Human Nervous System - Valhalla High School
... • Parasympathetic: Routine life, conserves energy, heart rate lowers, digestive organs back to normal. “Rest and Ruminate” response. ...
... • Parasympathetic: Routine life, conserves energy, heart rate lowers, digestive organs back to normal. “Rest and Ruminate” response. ...
Glossary
... Cardiac output The amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute. Catechols Chemicals with a structure that includes two adjacent hydroxyl groups on a benzene ring. The catecholamines norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), and dopamine are catechols, as are the non-catecholami ...
... Cardiac output The amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute. Catechols Chemicals with a structure that includes two adjacent hydroxyl groups on a benzene ring. The catecholamines norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), and dopamine are catechols, as are the non-catecholami ...
Ecstasy ("X") Drug Effects Information KNOW THE FACTS and DON
... direct roll in regulating aggression, mood, sexual activity, sleep, and sensitivity to pain. It can damage brain cells that produce dopamine. Scientists have now shown that Ecstasy not only makes the brain's nerve branches and endings degenerate, but also makes them "regrow", but abnormally - failin ...
... direct roll in regulating aggression, mood, sexual activity, sleep, and sensitivity to pain. It can damage brain cells that produce dopamine. Scientists have now shown that Ecstasy not only makes the brain's nerve branches and endings degenerate, but also makes them "regrow", but abnormally - failin ...
Tricyclic Antidepressants
... work by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, two important neurotransmitters in the central nervous system, back into brain cells. Neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, are chemicals produced by brain cells called neurons that enable them to communicate with on ...
... work by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, two important neurotransmitters in the central nervous system, back into brain cells. Neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, are chemicals produced by brain cells called neurons that enable them to communicate with on ...
Muscle Relaxants
... - infiltration: direct injection into tissues - field block: all around area affected ...
... - infiltration: direct injection into tissues - field block: all around area affected ...
The Endocrine System
... • There are four parathyroid glands which are normally about the size and shape of a grain of rice. • The sole purpose of the parathyroid glands are to regulate the calcium level in our bodies within a very narrow range so that the nervous and muscular systems can function properly. ...
... • There are four parathyroid glands which are normally about the size and shape of a grain of rice. • The sole purpose of the parathyroid glands are to regulate the calcium level in our bodies within a very narrow range so that the nervous and muscular systems can function properly. ...
Journal about antidepressant drugs U.N 42904891 Date:18
... Have a family or personal history of successful treatment with MAOIs ...
... Have a family or personal history of successful treatment with MAOIs ...
classical vs. neuropeptides
... 2. Autoreceptor: refers to transmitter receptors, on or near presynaptic terminals, which are sensitive to the transmitter(s) released by the terminal itself •Classification by transduction mechanism 1. Ligand-gated channels: - either excitatory or inhibitory actions - rapid action & rapidly reversi ...
... 2. Autoreceptor: refers to transmitter receptors, on or near presynaptic terminals, which are sensitive to the transmitter(s) released by the terminal itself •Classification by transduction mechanism 1. Ligand-gated channels: - either excitatory or inhibitory actions - rapid action & rapidly reversi ...
Lectuers as PPT - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Labetalol; It has a particular indication in the treatment of pregnancy-induced hypertension. It is also used to treat chronic hypertension and hypertensive crisis. 4. Centrally acting anti-adrenergics drugs They are capable of lowering transmitter output from sympathetic neurons. Their action is ...
... Labetalol; It has a particular indication in the treatment of pregnancy-induced hypertension. It is also used to treat chronic hypertension and hypertensive crisis. 4. Centrally acting anti-adrenergics drugs They are capable of lowering transmitter output from sympathetic neurons. Their action is ...
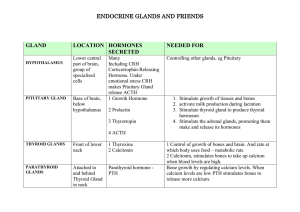
ENDOCRINE GLANDS ANSWER SHEET
... Gland (largest gland in body, only organ that can repair itself) ...
... Gland (largest gland in body, only organ that can repair itself) ...
FACT SHEET: Stimulants
... What is a stimulant ? A stimulant is any substance which increases or quickens a vital process. Within the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), stimulants increase alertness, relieve fatigue, reverse cataplexy (muscle weakness), and/or induce euphoria. Outside the brain and spinal cord, s ...
... What is a stimulant ? A stimulant is any substance which increases or quickens a vital process. Within the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), stimulants increase alertness, relieve fatigue, reverse cataplexy (muscle weakness), and/or induce euphoria. Outside the brain and spinal cord, s ...
11/3/2014 Psychedelic Drugs Continued
... Increases serotonin dopamine norepinephrine levels via release and/or reuptake inhibition Increases serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine levels via release and/or reuptake inhibition ...
... Increases serotonin dopamine norepinephrine levels via release and/or reuptake inhibition Increases serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine levels via release and/or reuptake inhibition ...
see p. A35 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... – number & location of –OH groups on benzene ring (determine catabolism rate); – substituent nature on amino nitrogen (more bulky substituent, greater potency at β receptors). ...
... – number & location of –OH groups on benzene ring (determine catabolism rate); – substituent nature on amino nitrogen (more bulky substituent, greater potency at β receptors). ...
