extracellular level of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine in the central nervous system by inhibiting its reuptake from the synaptic cleft into the presynaptic neuronal ...
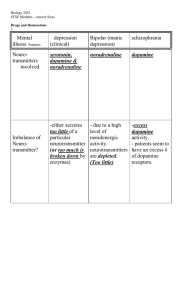
Drugs and Homeostasis STSE Answers File
... particular neurotransmitter (or too much is broken down by enzymes) ...
... particular neurotransmitter (or too much is broken down by enzymes) ...
biopsych –stress quiz
... e. Raising of the perceptual threshold of olfactory and gustatory receptors 19. In neurons, neurotransmitters are released at the: a. Axons b. Cell bodies c. Dendrites d. Receptor sites e. Synaptic vesicles 20. In an emergency situation, the adrenal glands secrete hormones that cause all of the foll ...
... e. Raising of the perceptual threshold of olfactory and gustatory receptors 19. In neurons, neurotransmitters are released at the: a. Axons b. Cell bodies c. Dendrites d. Receptor sites e. Synaptic vesicles 20. In an emergency situation, the adrenal glands secrete hormones that cause all of the foll ...
Neurotransmitter Test Assessment
... Norepinephrine is synthesized from dopamine by means of the enzyme dopamine beta-hydroxylase, with oxygen, copper, and vitamin C as co-factors. The noradrenergic system is most active when an individual is awake, which is important for focused attention. Elevated norepinephrine activity seems to be ...
... Norepinephrine is synthesized from dopamine by means of the enzyme dopamine beta-hydroxylase, with oxygen, copper, and vitamin C as co-factors. The noradrenergic system is most active when an individual is awake, which is important for focused attention. Elevated norepinephrine activity seems to be ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.