introduction to anatomy
... E. cells The cell is defined as the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms! Each cell has a set of organelles and performs a particular function (i.e. a red blood cell has a biconcave shape and is a nucleate. This structure increases its surface area, allowing for the transport of ...
... E. cells The cell is defined as the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms! Each cell has a set of organelles and performs a particular function (i.e. a red blood cell has a biconcave shape and is a nucleate. This structure increases its surface area, allowing for the transport of ...
Respiration - shscience.net
... Definition- the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it’s also the production of energy (ATP) • (it’s NOT just “breathing”. It is also the release of energy by our cells!) •it allows exchange of outside air and our circulatory system (blood transport) ...
... Definition- the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it’s also the production of energy (ATP) • (it’s NOT just “breathing”. It is also the release of energy by our cells!) •it allows exchange of outside air and our circulatory system (blood transport) ...
Frog 3322 Dissection Assessment sheet
... 1. Explain how the digestive system (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum) converts macromolecules from food into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth. In your answer, describe the different parts of the digestive system, ...
... 1. Explain how the digestive system (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum) converts macromolecules from food into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth. In your answer, describe the different parts of the digestive system, ...
LESSON 1 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1
... that as the volume of a gas-filled container increases, the pressure inside decreases. Conversely, as the volume of a closed container decreases, the pressure inside increases. When two connected spaces of air have different pressures, the air moves from the space with greater pressure to the one wi ...
... that as the volume of a gas-filled container increases, the pressure inside decreases. Conversely, as the volume of a closed container decreases, the pressure inside increases. When two connected spaces of air have different pressures, the air moves from the space with greater pressure to the one wi ...
Unit 1 exercises - Tick ( ) in front of true sentence, And Tick ( ) in
... f. The cells that have no nuclei. g. The small bodies that play a role in blood coagulation when the body is wounded. h. A yellow watery fluid in which blood cells float. i. The flow of blood to the lungs and its returning back again to the heart. j. Blood circulation between the heart and all body ...
... f. The cells that have no nuclei. g. The small bodies that play a role in blood coagulation when the body is wounded. h. A yellow watery fluid in which blood cells float. i. The flow of blood to the lungs and its returning back again to the heart. j. Blood circulation between the heart and all body ...
Evaluating a Method for Non-destructively Obtaining Small Volumes
... yielded by this procedure (~5 µl or 0.005 g) would constitute less than 1% of the body weight of A. talpoideum (the average weight of A. talpoideum in this study was 3.0 g ± 0.6 g SD) and of other similarly-sized salamanders, which is a criterion recommended by Wright and Whitaker (2001). Similarly- ...
... yielded by this procedure (~5 µl or 0.005 g) would constitute less than 1% of the body weight of A. talpoideum (the average weight of A. talpoideum in this study was 3.0 g ± 0.6 g SD) and of other similarly-sized salamanders, which is a criterion recommended by Wright and Whitaker (2001). Similarly- ...
Year 1 - StudyWise
... water and becomes dissolved. This is useful in cytoplasm of all cells and supports the reaction of these solutes, it is also useful in the processes of diffusion/active transport, and is also useful in transport such as blood and phloem. (III) Hydrostatic Pressure: Water when pressurised can provide ...
... water and becomes dissolved. This is useful in cytoplasm of all cells and supports the reaction of these solutes, it is also useful in the processes of diffusion/active transport, and is also useful in transport such as blood and phloem. (III) Hydrostatic Pressure: Water when pressurised can provide ...
Chapter 19b
... Extrinsic mechanisms • Maintain mean arterial pressure (MAP) • Redistribute blood during exercise and ...
... Extrinsic mechanisms • Maintain mean arterial pressure (MAP) • Redistribute blood during exercise and ...
Respiratory Assessment
... gas flowing past on one side and blood flowing past on the other. Gas exchanges occur by simple diffusion through the respiratory membrane. Oxygen passes from the alveolar air into the capillary blood and carbon dioxide leaves the blood to enter the gas-filled alveoli. 56) The pleural membranes, the ...
... gas flowing past on one side and blood flowing past on the other. Gas exchanges occur by simple diffusion through the respiratory membrane. Oxygen passes from the alveolar air into the capillary blood and carbon dioxide leaves the blood to enter the gas-filled alveoli. 56) The pleural membranes, the ...
