Non-Cardiac Chest Pain - Old
... • All motor neurons to skeletal muscles • Most postganglionic neurons of the SNS that go to sweat glands ...
... • All motor neurons to skeletal muscles • Most postganglionic neurons of the SNS that go to sweat glands ...
Homeostasis, Adaptation, and Stress Objectives: Objectives continue:
... http://www.biologymad.com/NervousSystem/nervoussystemintro.htm ...
... http://www.biologymad.com/NervousSystem/nervoussystemintro.htm ...
Lecture 17 (March 7th): STRESS RESPONSE AND HEALTH Lecture
... (branch of Autonomic Nervous System) First, a Quick Review of Autonomic Nervous System SYMPATHETIC: “fight or flight” system, energy spending Originates in the hypothalamus ……which receives from the Amygdala! (last slide) PARASYMPATHETIC: “rest and digest” system, energy conserving The two systems p ...
... (branch of Autonomic Nervous System) First, a Quick Review of Autonomic Nervous System SYMPATHETIC: “fight or flight” system, energy spending Originates in the hypothalamus ……which receives from the Amygdala! (last slide) PARASYMPATHETIC: “rest and digest” system, energy conserving The two systems p ...
Dopaminergic agents 拟多巴胺药levodopa, (L
... Prevent activation of cholinergic receptors Trihexyphenidyl 苯海索 ...
... Prevent activation of cholinergic receptors Trihexyphenidyl 苯海索 ...
Ch 15 ANS - Lake–Sumter State College
... peritonitis – usually evident in newborns who fail to have their first bowel movement ...
... peritonitis – usually evident in newborns who fail to have their first bowel movement ...
E4 Neurotransmitters and synapses trs
... transmission and others inhibit postsynaptic transmission. E.4.2 Explain how decision making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synapses. ...
... transmission and others inhibit postsynaptic transmission. E.4.2 Explain how decision making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synapses. ...
Psychotropic Drugs
... side effects Tyramine/Hypertensive crisis may occur when sympathomimetic drugs, L-dopa, narcotics, TCAs, or tyramine containing foods such as aged cheese, wine, pickled herring, fava beans are ingested – Onset is usually precipitated by a severe headache and may progress to a hypertensive ICH with s ...
... side effects Tyramine/Hypertensive crisis may occur when sympathomimetic drugs, L-dopa, narcotics, TCAs, or tyramine containing foods such as aged cheese, wine, pickled herring, fava beans are ingested – Onset is usually precipitated by a severe headache and may progress to a hypertensive ICH with s ...
02 02
... (3,4-dihydroxylphenyl group and an amine group) Catecholamines are hormones produced by the adrenal glands, brain and nerve tissues released into the blood during emotional or physical stress, fright or the ‘fight or flight’ response. They are part nervous system ...
... (3,4-dihydroxylphenyl group and an amine group) Catecholamines are hormones produced by the adrenal glands, brain and nerve tissues released into the blood during emotional or physical stress, fright or the ‘fight or flight’ response. They are part nervous system ...
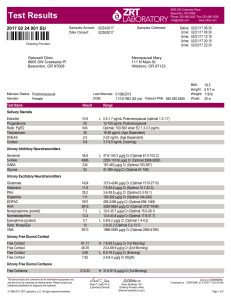
Laboratory Test Results
... Dopamine is low-normal (<20th percentile). Dopamine improves attention, focus, and motivation, helps with decision making, modulates movement control, promotes lactation, increases blood pressure, urine output and sodium excretion, and allows for feelings of reward and pleasure. Additionally, the qu ...
... Dopamine is low-normal (<20th percentile). Dopamine improves attention, focus, and motivation, helps with decision making, modulates movement control, promotes lactation, increases blood pressure, urine output and sodium excretion, and allows for feelings of reward and pleasure. Additionally, the qu ...
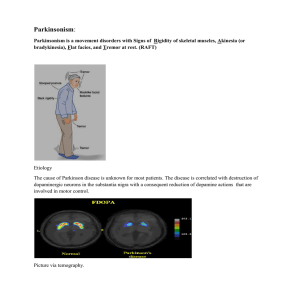
Drug Therapy of Parkinsonism
... * Like levodopa, brompcriptine and pergolide are contraindicated in patients with history of psychosis. * Pramipexole: Recently introduced dopamine receptor agonists; they are not ergot derivatives. # They are presently considered to be first-line drugs in the initial management of Parkinson’s disea ...
... * Like levodopa, brompcriptine and pergolide are contraindicated in patients with history of psychosis. * Pramipexole: Recently introduced dopamine receptor agonists; they are not ergot derivatives. # They are presently considered to be first-line drugs in the initial management of Parkinson’s disea ...
BioBases Exam 2
... Thymus: immune system (children) Pancreas: blood sugar control Adrenal: stress, many other functions – located “on top of kidneys” 1) Releases 3 major classes of hormones (a) Androgens: (e.g., testosterone in males) (b) Glucocorticoids, Cortisol: involved in stress response!! (c) E (adrenaline), NE: ...
... Thymus: immune system (children) Pancreas: blood sugar control Adrenal: stress, many other functions – located “on top of kidneys” 1) Releases 3 major classes of hormones (a) Androgens: (e.g., testosterone in males) (b) Glucocorticoids, Cortisol: involved in stress response!! (c) E (adrenaline), NE: ...
view article pdf
... The medications described in this article act to either block or stimulate receptors in the autonomic nervous system. These medications create an imbalance or pre dom i n at ion of one s y s te m’s physiological effects over the other. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is a chain of ganglia that ...
