Chordate Lab Handout
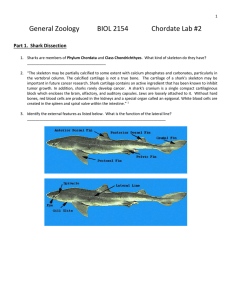
... 9. “Cut the intestine about one centimeter forward of the anus and begin gently lifting it out of the body cavity. The dorsal mesentery will likely inhibit this process and will therefore need to be cut away as the intestine is lifted forward. Care should be taken to not remove any structures but th ...
... 9. “Cut the intestine about one centimeter forward of the anus and begin gently lifting it out of the body cavity. The dorsal mesentery will likely inhibit this process and will therefore need to be cut away as the intestine is lifted forward. Care should be taken to not remove any structures but th ...
Chap._17_(Endocrine_System)
... An adrenal gland is situated superior to each kidney (suprarenal gland) Its’ outer part is called adrenal cortex (80% of gland) Its’ inner part is called adrenal medulla. Adrenal cortex is further divided into outer, middle & inner zones secreting different hormones: MINERALOCORTICOIDS (produced in ...
... An adrenal gland is situated superior to each kidney (suprarenal gland) Its’ outer part is called adrenal cortex (80% of gland) Its’ inner part is called adrenal medulla. Adrenal cortex is further divided into outer, middle & inner zones secreting different hormones: MINERALOCORTICOIDS (produced in ...
Document
... 1. Ganglia concentrated in foot, esophagus, adductor muscle and mantle. 2. Some have eyes for sensing light around shell rim. 3. Osphradia- chemoreceptors ...
... 1. Ganglia concentrated in foot, esophagus, adductor muscle and mantle. 2. Some have eyes for sensing light around shell rim. 3. Osphradia- chemoreceptors ...
Chapter 3 - Martinos Center
... vessel segment can be modeled reasonably well by Poisseuile’s Law (eq. 3.1, p.4), however the nonNewtonian rheology of blood becomes more important as the vessel size drops and the shear rate increases. According to Poisseuile’s Law, vessel diameter exerts a fourth-order influence on vascular resist ...
... vessel segment can be modeled reasonably well by Poisseuile’s Law (eq. 3.1, p.4), however the nonNewtonian rheology of blood becomes more important as the vessel size drops and the shear rate increases. According to Poisseuile’s Law, vessel diameter exerts a fourth-order influence on vascular resist ...
Unit A - apel slice
... The heart is an organ made up of muscle tissue, epithelial tissue, nervous tissue, and connective tissue. These tissues work together to pump blood to all parts of your body. Just as cells work together to form tissues, tissues work together to form organs. An organ is several kinds of tissue worki ...
... The heart is an organ made up of muscle tissue, epithelial tissue, nervous tissue, and connective tissue. These tissues work together to pump blood to all parts of your body. Just as cells work together to form tissues, tissues work together to form organs. An organ is several kinds of tissue worki ...
BIOL242Chap19VesselsOCT2012
... – regulated by sympathetic nervous system – Controls vasoconstriction/vasodilation of vessels – External elastic membrane (arteries only) separates tunica media from tunica externa – Thickest layer in a small artery ...
... – regulated by sympathetic nervous system – Controls vasoconstriction/vasodilation of vessels – External elastic membrane (arteries only) separates tunica media from tunica externa – Thickest layer in a small artery ...
Fetal Pig Dissection with Photos
... In the following laboratory exercise, you will examine in some detail the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig (Sus scrofa). As the pig is a mammal, many aspects of its structural and functional organization are identical with those of other mammals, including humans. Thus, a study of the fe ...
... In the following laboratory exercise, you will examine in some detail the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig (Sus scrofa). As the pig is a mammal, many aspects of its structural and functional organization are identical with those of other mammals, including humans. Thus, a study of the fe ...
body system objectives
... 1. Identify the organs of the respiratory system on a diagram. 2. Explain the structures and functions of the parts of the respiratory system. 3. Explain what is happening to the ribs and diaphragm in the breathing process. 4. Describe what happens between the alveoli and the capillaries. 5. What is ...
... 1. Identify the organs of the respiratory system on a diagram. 2. Explain the structures and functions of the parts of the respiratory system. 3. Explain what is happening to the ribs and diaphragm in the breathing process. 4. Describe what happens between the alveoli and the capillaries. 5. What is ...
Fetal_Pig_Dissection_Directions_100501.1
... In the following laboratory exercise, you will examine in some detail the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig (Sus scrofa). As the pig is a mammal, many aspects of its structural and functional organization are identical with those of other mammals, including humans. Thus, a study of the fe ...
... In the following laboratory exercise, you will examine in some detail the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig (Sus scrofa). As the pig is a mammal, many aspects of its structural and functional organization are identical with those of other mammals, including humans. Thus, a study of the fe ...
Is your pet microchipped? - Clifton Villa Veterinary Surgery
... heart. As the chambers of the left pets to lead a normal active life. Whilst most of our pets side contract, the blood is then thankfully take all this for granted, heart disease pumped to the tissues of the is nevertheless surprisingly common. body. This is illustrated below. In dogs it is generall ...
... heart. As the chambers of the left pets to lead a normal active life. Whilst most of our pets side contract, the blood is then thankfully take all this for granted, heart disease pumped to the tissues of the is nevertheless surprisingly common. body. This is illustrated below. In dogs it is generall ...
Cell Compounds
... areas. Plant vacuoles contain water, sugar, salts and pigments responsible for the many colors of flowers and some leaves. Some vacuoles contain toxic substances to protect the plant from predacious animals. Lysosomes - Lysosomes are vesicles formed by the Golgi apparatus. They contain hydrolytic en ...
