* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
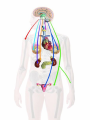
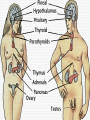
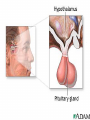
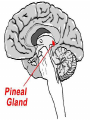
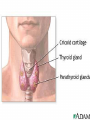
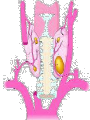
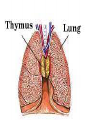
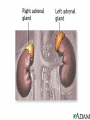
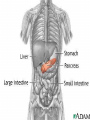
The Endocrine System •The Endocrine System are the glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream Hypothalamus • Brain region that controls the pituitary gland • Controls homeostasis – the bodies ability to remain at a status quo level Pituitary Gland • The “master gland” receives instructions from the brain, and in turn directs the rest of the endocrine system • Controls thirst by controlling the amount of water in the body’s cells • Controls female contractions, and tells the mammary glands to produce milk for newborns Pituitary Gland • May control grooming habits, companionship, and sexual behavior • Controls the flow of the human growth hormones – dwarfism and gigantism Pineal Gland • Responsible for the hormone “Melatonin” • Increased levels of Melatonin cause behaviors associated with sleep • Decreased levels of Melatonin cause behaviors associated with wakefulness Thyroid Gland • Releases the hormone “Thyroxin” • Thyroxin controls body temperature • Controls metabolism – our body’s ability to transform the food we eat into usable energy • Overactive? Behaviors may include excitability, insomnia, ADD, agitation, difficulty focusing • Reduced Activity? Behaviors may include Parathyroids • There are four parathyroid glands which are normally about the size and shape of a grain of rice. • The sole purpose of the parathyroid glands are to regulate the calcium level in our bodies within a very narrow range so that the nervous and muscular systems can function properly. Thymus Gland • Responsible for producing “TLymphocytes” – white-blood cells that fight infection • Regulates the body’s Immune System – protecting the body against infection • Hay fever, allergies, migraines may also be associated with poor thymus function Adrenal Glands • Located right above the kidneys and signaled by the autonomic system • Secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress • Increase heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar Pancreas • Controls the chemical “Insulin” • Insulin is needed in the body to break down sugars in the body • Too much insulin in the body devours all of the sugar in the blood. Behaviors exhibited include sluggishness and inattentiveness. • Too little insulin causes a buildup of sugar in the blood and makes the kidneys use a lot more water to flush it out of the body. The extra water needed to flush the sugar comes from surrounding cells, which in turn dehydrates them and leaves them vulnerable to infection and poisons. Gonads • Testicles – release androgens (male hormones) • Ovaries – release estrogens (female hormones) • The presence of these chemicals influence male and female reproductive characteristics.