Cocaine and Amphetamines (PDF Available)
... a neuronal system normally involved in promoting behaviour necessary for species survival and turning that system into a mechanism for drug abuse. It is important to stress that dopamine does not act alone. Much like its catecholamine partner, norepinephrine, dopamine acts mainly by modulating the e ...
... a neuronal system normally involved in promoting behaviour necessary for species survival and turning that system into a mechanism for drug abuse. It is important to stress that dopamine does not act alone. Much like its catecholamine partner, norepinephrine, dopamine acts mainly by modulating the e ...
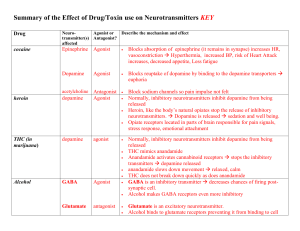
Mouse party Summary-the Effect of Drug use on Neurotransmitters
... Mimics serotonin. Serotonin transporters readily transport Ecstasy into the terminal bulb. Transporters start working in reverse, moving serotonin into the synapse. Affects part of the brain associated with mood, sleep and appetite. Excess serotonin stimulates dopamine release slightly addictive. ...
... Mimics serotonin. Serotonin transporters readily transport Ecstasy into the terminal bulb. Transporters start working in reverse, moving serotonin into the synapse. Affects part of the brain associated with mood, sleep and appetite. Excess serotonin stimulates dopamine release slightly addictive. ...
Chapter 5 - Psychology
... results in the release of the glucocorticoids including cortisol. glucocorticoids - including cortisol, raises levels of blood sugar to supply energy to the cells so they can respond to the emergency or stressor. adrenomedullary response - The response of the adrenal "medulla", prompted by sympathet ...
... results in the release of the glucocorticoids including cortisol. glucocorticoids - including cortisol, raises levels of blood sugar to supply energy to the cells so they can respond to the emergency or stressor. adrenomedullary response - The response of the adrenal "medulla", prompted by sympathet ...
Vasopressors and inotropes
... For example, norepinephrine infusions are usually accompanied by a decrease in renal blood flow but in patients with septic shock, renal blood flow is increased by norepinephrine infusions . Similar alterations may also occur with splanchnic blood flow (i.e., normally reduced, but not in septic ...
... For example, norepinephrine infusions are usually accompanied by a decrease in renal blood flow but in patients with septic shock, renal blood flow is increased by norepinephrine infusions . Similar alterations may also occur with splanchnic blood flow (i.e., normally reduced, but not in septic ...
Salomon Z
... transmitter release so you have to choose the areas of the brain rich in the transmitter you are targeting; in the striatum or putamen for dopamine; the occipital cortex for norepinephrine and the frontal cortex for serotonin. It all boils down to having a very richly innervated area of the brain as ...
... transmitter release so you have to choose the areas of the brain rich in the transmitter you are targeting; in the striatum or putamen for dopamine; the occipital cortex for norepinephrine and the frontal cortex for serotonin. It all boils down to having a very richly innervated area of the brain as ...
Lorem Ipsum - jan.ucc.nau.edu
... decarboxylase inhibitor that is combined with levadopa which enables levadopa to get to and cross over the blood-brain barrier This medication combination is called Sinemet ...
... decarboxylase inhibitor that is combined with levadopa which enables levadopa to get to and cross over the blood-brain barrier This medication combination is called Sinemet ...
Dr. Ghassan The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): After studying
... that there is an increase in the delivery of well-oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the working skeletal muscles. Both heart rate and myocardial contractility are increased so that the heart pumps more blood per minute. Sympathetic stimulation of vascular smooth muscle causes widespread vasoconstri ...
... that there is an increase in the delivery of well-oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the working skeletal muscles. Both heart rate and myocardial contractility are increased so that the heart pumps more blood per minute. Sympathetic stimulation of vascular smooth muscle causes widespread vasoconstri ...
Endocrine System
... Is called the “master gland.” The anterior pituitary lobe releases hormones that regulate other glands. The posterior lobe regulates water and salt balance. Regulates stress reactions and disease resistance; secrets growth hormone (cause of dwarfism and gigantism). ...
... Is called the “master gland.” The anterior pituitary lobe releases hormones that regulate other glands. The posterior lobe regulates water and salt balance. Regulates stress reactions and disease resistance; secrets growth hormone (cause of dwarfism and gigantism). ...
CLONIDINE PREMEDICATION AND ANESTHETIC EFFECTS
... norepinephrine release. This leads to an overall decrease in sympathetic outflow, causing peripheral vasodilatation, as well as negative chronotropic effects, therefore causing a reduction in blood pressure. This decrease in central sympathetic outflow does not affect baroreceptor reflexes, therefor ...
... norepinephrine release. This leads to an overall decrease in sympathetic outflow, causing peripheral vasodilatation, as well as negative chronotropic effects, therefore causing a reduction in blood pressure. This decrease in central sympathetic outflow does not affect baroreceptor reflexes, therefor ...
Document
... causes action potential in next cell, almost as if the tissue were one cell. • Important where contractile activity among a group of cells important. ...
... causes action potential in next cell, almost as if the tissue were one cell. • Important where contractile activity among a group of cells important. ...
Tales of Bath Salts and Legal Marijuana: TheRapidExpansion
... “hijacking the part of the brain important for many major functions: temperature control, food intake, perception, memory and problem solving. Many people taking these high-potency drugs are affecting important functions throughout their bodies-hormone functions for example.” Drugs may involve acute ...
... “hijacking the part of the brain important for many major functions: temperature control, food intake, perception, memory and problem solving. Many people taking these high-potency drugs are affecting important functions throughout their bodies-hormone functions for example.” Drugs may involve acute ...