... areas. Plant vacuoles contain water, sugar, salts and pigments responsible for the many colors of flowers and some leaves. Some vacuoles contain toxic substances to protect the plant from predacious animals. Lysosomes - Lysosomes are vesicles formed by the Golgi apparatus. They contain hydrolytic en ...
File - Miss Hanks` SPS1
... in heart volumes. The more blood pumped around the body per minute, the faster Oxygen is delivered to the working muscles. • The number of red blood cells increases, improving the bodies ability to transport Oxygen to the muscles for aerobic energy production. • The resting heart rate decreases in t ...
... in heart volumes. The more blood pumped around the body per minute, the faster Oxygen is delivered to the working muscles. • The number of red blood cells increases, improving the bodies ability to transport Oxygen to the muscles for aerobic energy production. • The resting heart rate decreases in t ...
Points to take note for Biology - Learning Made Simple Singapore
... - Carbohydrate metabolism. Fats metabolism. Proteins metabolism. Breakdown of haemoglobin and storage of iron. Detoxification. Carbohydrate metabolism - Excess glucose which passes through hepatic portal vein from small intestine to liver is converted to glycogen. - This conversion is stimulated by ...
... - Carbohydrate metabolism. Fats metabolism. Proteins metabolism. Breakdown of haemoglobin and storage of iron. Detoxification. Carbohydrate metabolism - Excess glucose which passes through hepatic portal vein from small intestine to liver is converted to glycogen. - This conversion is stimulated by ...
Functional Human Physiology for the Exercise and Sport Sciences
... Functions to generate the basic respiratory rhythm The respiratory cycle is repeated 12 - 15 times/minute Dorsal neurons have an intrinsic ability to spontaneously depolarize at a rhythmic rate Quiet breathing - Inhalation The dorsal inspiratory neurons transmit nerve impulses via the phreni ...
... Functions to generate the basic respiratory rhythm The respiratory cycle is repeated 12 - 15 times/minute Dorsal neurons have an intrinsic ability to spontaneously depolarize at a rhythmic rate Quiet breathing - Inhalation The dorsal inspiratory neurons transmit nerve impulses via the phreni ...
The lymphatic system 33_2
... Albumin and globulins transport substances such as fatty acids, hormones, and vitamins. Albumin also plays an important role in regulating osmotic pressure and blood volume. Some globulins fight viral and bacterial infections. Fibrinogen is necessary for blood to clot. ...
... Albumin and globulins transport substances such as fatty acids, hormones, and vitamins. Albumin also plays an important role in regulating osmotic pressure and blood volume. Some globulins fight viral and bacterial infections. Fibrinogen is necessary for blood to clot. ...
Blood and Lymph
... Albumin and globulins transport substances such as fatty acids, hormones, and vitamins. Albumin also plays an important role in regulating osmotic pressure and blood volume. Some globulins fight viral and bacterial infections. Fibrinogen is necessary for blood to clot. ...
... Albumin and globulins transport substances such as fatty acids, hormones, and vitamins. Albumin also plays an important role in regulating osmotic pressure and blood volume. Some globulins fight viral and bacterial infections. Fibrinogen is necessary for blood to clot. ...
Physiology – spinal anesthesia MGMC
... After lignocaine – 235 minutes After bupivacaine – 462 minutes S3 thin nerve ?? – lot of IV fluids ?? ...
... After lignocaine – 235 minutes After bupivacaine – 462 minutes S3 thin nerve ?? – lot of IV fluids ?? ...
Respiration
... • When this blood reaches lungs: – new O2 will combine with hemoglobin displacing H+ into plasma. – H+ recombines with bicarbonate ion producing H2O and CO2 which diffuses into alveoli to be exhaled ...
... • When this blood reaches lungs: – new O2 will combine with hemoglobin displacing H+ into plasma. – H+ recombines with bicarbonate ion producing H2O and CO2 which diffuses into alveoli to be exhaled ...
Bio 104 Chapter 21: Respiratory System 123
... • _________________are specialized cells that respond to changes in the concentration of a specific chemical § ____PCO2 or H+ concentration triggers hyperventilation § ____PCO2 or H+ concentration triggers hypoventilation § Most sensitive to PO2 in arterial blood ...
... • _________________are specialized cells that respond to changes in the concentration of a specific chemical § ____PCO2 or H+ concentration triggers hyperventilation § ____PCO2 or H+ concentration triggers hypoventilation § Most sensitive to PO2 in arterial blood ...
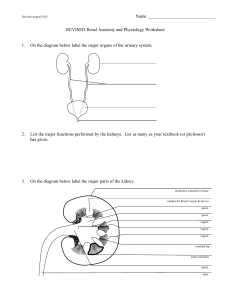
Renal Anatomy and Physiology Worksheet
... cuboidal cells shown in the diagram. So in parts b.-d. at the bottom of the page name the nephron segment(s) composed of the cell type listed. ...
... cuboidal cells shown in the diagram. So in parts b.-d. at the bottom of the page name the nephron segment(s) composed of the cell type listed. ...
Organ Systems - Cloudfront.net
... - used to release energy from nutrients • Heat - form of energy - partly controls rate of metabolic reactions • Pressure - application of force on an object - atmospheric pressure – important for breathing - hydrostatic pressure – keeps blood flowing ...
... - used to release energy from nutrients • Heat - form of energy - partly controls rate of metabolic reactions • Pressure - application of force on an object - atmospheric pressure – important for breathing - hydrostatic pressure – keeps blood flowing ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.