NURS 1950 Nancy Pares, RN, MSN Metro Community College
... Four groups (also called anxiolytics/tranquilizers) ...
... Four groups (also called anxiolytics/tranquilizers) ...
Vasopressors Final
... rate on all days of hospital stay (p<0.001) Mortality strongly associated with high lactate and low urine output “NE was associated with a highly significant decrease in hospital mortality. The data ...
... rate on all days of hospital stay (p<0.001) Mortality strongly associated with high lactate and low urine output “NE was associated with a highly significant decrease in hospital mortality. The data ...
Chapter 2 - Neuroscience and Behavior
... blood pressure, mood, learning, and memory. Some endorphins function as neurotransmitters. ...
... blood pressure, mood, learning, and memory. Some endorphins function as neurotransmitters. ...
ESSAY QUESTIONS WITH SAMPLE ANSWERS 1. Explain why the
... related to hallucinations and delusions. Happy may very well suffer from schizophrenia. Zippy has high norepinephrine production. Norepinephrine is related to energy. It is also related to anxiety and panic attacks. Zippy is probably getting treatment for stress and anxiety. Boozer looks like he’ ...
... related to hallucinations and delusions. Happy may very well suffer from schizophrenia. Zippy has high norepinephrine production. Norepinephrine is related to energy. It is also related to anxiety and panic attacks. Zippy is probably getting treatment for stress and anxiety. Boozer looks like he’ ...
Drugs for the treatment of Attention
... Child and Adolescent Behavior Letter. Mar96, Vol. 12, Issue 3. Health and Medicine Week, September 6, 2004, 79. Markowitz, John S., Patrick, Kennerly S.; “Pharmacology of Methylphenidate, Amphetamine Enantiomers and Pemoline in Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity ...
... Child and Adolescent Behavior Letter. Mar96, Vol. 12, Issue 3. Health and Medicine Week, September 6, 2004, 79. Markowitz, John S., Patrick, Kennerly S.; “Pharmacology of Methylphenidate, Amphetamine Enantiomers and Pemoline in Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity ...
Release of norepinephrine: Removal of norepinephrine:
... major subgroups, β 1, β 2, and β 3, based on their affinities for adrenergic agonists and antagonists. β 1 Receptors have approximately equal affinities for epinephrine and norepinephrine, whereas β 2 receptors have a higher affinity for epinephrine than for norepinephrine. Thus, tissues with a pred ...
... major subgroups, β 1, β 2, and β 3, based on their affinities for adrenergic agonists and antagonists. β 1 Receptors have approximately equal affinities for epinephrine and norepinephrine, whereas β 2 receptors have a higher affinity for epinephrine than for norepinephrine. Thus, tissues with a pred ...
CN510 Lecture 4 Drugs and the Brain and
... Prolonged exposure to cocaine leads to profound up and down regulation of various receptors, especially evident in DA system The 5-HT2 receptor shows influence in the evocation of hyperactivity displayed in cocaine use The lack of normal levels of DA and 5-HT are the primary causes of withdrawal ...
... Prolonged exposure to cocaine leads to profound up and down regulation of various receptors, especially evident in DA system The 5-HT2 receptor shows influence in the evocation of hyperactivity displayed in cocaine use The lack of normal levels of DA and 5-HT are the primary causes of withdrawal ...
from the brain
... • Receives information – within a fraction of a second, too minuscule to measure • Acts on the external universe – allows you to cry, walk, play a musical instrument • Utilizes language – one of your most ...
... • Receives information – within a fraction of a second, too minuscule to measure • Acts on the external universe – allows you to cry, walk, play a musical instrument • Utilizes language – one of your most ...
What are examples of common agonists and antogonists?
... hypothalamic peptides, brain-gut peptides, opioid peptides, and miscellaneous peptides. ...
... hypothalamic peptides, brain-gut peptides, opioid peptides, and miscellaneous peptides. ...
Adrenergic agonists:-
... Adrenergic agonists:A.) Catecholamines They are called catecholamines because they contain a catechol group, they are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins, so they circulate in the bloodstream. Sympathomimetic (mimic or mimetic = same action of) amines that contain the (catechol group) ...
... Adrenergic agonists:A.) Catecholamines They are called catecholamines because they contain a catechol group, they are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins, so they circulate in the bloodstream. Sympathomimetic (mimic or mimetic = same action of) amines that contain the (catechol group) ...
The Dope on Dru ain, Body and Behavior
... "rush" or "flash" lasts only a few minutes. These powerful stimulants are highly addictive and have been showing up in recent years as part of the club scene. Brain changes. Methamphetamines work in the brain on the so-called "pleasure circuit." They are chemically similar to two powerful neurotrans ...
... "rush" or "flash" lasts only a few minutes. These powerful stimulants are highly addictive and have been showing up in recent years as part of the club scene. Brain changes. Methamphetamines work in the brain on the so-called "pleasure circuit." They are chemically similar to two powerful neurotrans ...
Neurotransmitter Parameter Definitions
... Taurine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in neuromodulatory and neuroprotective actions. Supplementing with taurine can have a specific effect on GABA function.There are two primary ways in which taurine affects GABA.; First, it can inhibit GABA transaminase, an enzyme that metabolizes GAB ...
... Taurine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in neuromodulatory and neuroprotective actions. Supplementing with taurine can have a specific effect on GABA function.There are two primary ways in which taurine affects GABA.; First, it can inhibit GABA transaminase, an enzyme that metabolizes GAB ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... free to respond to acetylcholine. Parasympathetic response is absent or decreased depending on number of receptors blocked. ...
