![[j26] Chapter 14#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000367221_1-b8dd3faa03e0a519508f460a9af94122-300x300.png)
[j26] Chapter 14#
... ___ 23. Which statement about antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is false? a. ADH is a hormone also known as vasopressin. b. ADH is synthesized by neurons located in the hypothalamus. c. Receptors (osmoreceptors) release ADH when the plasma osmolality rises. d. ADH decreases water reabsorption from the glom ...
... ___ 23. Which statement about antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is false? a. ADH is a hormone also known as vasopressin. b. ADH is synthesized by neurons located in the hypothalamus. c. Receptors (osmoreceptors) release ADH when the plasma osmolality rises. d. ADH decreases water reabsorption from the glom ...
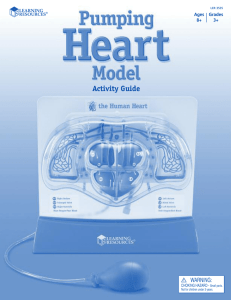
Pumping Heart Model - Learning Resources
... • Blood is bright red when it is rich in oxygen or comes in contact with oxygen. For this reason, when you cut yourself or have a nosebleed, you generally see bright red blood as it hits the air. • Blood may look blue through your skin, but it isn’t. Blood is always either dark red or bright red, de ...
... • Blood is bright red when it is rich in oxygen or comes in contact with oxygen. For this reason, when you cut yourself or have a nosebleed, you generally see bright red blood as it hits the air. • Blood may look blue through your skin, but it isn’t. Blood is always either dark red or bright red, de ...
Introduction - GEOCITIES.ws
... (1) The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs via (2) the pulmonary arteries. As blood flows through (3) capillary beds in the right and left lungs, it loads O2 and unloads CO2. Oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs via the pulmonary veins to (4) the left atrium of the heart. Next, the ...
... (1) The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs via (2) the pulmonary arteries. As blood flows through (3) capillary beds in the right and left lungs, it loads O2 and unloads CO2. Oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs via the pulmonary veins to (4) the left atrium of the heart. Next, the ...
Rat Dissection Lab
... Produce bile, help digest fat, filter blood of harmful substances Makes enzymes to help digest fats and carbohydrates Move food to stomach Blood storage and recycle damaged RBC’s Blood to lower body Blood from lower body to heart Stores urine ...
... Produce bile, help digest fat, filter blood of harmful substances Makes enzymes to help digest fats and carbohydrates Move food to stomach Blood storage and recycle damaged RBC’s Blood to lower body Blood from lower body to heart Stores urine ...
А. Э. Зайцева Основные анатомии и физиологии животных на
... The main approach in animal physiology is to study the evolutionary origins of the physiological mechanisms in order to understand the significance of these mechanisms for modern-day animals. Modern physiology which is based on chemical, physical and anatomical methods investigate biological organiz ...
... The main approach in animal physiology is to study the evolutionary origins of the physiological mechanisms in order to understand the significance of these mechanisms for modern-day animals. Modern physiology which is based on chemical, physical and anatomical methods investigate biological organiz ...
The main passageway that leads to the lungs from the throat is the
... a) move mucus and dirt upward c) produce dirt trapping mucus b) only beat when you inhale d) help in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide ...
... a) move mucus and dirt upward c) produce dirt trapping mucus b) only beat when you inhale d) help in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide ...
Every Circulation Question- Answers
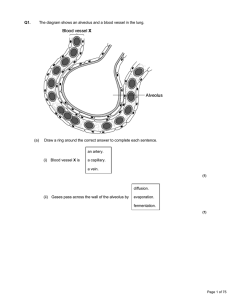
... passes through capillary walls to tissue fluid / AW; used up / stored, in tissues / AW (so little in lymph); ref, respiration / glycogen; high in vena cava as (absorbed) from gut / sent from liver / AW; ...
... passes through capillary walls to tissue fluid / AW; used up / stored, in tissues / AW (so little in lymph); ref, respiration / glycogen; high in vena cava as (absorbed) from gut / sent from liver / AW; ...
Biology 30 Student Notes Nervous Reproduction_1
... Thalamus: it relays sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex and motor impulses from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord Hypothalamus: receives sensory impulses from the internal organs by way of the thalamus, and allows us to feel hunger, thirst, aggression, rage, and pleasure. o It also controls ...
... Thalamus: it relays sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex and motor impulses from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord Hypothalamus: receives sensory impulses from the internal organs by way of the thalamus, and allows us to feel hunger, thirst, aggression, rage, and pleasure. o It also controls ...
Review for Final Semester Exam
... The network of nerves that branch out from the CNS are called Axons Spinal Cord PNS TNS ...