... The medications described in this article act to either block or stimulate receptors in the autonomic nervous system. These medications create an imbalance or pre dom i n at ion of one s y s te m’s physiological effects over the other. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is a chain of ganglia that ...
Stress Psychophysiology Introduction The Brain
... Actions of the Adrenal Gland (outside part) • Influenced by ACTH, the adrenal cortex (outer portion of the adrenal gland) will release two types of hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. • The primary glucocorticoid is cortisol, which is responsible for providing the body with increased e ...
... Actions of the Adrenal Gland (outside part) • Influenced by ACTH, the adrenal cortex (outer portion of the adrenal gland) will release two types of hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. • The primary glucocorticoid is cortisol, which is responsible for providing the body with increased e ...
Regulation - nervous and endocrine system
... • Somatic nervous system is for voluntary muscle control. These neurons control the skeletal muscles…. • Autonomic nervous system is automatic or involuntary – Control of heart rate, respiration, blood pressure, smooth muscle, etc. – This has 2 separate divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic ...
... • Somatic nervous system is for voluntary muscle control. These neurons control the skeletal muscles…. • Autonomic nervous system is automatic or involuntary – Control of heart rate, respiration, blood pressure, smooth muscle, etc. – This has 2 separate divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic ...
Adverse effects
... potentiates and prolongs the CNS and peripheral actions of these monoamines, producing the intense euphoria. Actions: CNS: Cocaine acutely increases mental awareness and produces a feeling of well-being and euphoria. at high doses, it causes tremors and convulsions, followed by respiratory depressio ...
... potentiates and prolongs the CNS and peripheral actions of these monoamines, producing the intense euphoria. Actions: CNS: Cocaine acutely increases mental awareness and produces a feeling of well-being and euphoria. at high doses, it causes tremors and convulsions, followed by respiratory depressio ...
S 06 Adrenoceptor Agonists And Sympathomimetic Drugs
... These agents may be: a) Selective: for a specific receptor subtype (e.g., phenylephrine for α1, terbutaline for β2) b) None selective: have no or minimal selectivity and act on several receptor types (e.g., epinephrine for α1, α2, β1, β2, and β3 receptors) ...
... These agents may be: a) Selective: for a specific receptor subtype (e.g., phenylephrine for α1, terbutaline for β2) b) None selective: have no or minimal selectivity and act on several receptor types (e.g., epinephrine for α1, α2, β1, β2, and β3 receptors) ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... – Alpha receptors with subtypes - stimulated more by norepi or epi – Beta receptors with subtypes - stimulated more by epi – Alpha and Beta -1 are excitatory, -2 are inhibitory – Agonist - mimics neurotransmitter or hormone release (promotes effect), antogonist - blocks receptors (minimizes effect) ...
... – Alpha receptors with subtypes - stimulated more by norepi or epi – Beta receptors with subtypes - stimulated more by epi – Alpha and Beta -1 are excitatory, -2 are inhibitory – Agonist - mimics neurotransmitter or hormone release (promotes effect), antogonist - blocks receptors (minimizes effect) ...
Test bank module 3 4 5 6 11 12
... (C) Facilitate the incoming stimulus signals at sensory receptors (D) Reduce the amount of unused neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft (E) Protect the terminal buttons of the neuron from destruction by enzymes 3 92. Which of the following occurs when a neuron is stimulated to its threshold? (A) Th ...
... (C) Facilitate the incoming stimulus signals at sensory receptors (D) Reduce the amount of unused neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft (E) Protect the terminal buttons of the neuron from destruction by enzymes 3 92. Which of the following occurs when a neuron is stimulated to its threshold? (A) Th ...
4._Bipolar_disorder_def
... malignant syndrome history, Parkinson´s syndrome, be carefull at patients with kidney and liver problems ...
... malignant syndrome history, Parkinson´s syndrome, be carefull at patients with kidney and liver problems ...
4._Bipolar_disorder_def
... malignant syndrome history, Parkinson´s syndrome, be carefull at patients with kidney and liver problems ...
... malignant syndrome history, Parkinson´s syndrome, be carefull at patients with kidney and liver problems ...
file (Poison Prevention Outreach Mt. Lebanon High School)
... Metabolized in the liver to a reactive intermediate molecule (NAPQI) Normally neutralized by a sulfyhydryl compound in liver (glutathione) Glutathione depletion during overdose, so reactive NAPQI is available to react with sulfyhydrl compounds in cytsol, cell wall, and endoplasmic ...
... Metabolized in the liver to a reactive intermediate molecule (NAPQI) Normally neutralized by a sulfyhydryl compound in liver (glutathione) Glutathione depletion during overdose, so reactive NAPQI is available to react with sulfyhydrl compounds in cytsol, cell wall, and endoplasmic ...
The Effects of Short-Term Norepinephrine Up
... Neurohumoral activation, including increased endogenous catecholamine levels (norepinephrine and epinephrine), is a hallmark of pathophysiological condition in chronic heart failure patients and it has several long-term harmful effects (Francis 1985). Conversely, exogenous catecholamines are widely ...
... Neurohumoral activation, including increased endogenous catecholamine levels (norepinephrine and epinephrine), is a hallmark of pathophysiological condition in chronic heart failure patients and it has several long-term harmful effects (Francis 1985). Conversely, exogenous catecholamines are widely ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.