Ch. 13 - The Respiratory System
... A small dissolved amount is carried in the plasma 2. Carbon dioxide transport in the blood a. Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3–) b. A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, but at different binding sites than those of oxygen c. For carbon dioxide to d ...
... A small dissolved amount is carried in the plasma 2. Carbon dioxide transport in the blood a. Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3–) b. A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, but at different binding sites than those of oxygen c. For carbon dioxide to d ...
ch_19_lecture_outline_a
... • Abrupt changes in diameter or fatty plaques from atherosclerosis dramatically increase resistance – Disrupt laminar flow and cause turbulent flow • Irregular fluid motion increased resistance ...
... • Abrupt changes in diameter or fatty plaques from atherosclerosis dramatically increase resistance – Disrupt laminar flow and cause turbulent flow • Irregular fluid motion increased resistance ...
Respiratory System - Napa Valley College
... produced when oxygen and food combine in cells) passes from the capillary blood vessels into the air spaces of the lungs to be exhaled. Exhaled air contains 16% oxygen Mostly an involuntary activity ...
... produced when oxygen and food combine in cells) passes from the capillary blood vessels into the air spaces of the lungs to be exhaled. Exhaled air contains 16% oxygen Mostly an involuntary activity ...
Lecture 7
... O2 which allows greater amount of CO2 to be carried in blood • At the lung, high O2 forces CO2 from Hb (and plasma) and it is then exhaled ...
... O2 which allows greater amount of CO2 to be carried in blood • At the lung, high O2 forces CO2 from Hb (and plasma) and it is then exhaled ...
Physiology PPT - MHC LEVEL 3 PED
... However, oxygen availability only determines the fate of the end product and is not required for the actual process of glycolysis itself. In fact, oxygen availability has been shown to have little to do with which of the two end products, lactate or pyruvate is produced. Hence the terms aerobic mean ...
... However, oxygen availability only determines the fate of the end product and is not required for the actual process of glycolysis itself. In fact, oxygen availability has been shown to have little to do with which of the two end products, lactate or pyruvate is produced. Hence the terms aerobic mean ...
Mathematical Model for Diabetes Use Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT)
... stomach, makeser hormone called insulin to help glucose get into our body cells. When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t doesn’tmake makeenough enough insulin or can’t useown its own insulin or can’t use its insulin very well. This problem causes glucose to build up in your blood. Diabetes ...
... stomach, makeser hormone called insulin to help glucose get into our body cells. When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t doesn’tmake makeenough enough insulin or can’t useown its own insulin or can’t use its insulin very well. This problem causes glucose to build up in your blood. Diabetes ...
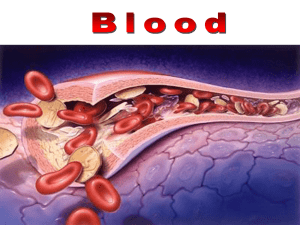
blood ppt
... • Hemorrhage or increased RBC destruction reduces RBC numbers • Insufficient hemoglobin (e.g., iron deficiency) • Reduced availability of O2 (e.g., high altitudes) ...
... • Hemorrhage or increased RBC destruction reduces RBC numbers • Insufficient hemoglobin (e.g., iron deficiency) • Reduced availability of O2 (e.g., high altitudes) ...
Blood Vessels
... • Delivery system of dynamic structures that begins and ends at the heart • Arteries: carry blood away from the heart; oxygenated except for pulmonary circulation • Capillaries: contact tissue cells and directly ...
... • Delivery system of dynamic structures that begins and ends at the heart • Arteries: carry blood away from the heart; oxygenated except for pulmonary circulation • Capillaries: contact tissue cells and directly ...
AgriSETA
... The biochemical processes which occur during digestion are important for meat, milk and fibre production since this allows feed nutrients to be built into the product. * Digestion of cellulose After thorough mixing of the food in the rumen the cellulose is broken down by ruminal organisms to fatty a ...
... The biochemical processes which occur during digestion are important for meat, milk and fibre production since this allows feed nutrients to be built into the product. * Digestion of cellulose After thorough mixing of the food in the rumen the cellulose is broken down by ruminal organisms to fatty a ...
Tuesday, January 06, 1998: (Day 1) Syllabus and course policy. No
... MD (macula densa) notes passage of chloride through tubules. When MD sense decline in chloride ions, it tells juxtaglomerular cells to release renin. Renin meets angiotensinogen and a cleaving operation takes places to produce angiotensin I (not an active molecule yet). Another cleaving takes plac ...
... MD (macula densa) notes passage of chloride through tubules. When MD sense decline in chloride ions, it tells juxtaglomerular cells to release renin. Renin meets angiotensinogen and a cleaving operation takes places to produce angiotensin I (not an active molecule yet). Another cleaving takes plac ...
Notes: Human Systems, Homeostasis and Feedback Inhibition
... generally fully automated and very stable. • Feedback inhibition is what biological systems (like the human body) use to achieve homeostasis. ...
... generally fully automated and very stable. • Feedback inhibition is what biological systems (like the human body) use to achieve homeostasis. ...