Human Body: Organ Systems Study Guide Packet
... 4. Steroid hormones are made of cholesterol, which is a type of lipid. Using what you know about cell membranes, why do you think steroids can diffuse into a cell, while non-steroid hormones cannot? ...
... 4. Steroid hormones are made of cholesterol, which is a type of lipid. Using what you know about cell membranes, why do you think steroids can diffuse into a cell, while non-steroid hormones cannot? ...
Transvascular and Intrastitial Transport File
... – J= rate of mass flow kg/s (not kg/m2*s) – S= vessel wall surface area in m2 – ∆C= pressure difference across vessel wall in kg m-3 • Permeability coefficient P=J/(S*∆C) (m s-1) – units of distance per unit time ...
... – J= rate of mass flow kg/s (not kg/m2*s) – S= vessel wall surface area in m2 – ∆C= pressure difference across vessel wall in kg m-3 • Permeability coefficient P=J/(S*∆C) (m s-1) – units of distance per unit time ...
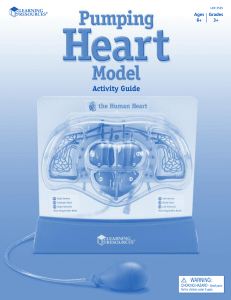
Activity Guide - Learning Resources
... • Blood is bright red when it is rich in oxygen or comes in contact with oxygen. For this reason, when you cut yourself or have a nosebleed, you generally see bright red blood as it hits the air. • Blood may look blue through your skin, but it isn’t. Blood is always either dark red or bright red, de ...
... • Blood is bright red when it is rich in oxygen or comes in contact with oxygen. For this reason, when you cut yourself or have a nosebleed, you generally see bright red blood as it hits the air. • Blood may look blue through your skin, but it isn’t. Blood is always either dark red or bright red, de ...
Pulmonary System_Lecture II - Medical
... The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases is the respira ...
... The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases is the respira ...
No Slide Title
... • The activity of the upper airway muscles (nose, pharynx and larynx) also decreases during sleep. • The negative pressure during inspiration is normally counterbalanced by activity of the upper airway muscles that function to keep the upper airway open. • Inspiration tends to collapse the upper air ...
... • The activity of the upper airway muscles (nose, pharynx and larynx) also decreases during sleep. • The negative pressure during inspiration is normally counterbalanced by activity of the upper airway muscles that function to keep the upper airway open. • Inspiration tends to collapse the upper air ...
Presentation
... blood is transported as oxyhemoglobin; carbon dioxide is transported mainly as bicarbonate ions ...
... blood is transported as oxyhemoglobin; carbon dioxide is transported mainly as bicarbonate ions ...
Taking Out the Garbage
... produce things you need. But they also produce waste. This waste must be removed from your cells. And then it must be excreted, or released from your body. Your body has a waste removal system to do these things. It is called the excretory system. Your excretory system helps keep you healthy. If was ...
... produce things you need. But they also produce waste. This waste must be removed from your cells. And then it must be excreted, or released from your body. Your body has a waste removal system to do these things. It is called the excretory system. Your excretory system helps keep you healthy. If was ...
www.ourpgs.com
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Welcome to the Frog Hospital
... Liver: This is the LARGEST organ in the body. It contains enzymes that detoxify the blood, processes fats and stores carbohydrates or starches. Pancreas: Produces digestive enzymes to help break down food in the small intestine where nutrient absorption occurs. Also, it controls insulin and sugar le ...
... Liver: This is the LARGEST organ in the body. It contains enzymes that detoxify the blood, processes fats and stores carbohydrates or starches. Pancreas: Produces digestive enzymes to help break down food in the small intestine where nutrient absorption occurs. Also, it controls insulin and sugar le ...
Science – Grade6
... soil. Explain the role of micro organisms in making compost. compost. Realise the effect of microbes on the soil and explain how it helps. Explain why landfill sites are needed. Identify the safety precautions we need to take so that we are not affected by harmful microbes. Describe how food must be ...
... soil. Explain the role of micro organisms in making compost. compost. Realise the effect of microbes on the soil and explain how it helps. Explain why landfill sites are needed. Identify the safety precautions we need to take so that we are not affected by harmful microbes. Describe how food must be ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.