... The network of nerves that branch out from the CNS are called Axons Spinal Cord PNS TNS ...
Unit 3 This scheme of work suggests possible teaching and learning
... Discuss: Discuss in terms of energy used and show images of kidney and root hair cells with mitochondria. Why must soil and hydroponics solutions be ...
... Discuss: Discuss in terms of energy used and show images of kidney and root hair cells with mitochondria. Why must soil and hydroponics solutions be ...
2010-2011 Human Body Systems iv
... Complete a new unit title page on the left side of your notebook under today’s bell work. For your unit page for this unit, I want you to draw two body systems INSIDE the human body. The first is the system with which you are most familiar. The second system should be one that you want to learn more ...
... Complete a new unit title page on the left side of your notebook under today’s bell work. For your unit page for this unit, I want you to draw two body systems INSIDE the human body. The first is the system with which you are most familiar. The second system should be one that you want to learn more ...
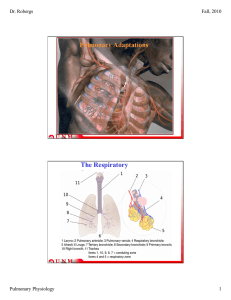
Pulmonary Adaptations The Respiratory System
... • temperature • PCO2 • 2,3-BPG • acidosis ...
... • temperature • PCO2 • 2,3-BPG • acidosis ...
Now! - Soojeede.com
... • Birds are one of the most interesting and widely known group of animals. There are more than 8600 species of birds distributed all over the world. Birds as a group exhibit a characteristic uniformity in structure. • Aves are warm blooded vertebrates with an exoskeleton of feathers. The feet are co ...
... • Birds are one of the most interesting and widely known group of animals. There are more than 8600 species of birds distributed all over the world. Birds as a group exhibit a characteristic uniformity in structure. • Aves are warm blooded vertebrates with an exoskeleton of feathers. The feet are co ...
Exam 1 (Intro/Endo/Repro) Name
... Full credit for any answer conveying the idea that feedforward control anticipates a need for enhanced O2 delivery or CO2 disposal (rather than waiting for an error signal to develop). For example, you might start breathing hard at the starting line of a race as you anticipate the forthcoming need f ...
... Full credit for any answer conveying the idea that feedforward control anticipates a need for enhanced O2 delivery or CO2 disposal (rather than waiting for an error signal to develop). For example, you might start breathing hard at the starting line of a race as you anticipate the forthcoming need f ...
Respiration - segaran1996
... enzymes that transfer energy in food molecules, eg. sugars and lipids, to ATP. • ATP is compound that is able to supply on-the-spot, instant and usable energy for cell activities. • Mitochondria are the organelles that house the enzymes and substrates associated with aerobic ...
... enzymes that transfer energy in food molecules, eg. sugars and lipids, to ATP. • ATP is compound that is able to supply on-the-spot, instant and usable energy for cell activities. • Mitochondria are the organelles that house the enzymes and substrates associated with aerobic ...
BIO101
... The student will become familiar with some representative groups of drugs and their effect on the body. The student will also learn how the endocrine system influences the physiology, homeostasis and behavior of the body. Intermediate Objectives: Upon completion of this unit the student will be able ...
... The student will become familiar with some representative groups of drugs and their effect on the body. The student will also learn how the endocrine system influences the physiology, homeostasis and behavior of the body. Intermediate Objectives: Upon completion of this unit the student will be able ...
Organ/body system
... UNIT 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Learning Goal: I can evaluate the structural organization of the body, homeostasis & homeostatic control mechanisms. I will be able to: Describe the structural organization of the body from microscopic to macroscopic realms. Describe homeostasis & homeostatic ...
... UNIT 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Learning Goal: I can evaluate the structural organization of the body, homeostasis & homeostatic control mechanisms. I will be able to: Describe the structural organization of the body from microscopic to macroscopic realms. Describe homeostasis & homeostatic ...
Ch 40 Notes - Dublin City Schools
... slow acting, but can have long-lasting effects Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... slow acting, but can have long-lasting effects Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
f869c698c70a3fe
... • Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level by crossing the plasma membrane • In unicellular organisms, these exchanges occur directly with the environment ...
... • Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level by crossing the plasma membrane • In unicellular organisms, these exchanges occur directly with the environment ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... The earthworm must keep its epidermis moist to facilitate gas exchange across its body surface. 5. How do an animal’s size, activity level, and environment influence the structure and function of its respiratory surface? The larger and more active the organism, the ATP it needs, and the more O2 it n ...
... The earthworm must keep its epidermis moist to facilitate gas exchange across its body surface. 5. How do an animal’s size, activity level, and environment influence the structure and function of its respiratory surface? The larger and more active the organism, the ATP it needs, and the more O2 it n ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.