View - Australian Endurance Riders Association
... As the body works, stored energy is burned up in the presence of oxygen to release useable energy and carbon-dioxide. The respiratory system has the function of replacing the oxygen and removing the carbon dioxide. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in ...
... As the body works, stored energy is burned up in the presence of oxygen to release useable energy and carbon-dioxide. The respiratory system has the function of replacing the oxygen and removing the carbon dioxide. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in ...
EVERYTHING YOU`VE EVER WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT WORMS
... skin, along with the behavioral adaptations that keeps worms in moist soil. To transport absorbed oxygen to all cells, the earthworm utilizes the blood fluid system (hemoglobin!). ...
... skin, along with the behavioral adaptations that keeps worms in moist soil. To transport absorbed oxygen to all cells, the earthworm utilizes the blood fluid system (hemoglobin!). ...
PowerPoint Presentation - EVERYTHING YOU’VE EVER WANTED …
... skin, along with the behavioral adaptations that keeps worms in moist soil. To transport absorbed oxygen to all cells, the earthworm utilizes the blood fluid system (hemoglobin!). ...
... skin, along with the behavioral adaptations that keeps worms in moist soil. To transport absorbed oxygen to all cells, the earthworm utilizes the blood fluid system (hemoglobin!). ...
HumanAnatomyPhysiologyBodyStructureTerminologyPresentation
... and changed into other forms that can be used or can be eliminated from the body. ...
... and changed into other forms that can be used or can be eliminated from the body. ...
Respiratory system
... in to arteries. Lung expansion causes further reduction in O tension. Further decrease in O tension will reduce pressure less than venous pressure Divers: reduce lung-blood gas exchange. Much lower partial pressures of O in their brains ...
... in to arteries. Lung expansion causes further reduction in O tension. Further decrease in O tension will reduce pressure less than venous pressure Divers: reduce lung-blood gas exchange. Much lower partial pressures of O in their brains ...
Respiration
... Animals in Moist Environments • Other animals combine large skin surface area with well-developed circulation for delivery to cells – Skin has many capillaries that carry O2 to internal body tissues – This arrangement sustains a favorable O2 concentration gradient between skin and blood – Example ...
... Animals in Moist Environments • Other animals combine large skin surface area with well-developed circulation for delivery to cells – Skin has many capillaries that carry O2 to internal body tissues – This arrangement sustains a favorable O2 concentration gradient between skin and blood – Example ...
Blue Sky Border
... –~178 L/day of liquid is reabsorbed into body –Glucose (usually) , amino acids, etc—anything the body needs will usually be reabsorbed. –Sodium reabsorption rates vary— depending on amount in body ...
... –~178 L/day of liquid is reabsorbed into body –Glucose (usually) , amino acids, etc—anything the body needs will usually be reabsorbed. –Sodium reabsorption rates vary— depending on amount in body ...
HCCS - HCC Learning Web
... the nephron and physiology in maintaining the blood pressure and hydration. Kidney filtration, secretion and absorption across the nephron. Endocrine function of the kidneys. Calculate renal plasma clearance etc. Structure of ureters and urine bladder, urethra. LAB: Buffer system by the kidneys. Med ...
... the nephron and physiology in maintaining the blood pressure and hydration. Kidney filtration, secretion and absorption across the nephron. Endocrine function of the kidneys. Calculate renal plasma clearance etc. Structure of ureters and urine bladder, urethra. LAB: Buffer system by the kidneys. Med ...
Internal Respiration and CO 2 Exchange
... to chest wall and diaphragm In between 2 pleural membranes is thin layer of fluid (mostly H2O) __________ _________ is about 4mm Hg less than atmosphere— keeps them together _____________—condition whereby air enters intrapleural space and causes lungs to collapse ...
... to chest wall and diaphragm In between 2 pleural membranes is thin layer of fluid (mostly H2O) __________ _________ is about 4mm Hg less than atmosphere— keeps them together _____________—condition whereby air enters intrapleural space and causes lungs to collapse ...
document
... smokers are at increased risk for cancer of the larynx, oral cavity, esophagus, bladder, kidney, and pancreas. About 48 million people in the United States smoke an estimated total of 430 billion cigarettes each year the average cigarette contains around 4,000 chemicals, some of which are highly tox ...
... smokers are at increased risk for cancer of the larynx, oral cavity, esophagus, bladder, kidney, and pancreas. About 48 million people in the United States smoke an estimated total of 430 billion cigarettes each year the average cigarette contains around 4,000 chemicals, some of which are highly tox ...
1.5 Powerpoint - WordPress.com
... 1. Glucose is made available by the breakdown of glycogen stored Energy for muscles to contract in the working muscles. and create movement 2. The glucose is used by the muscles of the body to produce energy, Glucose without the use of oxygen. Acidpasses back into the blood ...
... 1. Glucose is made available by the breakdown of glycogen stored Energy for muscles to contract in the working muscles. and create movement 2. The glucose is used by the muscles of the body to produce energy, Glucose without the use of oxygen. Acidpasses back into the blood ...
Acid-Base Balance
... Carbonic acid splits into hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions For each hydrogen ion secreted, a sodium ion and a bicarbonate ion are reabsorbed by the PCT cells Secreted hydrogen ions form carbonic acid; thus, bicarbonate disappears from filtrate at the same rate that it enters the peritubular capill ...