... free to respond to acetylcholine. Parasympathetic response is absent or decreased depending on number of receptors blocked. ...
Adrenergic Receptor Agonists
... • Dobutamine can cause vomiting and seizures in cats – must be used at very low doses ...
... • Dobutamine can cause vomiting and seizures in cats – must be used at very low doses ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... A. Caving in of the esophagus B. Physiological sphincter similar to the pylorus C. Esophageal constriction D. Stomach contraction 22. Stimulation of gut smooth muscle by the sympathetic nervous system causes? A. Hyperpolarization & function B. Increased positively of membrane potential C. rate a ...
... A. Caving in of the esophagus B. Physiological sphincter similar to the pylorus C. Esophageal constriction D. Stomach contraction 22. Stimulation of gut smooth muscle by the sympathetic nervous system causes? A. Hyperpolarization & function B. Increased positively of membrane potential C. rate a ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Drugs act by occupying receptor sites on target organs innervated by parasympathetic nervous system leaving fewer receptor sites free to respond to acetylcholine. Parasympathetic response is absent or decreased depending on number of receptors ...
... Drugs act by occupying receptor sites on target organs innervated by parasympathetic nervous system leaving fewer receptor sites free to respond to acetylcholine. Parasympathetic response is absent or decreased depending on number of receptors ...
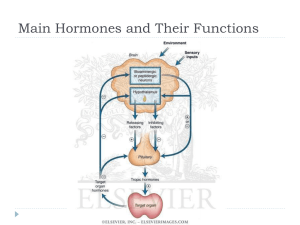
Main Hormones and Their functions
... stimulates liver to secrete growth factors protein synthesis, cell division/growth, breakdown fats ...
... stimulates liver to secrete growth factors protein synthesis, cell division/growth, breakdown fats ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Only neurotransmitter found between motor neurons and voluntary muscles. • Contributes to the regulation of attention, arousal and memory--Alzheimer's patients have decreased levels of ACh. – Nicotine is an Agonist – Alzheimer’s medication is an Agonist – Curare is an Antagonist – Botox is an Anta ...
... • Only neurotransmitter found between motor neurons and voluntary muscles. • Contributes to the regulation of attention, arousal and memory--Alzheimer's patients have decreased levels of ACh. – Nicotine is an Agonist – Alzheimer’s medication is an Agonist – Curare is an Antagonist – Botox is an Anta ...
TB1 Module 3: Web Quiz 2 TB1 Module 3: Web Quiz 2 1. An axon
... C) depression; elation B) convulsions; paralysis D) elation; depression Ans: B Page: 43 4. A drug that blocks the reuptake of a particular neurotransmitter is called a(n): A) opiate. B) antagonist. C) glutamate. D) agonist. Ans: D Page: 44 5. The peripheral nervous system consists of: A) synaptic ga ...
... C) depression; elation B) convulsions; paralysis D) elation; depression Ans: B Page: 43 4. A drug that blocks the reuptake of a particular neurotransmitter is called a(n): A) opiate. B) antagonist. C) glutamate. D) agonist. Ans: D Page: 44 5. The peripheral nervous system consists of: A) synaptic ga ...
Medication Strategies for Behavior Patients Lynne Seibert DVM, MS
... parasympathetic post-ganglionic synapses. Nicotinic cholinergic synapses are found at the neuromuscular junction. Blockade of muscarinic cholinergic receptors is responsible for atropine-like side effects of the antipsychotics and tricyclic antidepressants: dry mouth and eyes, urine retention, const ...
... parasympathetic post-ganglionic synapses. Nicotinic cholinergic synapses are found at the neuromuscular junction. Blockade of muscarinic cholinergic receptors is responsible for atropine-like side effects of the antipsychotics and tricyclic antidepressants: dry mouth and eyes, urine retention, const ...
Adrenergic and anti-adrenergic drugs
... Mainly for cardiovascular disorders (angina, dysrhythmias, hypertension, MI and glaucoma) ´ In angina, beta blockers decrease myocardial oxygen consumption by decreasing rate, BP and contractility. Slow conduction both in SA node and AV node. ...
... Mainly for cardiovascular disorders (angina, dysrhythmias, hypertension, MI and glaucoma) ´ In angina, beta blockers decrease myocardial oxygen consumption by decreasing rate, BP and contractility. Slow conduction both in SA node and AV node. ...
Uncovering the Mysteries of Psychiatry
... Works on norepinephrine and serotonin In same family as cymbalta, pristiq, effexor ...
... Works on norepinephrine and serotonin In same family as cymbalta, pristiq, effexor ...
3 Lec 5 NS4 - Autonomic Nervous System V9
... constrict blood vessels and cause blood pressure to rise • Sympathetic fibers fire less rapidly to prompt vessels to dilate to decrease blood pressure • Alpha-blocker drugs interfere with vasomotor fibers – Used to treat hypertension ...
... constrict blood vessels and cause blood pressure to rise • Sympathetic fibers fire less rapidly to prompt vessels to dilate to decrease blood pressure • Alpha-blocker drugs interfere with vasomotor fibers – Used to treat hypertension ...
Endocrine System - TWHS 9th Grade Campus
... Pituitary Gland • Description- found at the base of skull • Hormones- Human Growth Hormone (HGH) • Diseases– Gigantism= too much HGH – Dwarfism= not enough HGH ...
... Pituitary Gland • Description- found at the base of skull • Hormones- Human Growth Hormone (HGH) • Diseases– Gigantism= too much HGH – Dwarfism= not enough HGH ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.