Neurobiology - New England Institute of Addiction Studies
... The brain's major excitatory neurotransmitter, vital for forging the links between neurons that are the basis of learning and long-term memory. Makes it more likely any neuron affected will send a signal. Can be thought of as a gas pedal for the brain. Enkephalins and Endorphins. These are internal ...
... The brain's major excitatory neurotransmitter, vital for forging the links between neurons that are the basis of learning and long-term memory. Makes it more likely any neuron affected will send a signal. Can be thought of as a gas pedal for the brain. Enkephalins and Endorphins. These are internal ...
1-Antipsychotic drug..
... of dopamine receptors that are synthesized in response to long-term dopamine receptor blockade, which leads to neuronal supersensitivity to dopamine ...
... of dopamine receptors that are synthesized in response to long-term dopamine receptor blockade, which leads to neuronal supersensitivity to dopamine ...
Central Nervous System
... Vital Centers in the MO include: 1. Cardiac Control Center 2. Vasomotor Center 3. Respiratory Center (Medullary) * Also contains the centers for hiccupping, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting and coughing ...
... Vital Centers in the MO include: 1. Cardiac Control Center 2. Vasomotor Center 3. Respiratory Center (Medullary) * Also contains the centers for hiccupping, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting and coughing ...
幻灯片 1
... Mild hypertension can often be controlled with a single drug. More severe hypertension may require treatment with several drugs that are selected to minimize adverse effects of the combined regimen. Treatment is initiated with any of four drugs depending on the individual patient: a diuretic, a b-bl ...
... Mild hypertension can often be controlled with a single drug. More severe hypertension may require treatment with several drugs that are selected to minimize adverse effects of the combined regimen. Treatment is initiated with any of four drugs depending on the individual patient: a diuretic, a b-bl ...
Endocrine Quiz Review
... -Autocrines: Act on cells that secrete them vs. Paracrines: Act on cells nearby -Endocrine glands become less effective with age Hormones: Steroid or amino acid based -Stimulate or inhibit target cell -Mechanisms: alter membrane permeability, enzyme synthesis, secretion, and mitosis -Many interact w ...
... -Autocrines: Act on cells that secrete them vs. Paracrines: Act on cells nearby -Endocrine glands become less effective with age Hormones: Steroid or amino acid based -Stimulate or inhibit target cell -Mechanisms: alter membrane permeability, enzyme synthesis, secretion, and mitosis -Many interact w ...
Side Effects of Vasodilator Therapy
... few minutes after administration when the protein reaches an equilibrium state, only 3% is free, and 97% is bound to albumin. Thus, in a few minutes, there is a 30-fold reduction of vasodilatory activity after a rapid bolus injection. To minimize the possibility of drastic blood pressure reduction, ...
... few minutes after administration when the protein reaches an equilibrium state, only 3% is free, and 97% is bound to albumin. Thus, in a few minutes, there is a 30-fold reduction of vasodilatory activity after a rapid bolus injection. To minimize the possibility of drastic blood pressure reduction, ...
File - Ms. G`s Classroom
... Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary. Acts on the kidneys to increase water retention by decreasing the amount of water released in the urine. Increases growth of long bones of the body Stimulates and maintains metabolic activities; lack of thyroxin in children can cause mental ...
... Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary. Acts on the kidneys to increase water retention by decreasing the amount of water released in the urine. Increases growth of long bones of the body Stimulates and maintains metabolic activities; lack of thyroxin in children can cause mental ...
So what do my Adrenal Glands do?
... triangular-shaped organs that rest on top of the kidneys. They normally weigh about 5g each and have two parts. The cortex or outer section is responsible for the production of the hormones cortisone, cortisol, aldosterone, androstenedione and dehydrepiandrosterone (DHEA). The medulla or central sec ...
... triangular-shaped organs that rest on top of the kidneys. They normally weigh about 5g each and have two parts. The cortex or outer section is responsible for the production of the hormones cortisone, cortisol, aldosterone, androstenedione and dehydrepiandrosterone (DHEA). The medulla or central sec ...
The Endocrine system - Aurora City Schools
... Endocrine glands- ductless, or tubeless organs or group of cells that secrete hormones directly into the blood stream Hormones- chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate many of your body’s functions ...
... Endocrine glands- ductless, or tubeless organs or group of cells that secrete hormones directly into the blood stream Hormones- chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate many of your body’s functions ...
Biopsychology of Psychiatric Disorders - U
... • Bipolar affective illness - suffer from mania and depression • Unipolar affective illness - suffer from depression ...
... • Bipolar affective illness - suffer from mania and depression • Unipolar affective illness - suffer from depression ...
chapter2
... Corpus Callosum is cut; done to control severe epilepsy (seizure disorder). Result: The person now has two brains in one body. This operation is rare and is often used as a last resort ...
... Corpus Callosum is cut; done to control severe epilepsy (seizure disorder). Result: The person now has two brains in one body. This operation is rare and is often used as a last resort ...
Adrenergic System Adrenoceptor Blocking Drugs
... If Beta-blockers or diuretics fail to control hypertension, Prazosin or other SELECTIVE alpha1-blockers may be added. B) Secondary Hypertension: The alpha Adrenoceptor antagonists are most useful when increased blood pressure reflects excess circulating concentration of catecholamines which may resu ...
... If Beta-blockers or diuretics fail to control hypertension, Prazosin or other SELECTIVE alpha1-blockers may be added. B) Secondary Hypertension: The alpha Adrenoceptor antagonists are most useful when increased blood pressure reflects excess circulating concentration of catecholamines which may resu ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.