The Cardiovascular System: The Blood
... Blood contributes to homeostasis by transporting oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and hormones to and from the body’s cells. It helps regulate body pH, provides protection against disease through phagocytosis and the production of antibodies. The cardiovascular system consists of three interrelate ...
... Blood contributes to homeostasis by transporting oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and hormones to and from the body’s cells. It helps regulate body pH, provides protection against disease through phagocytosis and the production of antibodies. The cardiovascular system consists of three interrelate ...
Respiratorystudent - Dr. Brahmbhatt`s Class Handouts
... ______________ rings as they enter the lungs • Trachea divides into the – _________________________ on the right and left sides as they enter the lungs (site of division is called the bifurcation), – Further divide into the ________________________________ ...
... ______________ rings as they enter the lungs • Trachea divides into the – _________________________ on the right and left sides as they enter the lungs (site of division is called the bifurcation), – Further divide into the ________________________________ ...
PH Balance and You - Midwest Health and Wellness
... A surprising number and variety of physical problems and diseases can be caused by the problem of foods that are acid-producing after digestion. Today the vast majority of the populace in industrialized nations suffer from problems caused by the stress of acidosis, because both modern lifestyle and ...
... A surprising number and variety of physical problems and diseases can be caused by the problem of foods that are acid-producing after digestion. Today the vast majority of the populace in industrialized nations suffer from problems caused by the stress of acidosis, because both modern lifestyle and ...
Development of blood pressure and cardiac reflexes in the frog
... representingthe completetransition from aquatic larvae to primarily air-breathing adults. fH (49-66 beats/min) was not significantly affected by development,whereasmeanarterial blood pressurewas strongly affected, being lowest in the stage37-39 larvae (10 mmHg), intermediate in the stage44-45 larvae ...
... representingthe completetransition from aquatic larvae to primarily air-breathing adults. fH (49-66 beats/min) was not significantly affected by development,whereasmeanarterial blood pressurewas strongly affected, being lowest in the stage37-39 larvae (10 mmHg), intermediate in the stage44-45 larvae ...
GCSE Revision bookle..
... To improve or work aerobically a person needs to work between 60%-80% of their maximum heart rate. To work more anaerobically a person needs to work at above 80% of there Maximum heart rate. E.g. a 20 year old would have a maximum heart rate of 200 bpm. To improve their target heart they need to wor ...
... To improve or work aerobically a person needs to work between 60%-80% of their maximum heart rate. To work more anaerobically a person needs to work at above 80% of there Maximum heart rate. E.g. a 20 year old would have a maximum heart rate of 200 bpm. To improve their target heart they need to wor ...
Blood ph and other details
... normal (ie. keeping homeostasis). The body’s balance between acidity and alkalinity is referred to as acid-base balance. The acidity or alkalinity of any solution, including blood, is indicated on the pH scale. The blood’s acid-base balance is precisely controlled, because even a minor deviation fro ...
... normal (ie. keeping homeostasis). The body’s balance between acidity and alkalinity is referred to as acid-base balance. The acidity or alkalinity of any solution, including blood, is indicated on the pH scale. The blood’s acid-base balance is precisely controlled, because even a minor deviation fro ...
Respiratory System Part B
... Breathing becomes deeper and more vigorous, but respiratory rate may not be significantly changed (hyperpnea) ...
... Breathing becomes deeper and more vigorous, but respiratory rate may not be significantly changed (hyperpnea) ...
Day 4 FETAL PIG DISSECTION HAND-IN
... 5. Notice that the surface of the heart is covered with blood vessels. These are part of the coronary circulation, a set of arteries and veins whose only job is to nourish the heart tissue. Blockage in these vessels causes heart attacks. 6. Anterior to the heart, locate another large vein that enter ...
... 5. Notice that the surface of the heart is covered with blood vessels. These are part of the coronary circulation, a set of arteries and veins whose only job is to nourish the heart tissue. Blockage in these vessels causes heart attacks. 6. Anterior to the heart, locate another large vein that enter ...
Unit 2 form 2 Respiration scheme of work
... area for gas exchange Ask pupils to predict what happens in the alveolus. Help pupils to annotate diagrams with arrows to show the direction of movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide and describe gas exchange in terms of a supply of oxygen to the blood and removal of carbon dioxide from the blood. Sh ...
... area for gas exchange Ask pupils to predict what happens in the alveolus. Help pupils to annotate diagrams with arrows to show the direction of movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide and describe gas exchange in terms of a supply of oxygen to the blood and removal of carbon dioxide from the blood. Sh ...
Arthropods (Notebook Copy)
... Protostomes (blastopore develops into mouth) Coelomate (mesoderm-lined body cavity) Ventral nervous system Open circulatory system Specialized sensory receptors & high degree of cephalization Have simple or compound eyes & segmented antenna ...
... Protostomes (blastopore develops into mouth) Coelomate (mesoderm-lined body cavity) Ventral nervous system Open circulatory system Specialized sensory receptors & high degree of cephalization Have simple or compound eyes & segmented antenna ...
CH14
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.