Lecture 3 - Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol plus CO2. Under aerobic conditions, gluco ...
... Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol plus CO2. Under aerobic conditions, gluco ...
Bio102 Problems
... 15. Why can your cells produce more usable cellular energy per carbon atom from a lipid molecule than from a carbohydrate molecule? Both are ultimately expelled from the body as CO2. To get there, each carbon atom from a lipid must be more oxidized more times than each carbon atom from a carbohydrat ...
... 15. Why can your cells produce more usable cellular energy per carbon atom from a lipid molecule than from a carbohydrate molecule? Both are ultimately expelled from the body as CO2. To get there, each carbon atom from a lipid must be more oxidized more times than each carbon atom from a carbohydrat ...
OverallQuiz2Ch5-8.doc
... continuously lost from the reaction center of photosystem II. What source is used to replace these electrons? a. sunlight b. oxygen c. water d. carbon dioxide ...
... continuously lost from the reaction center of photosystem II. What source is used to replace these electrons? a. sunlight b. oxygen c. water d. carbon dioxide ...
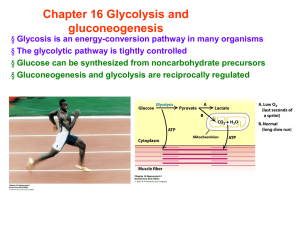
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis § Glycosis is an energy-conversion pathway in many organisms § The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled § Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors § Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated ...
... Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis § Glycosis is an energy-conversion pathway in many organisms § The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled § Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors § Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated ...
Gluconeogenesis
... humans. In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. The human brain alone requires 120 g of glucose each day, more than half of which is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. ...
... humans. In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. The human brain alone requires 120 g of glucose each day, more than half of which is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. ...
Practice Exam 3
... Short Answer 7. In the conversion of glucose to pyruvate via glycolysis, all of the following enzymes participate. Indicate the order in which they function by numbering them one through ten. ___ phosphofructokinase ___ triose phosphate isomerase ___ glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ___ phos ...
... Short Answer 7. In the conversion of glucose to pyruvate via glycolysis, all of the following enzymes participate. Indicate the order in which they function by numbering them one through ten. ___ phosphofructokinase ___ triose phosphate isomerase ___ glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ___ phos ...
Practice Exam 3 Answers
... Short Answer 7. In the conversion of glucose to pyruvate via glycolysis, all of the following enzymes participate. Indicate the order in which they function by numbering them one through ten. ___ phosphofructokinase ___ triose phosphate isomerase ___ glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ___ phos ...
... Short Answer 7. In the conversion of glucose to pyruvate via glycolysis, all of the following enzymes participate. Indicate the order in which they function by numbering them one through ten. ___ phosphofructokinase ___ triose phosphate isomerase ___ glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase ___ phos ...
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration - SBI
... Aerobic Cellular Respiration • Glucose reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water and energy (ATP) • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP) • For one molecule of glucose, 36 molecules of ATP are formed ...
... Aerobic Cellular Respiration • Glucose reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water and energy (ATP) • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP) • For one molecule of glucose, 36 molecules of ATP are formed ...
1. Metabolism refers to A) pathways of chemical reactions that build
... A) ATP releases a phosphate group and becomes ADP. B) ADP releases a phosphate group and becomes ATP. C) ATP gains a phosphate group and becomes ADP. D) ADP gains a phosphate group and becomes ATP. 4. In metabolism, glucose is degraded to carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide is produced in: ...
... A) ATP releases a phosphate group and becomes ADP. B) ADP releases a phosphate group and becomes ATP. C) ATP gains a phosphate group and becomes ADP. D) ADP gains a phosphate group and becomes ATP. 4. In metabolism, glucose is degraded to carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide is produced in: ...
Glycolysis
... • In this series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, energy is first extracted from the food (glucose) • The energy is captured in two forms: • NAD+ is reduced to NADH (one per 3 carbon unit) Carries energy as “reducing power” (more on this later) • ADP+Pi ...
... • In this series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, energy is first extracted from the food (glucose) • The energy is captured in two forms: • NAD+ is reduced to NADH (one per 3 carbon unit) Carries energy as “reducing power” (more on this later) • ADP+Pi ...
BIOS 1700 Dr. Tanda Week 6, Session 3 1. What two subunits made
... __________________ and ______________. Ethanol fermentation occurs in ______________ and _______________. 4. T/F Glucose is more efficient than fat. 5. One fatty acid molecule can produce a large number of ATP. Why? ...
... __________________ and ______________. Ethanol fermentation occurs in ______________ and _______________. 4. T/F Glucose is more efficient than fat. 5. One fatty acid molecule can produce a large number of ATP. Why? ...
Key Terms and Ideas: Fill in the blanks or provide a definition in your
... 2. Describe the steps in the citric acid cycle pictorially. Only provide the names of important carbon compounds. List out the net products and wastes from this reaction. ...