... Carbonic acid splits into hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions For each hydrogen ion secreted, a sodium ion and a bicarbonate ion are reabsorbed by the PCT cells Secreted hydrogen ions form carbonic acid; thus, bicarbonate disappears from filtrate at the same rate that it enters the peritubular capill ...
BIOL 2402 Acid Base Homeostasis
... Humans consume more phosphate than needed. The excess is filtered into the nephrons and is not re-absorbed by the kidney. The phosphate helps to buffer urine pH in the nephron. It binds the secreted protons and keeps the pH above 5. If it were not for this buffer, urine pH would be extremely acidic ...
... Humans consume more phosphate than needed. The excess is filtered into the nephrons and is not re-absorbed by the kidney. The phosphate helps to buffer urine pH in the nephron. It binds the secreted protons and keeps the pH above 5. If it were not for this buffer, urine pH would be extremely acidic ...
Sherwood 14
... Unregulated influences on the GFR – Pathologically plasma-colloid osmotic pressure and Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure can change • Plasma-colloid osmotic pressure – Severely burned patient ↑ GFR – Dehydrating diarrhea ↓ GFR • Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure – Obstructions such as kidney ...
... Unregulated influences on the GFR – Pathologically plasma-colloid osmotic pressure and Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure can change • Plasma-colloid osmotic pressure – Severely burned patient ↑ GFR – Dehydrating diarrhea ↓ GFR • Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure – Obstructions such as kidney ...
Respiratory System Notes
... • Reflex plays a role in regulating basic rhythm of breathing and preventing overinflation of lungs ...
... • Reflex plays a role in regulating basic rhythm of breathing and preventing overinflation of lungs ...
Gas Exchange in Mammals - Miss Jan`s Science Wikispace
... Surfactant Lipoprotein produced by alveolar cells Reduced surface tension (if no ...
... Surfactant Lipoprotein produced by alveolar cells Reduced surface tension (if no ...
excretory system exercise
... 27. What is the cause that right kidney is at slightly lower level than the left kidney in human being (1) Due to improper ascentment of kidney during embryonic life. ...
... 27. What is the cause that right kidney is at slightly lower level than the left kidney in human being (1) Due to improper ascentment of kidney during embryonic life. ...
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... Single-celled organisms exchange gases directly across their cell membrane. However, the slow diffusion rate of oxygen relative to carbon dioxide limits the size of single-celled organisms. Simple animals that lack specialized exchange surfaces have flattened, tubular, or thin shaped body plans, whi ...
... Single-celled organisms exchange gases directly across their cell membrane. However, the slow diffusion rate of oxygen relative to carbon dioxide limits the size of single-celled organisms. Simple animals that lack specialized exchange surfaces have flattened, tubular, or thin shaped body plans, whi ...
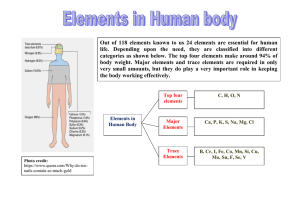
Elements in the Human Body
... Biological role: The heme group present in hemoglobin binds with oxygen and transport it from lungs to tissues. Molecular oxygen is essential for cellular respiration in all organisms. It is used as an electron acceptor in mitochondria present ...
... Biological role: The heme group present in hemoglobin binds with oxygen and transport it from lungs to tissues. Molecular oxygen is essential for cellular respiration in all organisms. It is used as an electron acceptor in mitochondria present ...
BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION - Prof. Dr. Joyanta Kumar Roy
... capillaries. The heart itself is supplied by two small but highly important arteries, called Coronary arteries. If they blocked by Coronary Thrombosis, Myocardial infraction follows, often leading to fatal situation. The Heart rate is partially controlled by autonomic nervous system and partially by ...
... capillaries. The heart itself is supplied by two small but highly important arteries, called Coronary arteries. If they blocked by Coronary Thrombosis, Myocardial infraction follows, often leading to fatal situation. The Heart rate is partially controlled by autonomic nervous system and partially by ...
CARDIOVASCULAR INTERACTIONS
... 7. Bioengineers needing more physics applied to physiology and an example of a complex mechanical system with negative feedback control. Topics included for helping the Learner: ⇒ Explain the difference between Emax (related to afterload, that is ventricular end systolic pressure) and the Frank-Star ...
... 7. Bioengineers needing more physics applied to physiology and an example of a complex mechanical system with negative feedback control. Topics included for helping the Learner: ⇒ Explain the difference between Emax (related to afterload, that is ventricular end systolic pressure) and the Frank-Star ...
chapter 44 - Biology Junction
... The physiological systems of animals operate within a fluid environment. The relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within narrow limits, despite variations in the animal’s external environment. Metabolism also poses the problem of disposal of wastes. The breakdown o ...
... The physiological systems of animals operate within a fluid environment. The relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within narrow limits, despite variations in the animal’s external environment. Metabolism also poses the problem of disposal of wastes. The breakdown o ...
bio 12 8.1 TISSUES
... UNIT B Chapter 8: Human Organization Formed elements of blood: • Red blood cells (erythrocytes) o Small, biconcave, disk-shaped cells without nuclei o Contain the pigment hemoglobin, which makes the cells and blood red o Hemoglobin associates with oxygen, allowing red blood cells to transport oxyge ...
... UNIT B Chapter 8: Human Organization Formed elements of blood: • Red blood cells (erythrocytes) o Small, biconcave, disk-shaped cells without nuclei o Contain the pigment hemoglobin, which makes the cells and blood red o Hemoglobin associates with oxygen, allowing red blood cells to transport oxyge ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.