* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychotropic Agents Unit 1
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Serotonin syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atypical antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Non-specific effect of vaccines wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
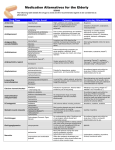
NURS 1950 Nancy Pares, RN, MSN Metro Community College http://www.cafeoflifepikespeak.com/Videos/Licensed%20To%20Pill.swf Four groups (also called anxiolytics/tranquilizers) ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Antidepressants (Chap 16) Benzodiazepines Barbiturates Nonbenzodiazepines/nonbarbiturate CNS depressants Baseline data ◦ Cause of anxiety ◦ Vitals ◦ Blood dyscrasias, liver disease, pregnancy or breastfeeding WHY? Prototype: Phenobarbital (Luminal) Action: enhances the action of the neurotransmitter GABA-which suppresses abnormal neuronal discharges Rarely used today due to significant side effects—high chem dependency & overdose New studies show ◦ No effect on anxiety—too much CNS depression Overdoses are common; increase enzyme activity…which causes_resp depression Advantages End in ‘pam’ ◦ Diazapam (Valium),oxazepam (Serax), lorazapam (Ativan)** Drugs of choice for anxiety and insomnia Action: ◦ bind to the GABA receptor (what is this? And what does it do? Uses: ◦ Acute anxiety, medical illness, ETOH w/drawal Adverse effects: ◦ Hypotension, confusion, syncope Interactions: ◦ ETOH, anesthetics, MAO inhibitors, antihistamines, TCA’s, narcotics, barbiturates ◦ Caffeine and smoking interfere with desired effect ◦ Overdose: Flumazenil (Romazicon) Nursing Implications ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Tolerance develops Can cause physical and psychological dependence No abrupt w/drawal of meds Drug doses vary---check for appropriate dosing Interacts with phenytoin and coumadin Buspirone (BuSpar) ◦ Unrelated to benzo or barbiturates chemically Action: not well known; may be related to dopamine receptors Advantages: ◦ Less potential for abuse; lower sedative properties Adverse effects: ◦ Dizziness, HA, drowsiness; may take 3-4 wks for optimal effects Buspar ◦ Schedule regular assessments for slurred speech, dizziness, CNS disturbances; give at regular intervals (not PRN); do not use with MAO Inhibitors or ETOH Diphenhydramine (Benedryl) and Hydroxyzine (Vistaril) Uses: sedative and antiemetic properties; anticholinergic effects are least with these agents; preop sedation, pruititis Side effects: ◦ Blurred vision, constipation, dry mucosa, sedation; drowsiness will decrease with use Before giving an antianxiety, what would you assess? After giving an antianxiety, what would you assess? What are some common nursing diagnosis for clients taking anxiolytics? Classifications ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Tricyclics MAO inhibitors (monoamine oxidase) SSRI Atypical Antidepressants Action is on serotonin and catecholamines Therapy requires 2-3 wks for mood change Overdoses do occur common side effects: ◦ Sedation, anticholinergic activity, tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, confusion, tremors TCA ◦ Action: inhibits reuptake of norepinephrine and seratonin into presynaptic nerve terminals ◦ Uses: depression, Manic-depressive (bipolar)disorder, panic disorders ◦ Desired effects: mood elevation, increase activity, improve appetite, normalize sleep patterns….. What s/s of depression make these desirable effects? ◦ Takes 1-2 months for maximal effect Adverse effects: ◦ Tremor, numbness, tingling, Parkinsonian symptoms, orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects (which are?) ◦ Cardiac arrhythmias, suicidal actions Do not use with MAOI..why? Sympathomimetics increase effects of anticholinergic effects Avoid OTC antihistamines Prototype: imipramine (Tofranil) Sertraline (Zoloft) ◦ Action: inhibits reuptake of serotonin ◦ Use: depression, anxiety, OCD and panic disorder ◦ Adverse effects: agitation, HA , dizziness and fatigue; sexual dysfunction; weight gain; ◦ Contraindications: antabuse should be avoided; no MAOI ; use precaution with St. John Wart • • • • • • May take wks to get effect; effects last 2-3 months after d/c Give in am or pm Note eating disorders hx Exercise and caloric restriction Monitor labs for pro-bound drugs…ex: coumadin May need increase of dilantin due to interactions • • • • • Phenelzine (Nardil) Action:intensifies effects of norepinephrine in adrenergic synapses Use: depression not responsive to other drugs Common S/E: constipation, dry mouth, orthostatic hypertension; severe hypertension with foods containing tyramine (see pg 195) Contraindications: cardiac disease, renal/hepatic impairment Refrain from foods that contain tyramine Assess cardiac status Assess lab values (why?) No OTC or herbal meds Avoid caffeine Observe for s/s of stroke or MI General anesthesia, diuretics, antihypertensives: potentiate the hypotensive effects Insulin and oral hypoglycemics: additive effects Meperidine and MAOI= severe reactions What assessments need to be made before antidepressant medications? What are the nursing diagnosis you would write for clients with antidepressant meds.? Hypertensive Crisis ◦ Ingestion of foods with tyramine (this substance promotes release of norepinephrine) ◦ Avocados, soybeans, figs, bananas, aged meat, smoked meat, bologna, pepperoni, salami, cheese, caffeine Lithium carbonate (Eskalith) ◦ Action: stabalizes the neuronal membrane, reduces release of norepinephrine ◦ Uses: reduces euphoria of mania without sedation; may take a week to develop desired effects; begin with low doses and increase q 3-5 days. ◦ Common S/E: n/v, anorexia, abd cramps, excessive thirst and urination Adverse effects: persistant vomiting; progressive wt gain, fatigue, nephrotoxicity Serum levels need to be below 1.5mEq/L >1.5: n/v, diarrhea, thirst, polyuria, slurred speech 1.5-2.0: GI upset, confusion 2.0-2.5: ataxia. Blurred vision, coma 2.5 and >: convulsion, oliguria, death normal blood level: Nutrition needs: Desired effects in 5-7 days; full effect in 21 days Give with food or milk Phenothiazines Non phenothiazine Atypical anti psychotics Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) Action: ◦ Prevent dopamine and serotonin from occupying their receptor sites and block the excitement symptoms Use: ◦ Schizophrenia, bipolar (manic state), depression, antiemetic Adverse effects: (see page 213 table) ◦ Extrapyramidal effects Acute dystonia, spasms of tongue, opisthostonos Treat: anticholinergics ◦ Parkinsonism (why?) ◦ Akathesia ◦ Tardive dyskinesia May be irreversible ◦ Other common: sedation, sexual dysfunction, breast growth, galactorrhea Nursing Interventions ◦ Increases effect with anticholinergics ◦ ETOH and CNS depressants intensify depressant effect ◦ NOTE: most phenothiazines end in ‘zine’ ; ex: fluphenzine, prochorperazine, promazine, thiroidazine ◦ Careful monitoring of client condition; report EPS symptoms to MD..may need to d/c med ◦ Life threatening adverse effect: neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) Haloperidol (Haldol) Action/Use: chemically a butyrphenone; primary use is psychotic disorder—has less sedation than phenothiazine, but greater EPS Nursing Interventions: ◦ Same as pheno—monitor carefully, esp. elderly Clozapine (Clozaril) Action/Use: ◦ Largely unknown—block several receptor sites; broader spectrum of action, fewer EPS symptoms Nursing Interventions: ◦ Basically same as pheno..give wkly supply to assure lab values get drawn New drug aripiprazole (Abilify) ◦ Dopamine stabilizer with fewer EPS ◦ Adverse effects: HA, N/V, fevers constipation, anxiety ◦ Nursing implications As all other categories