... 2. Describe the steps in the citric acid cycle pictorially. Only provide the names of important carbon compounds. List out the net products and wastes from this reaction. ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... with carbon dioxide & water Overall equation (aerobic) Glucose-high energy molecule Electrons are removed from substrates & received by oxygen (oxidation) ...
... with carbon dioxide & water Overall equation (aerobic) Glucose-high energy molecule Electrons are removed from substrates & received by oxygen (oxidation) ...
Study Guide and Potential Essay Questions for Chapter 25
... step, reduction, substrate level phosphorylation, thermoneutral zone Study suggestions and potential essay questions What is meant by the term substrate level phosphorylation? What is meant by the term oxidative phosphorylation? Where in the cell does each of these processes occur? • electron transp ...
... step, reduction, substrate level phosphorylation, thermoneutral zone Study suggestions and potential essay questions What is meant by the term substrate level phosphorylation? What is meant by the term oxidative phosphorylation? Where in the cell does each of these processes occur? • electron transp ...
AP Biology: Chapter 9
... 23. Write the summary equation for cellular respiration: a. Where did the glucose come from? b. Where did the O2 come from? c. Where did the CO2 come from? d. Where did the H2O come from? e. Where did the ATP come from? f. What else is produced that is not listed in this equation? ...
... 23. Write the summary equation for cellular respiration: a. Where did the glucose come from? b. Where did the O2 come from? c. Where did the CO2 come from? d. Where did the H2O come from? e. Where did the ATP come from? f. What else is produced that is not listed in this equation? ...
Document
... Mainly occurs in cytosol Some precursors are produced in mitochondria Takes place in liver and kidney Synthesis of glucose or glycogen from non carbohydrates like pyruvate, lactate glucogenic amino acids, glycerol and propionic acid Pathway involves steps of TCA cycle and reversal of glycolysis ...
... Mainly occurs in cytosol Some precursors are produced in mitochondria Takes place in liver and kidney Synthesis of glucose or glycogen from non carbohydrates like pyruvate, lactate glucogenic amino acids, glycerol and propionic acid Pathway involves steps of TCA cycle and reversal of glycolysis ...
Exam 3 - Chemistry Courses: About
... 2. 10 pts. Write True or False (1 points each) A. ____________ Transfer of three carbon atoms from a seven carbon sugar to a three carbon sugar to make a six carbon and four carbon sugar is catalyzed by a transketalase. B. ____________ Converting glucose to pyruvate through glycolysis involves ten ...
... 2. 10 pts. Write True or False (1 points each) A. ____________ Transfer of three carbon atoms from a seven carbon sugar to a three carbon sugar to make a six carbon and four carbon sugar is catalyzed by a transketalase. B. ____________ Converting glucose to pyruvate through glycolysis involves ten ...
2 ATP - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Question: “I thought energy was relesed when bonds were formed, not when they are broken!” ...
... Question: “I thought energy was relesed when bonds were formed, not when they are broken!” ...
Name: #: Cellular Respiration Review 2 Process Where does it
... 6. Write the complete overall chemical equation for cellular respiration using chemical symbols instead of words: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6H2O + 6CO2 + 36ATP 7. Why do we say there is a ‘net’ gain of 2 ATP at the end of glycolysis? Glycolysis produces 4ATP but since it needs 2 ATP to start, the cell only in ...
... 6. Write the complete overall chemical equation for cellular respiration using chemical symbols instead of words: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6H2O + 6CO2 + 36ATP 7. Why do we say there is a ‘net’ gain of 2 ATP at the end of glycolysis? Glycolysis produces 4ATP but since it needs 2 ATP to start, the cell only in ...
Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is a ______(metabolic
... a. During the early steps of glycolysis, glucose is converted to glucose 6-P, and then glucose 6-P is converted directly to: A. aldolase. B. fructose 6-P. b. In the process of glycolysis: A. one enzyme converts glucose into NADH. B. two enzymes are involved in breaking glucose down to ten pyruvate m ...
... a. During the early steps of glycolysis, glucose is converted to glucose 6-P, and then glucose 6-P is converted directly to: A. aldolase. B. fructose 6-P. b. In the process of glycolysis: A. one enzyme converts glucose into NADH. B. two enzymes are involved in breaking glucose down to ten pyruvate m ...
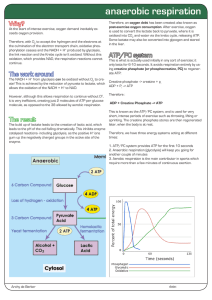
anaerobic respiration
... This is known as the ATP/PC system, and is used for very short, intense periods of exercise such as throwing, lifting or sprinting. The creatine phosphate stores are then regenerated later, when the body is at rest. Therefore, we have three energy systems acting at different ...
... This is known as the ATP/PC system, and is used for very short, intense periods of exercise such as throwing, lifting or sprinting. The creatine phosphate stores are then regenerated later, when the body is at rest. Therefore, we have three energy systems acting at different ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