Mechanism of Actions of Antidepressants: Beyond the Receptors
... behavioral effects (other than side effects). Substantial improvement in depressive symptoms occurs only if the drugs are taken at adequate dosage and with adequate frequency and permanence. However, it may not be necessary to maintain constant therapeutic serum levels for efficacy (25,26). Therefor ...
... behavioral effects (other than side effects). Substantial improvement in depressive symptoms occurs only if the drugs are taken at adequate dosage and with adequate frequency and permanence. However, it may not be necessary to maintain constant therapeutic serum levels for efficacy (25,26). Therefor ...
Definitions
... air, exercise or exertion, or emotional stress. In children, the most common triggers are viral illnesses such as those that cause the common cold.[1] This airway narrowing causes symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing, which respond to bronchodilators. Between ...
... air, exercise or exertion, or emotional stress. In children, the most common triggers are viral illnesses such as those that cause the common cold.[1] This airway narrowing causes symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing, which respond to bronchodilators. Between ...
eprint_1_30658_130
... with clinically observed antidepressant effects. This suggests that decreased uptake of neurotransmitter is only an initial effect of the drugs, which may not be directly responsible for the antidepressant effects. It has been proposed that presynaptic inhibitory receptor densities in the brain decr ...
... with clinically observed antidepressant effects. This suggests that decreased uptake of neurotransmitter is only an initial effect of the drugs, which may not be directly responsible for the antidepressant effects. It has been proposed that presynaptic inhibitory receptor densities in the brain decr ...
Chapter 2
... neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node the next. A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. The action potential is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s ...
... neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node the next. A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. The action potential is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s ...
SANS
... (parasympathomimetic) agents Classified as either direct or indirect acting agents. Direct acting drugs act directly on the parasympathetic receptors (Eg. Pilocarpine acts on Nicotinic). Indirect acting drugs either cause release of neurotransmitter which then goes to the receptor site OR they ...
... (parasympathomimetic) agents Classified as either direct or indirect acting agents. Direct acting drugs act directly on the parasympathetic receptors (Eg. Pilocarpine acts on Nicotinic). Indirect acting drugs either cause release of neurotransmitter which then goes to the receptor site OR they ...
Beta blockers
... The blood pressure lowering effect of B antagonists develops gradually during a few weeks of treatment. Carvedilol is particularly suitable for treating congestive heart failure because this compound can block cardiac muscle remodeling by 2 mechanisms: (1) it antagonizes the effect of catecholamines ...
... The blood pressure lowering effect of B antagonists develops gradually during a few weeks of treatment. Carvedilol is particularly suitable for treating congestive heart failure because this compound can block cardiac muscle remodeling by 2 mechanisms: (1) it antagonizes the effect of catecholamines ...
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Signalling Mechanisms 145000 >>> 0
... Important regarding vascular smooth muscle Cyclic GMP is a 2nd messenger in vasculature, facilitating dephosphorylation of myosin light chains preventing their interaction with actin - thus causing vasodilation Nitric oxide (NO), which can be formed from nitrates (eg, nitroglycerin) and released fro ...
... Important regarding vascular smooth muscle Cyclic GMP is a 2nd messenger in vasculature, facilitating dephosphorylation of myosin light chains preventing their interaction with actin - thus causing vasodilation Nitric oxide (NO), which can be formed from nitrates (eg, nitroglycerin) and released fro ...
general principles of pharmacology
... Immediate release of MPH in overcoat of the tablet (22%) followed by progressive 8-hour release by an osmotic pump from 2 separate drug subcompartments (78%) with increasing concentration of medication in the afternoon Designed to mimic TID IR MPH with a 12 hour ...
... Immediate release of MPH in overcoat of the tablet (22%) followed by progressive 8-hour release by an osmotic pump from 2 separate drug subcompartments (78%) with increasing concentration of medication in the afternoon Designed to mimic TID IR MPH with a 12 hour ...
Ora Adren 80 - Douglas Labs
... 1 capsule contains: Adrenal Concentrate ............................................................................................. 80mg ...
... 1 capsule contains: Adrenal Concentrate ............................................................................................. 80mg ...
Lecture 2
... • Overall functions – Regulate organic metabolism & H2O & electrolyte balance – Induce adaptive changes to help body cope with stressful situations – Promote smooth, sequential growth & development – Control reproduction – Regulate red blood cell production – Along with autonomic nervous system, con ...
... • Overall functions – Regulate organic metabolism & H2O & electrolyte balance – Induce adaptive changes to help body cope with stressful situations – Promote smooth, sequential growth & development – Control reproduction – Regulate red blood cell production – Along with autonomic nervous system, con ...
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, also called noradrenaline, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and neurotransmitter. Noradrenaline is the common name in the United Kingdom (BAN), while norepinephrine is the International Nonproprietary Name and typically used in the United States. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are referred to everywhere as noradrenergic.Norepinephrine is synthesized and released by the central nervous system and also by a division of the autonomic nervous system called the sympathetic nervous system. In the brain, norepinephrine comes from several nuclei that are small in size but project to most other parts of the brain and exert powerful effects on their targets. The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. In the sympathetic nervous system norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating noradrenergic receptors located on the cell surface.In the most basic terms, the function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in what has been called the fight-or-flight response. In the brain norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and promotes voiding of the bladder and large intestines.A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of norepinephrine systems. Norepinephrine itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of norepinephrine, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of norepinephrine effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect, and are commonly used as anesthesia-enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on norepinephrine systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.