EXTRAEMBRYONIC MEMBRANE
... fetal erythrocytes are Rh-positive but the mother is Rhnegative, the mother’s body can form antibodies to the Rh antigen, which cross the placental barrier and destroy the fetus. The immunological memory of the mother’s immune system means this problem is much greater with second and subsequent preg ...
... fetal erythrocytes are Rh-positive but the mother is Rhnegative, the mother’s body can form antibodies to the Rh antigen, which cross the placental barrier and destroy the fetus. The immunological memory of the mother’s immune system means this problem is much greater with second and subsequent preg ...
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PD A ) - Specialist Veterinary Cardiology
... Most PDA’s are found in young dogs. Often, the only sign of the heart defect is a continuous murmur detected on routine physical exam by a veterinarian. The murmur that is associated with PDA is usually loudest far forward on the left chest wall. Once a murmur is detected in an animal, further diagn ...
... Most PDA’s are found in young dogs. Often, the only sign of the heart defect is a continuous murmur detected on routine physical exam by a veterinarian. The murmur that is associated with PDA is usually loudest far forward on the left chest wall. Once a murmur is detected in an animal, further diagn ...
Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet
... (b) Which glands in the human body release hormones? ...
... (b) Which glands in the human body release hormones? ...
Basics of the Respiratory System General Functions
... conducting airways are removed by a moving staircase of mucus that continually sweeps debris up to the epiglottis, where it is swallowed. The mucus, secreted by mucous glands and also by goblet cells in the bronchial walls, is propelled by millions of tiny cilia, which move rhythmically under normal ...
... conducting airways are removed by a moving staircase of mucus that continually sweeps debris up to the epiglottis, where it is swallowed. The mucus, secreted by mucous glands and also by goblet cells in the bronchial walls, is propelled by millions of tiny cilia, which move rhythmically under normal ...
NSF
... a. They haven’t moved it b. They are free of Cyanosis in fingers or toes c. They are free of arthritis d. Other residents aren’t writing on their cast ...
... a. They haven’t moved it b. They are free of Cyanosis in fingers or toes c. They are free of arthritis d. Other residents aren’t writing on their cast ...
My bone/Muscle project
... food down into smaller molecules that it can process; it also has to excrete waste. Most Digestive organs are tube-like shaped and contains food as it makes it way through the body. The Digestive System is a long, twisting tube that runs from the mouth to the anus plus a few other organs that produc ...
... food down into smaller molecules that it can process; it also has to excrete waste. Most Digestive organs are tube-like shaped and contains food as it makes it way through the body. The Digestive System is a long, twisting tube that runs from the mouth to the anus plus a few other organs that produc ...
Пособие для самостоятельной работы студентов
... constituent of nucleic acid lodged within an outer ...
... constituent of nucleic acid lodged within an outer ...
25.4 Absorption of Water and Mineral Salts by
... o To transport digested food substances form the small intestines to other parts of the body. o To transport carbon dioxide and waste products formed in cells to the excretory organs for removal. o To transport other substances such as enzymes and special chemicals called hormones. ...
... o To transport digested food substances form the small intestines to other parts of the body. o To transport carbon dioxide and waste products formed in cells to the excretory organs for removal. o To transport other substances such as enzymes and special chemicals called hormones. ...
Bio_132_files/respiratory lecture
... • Gas flow is inversely proportional to resistance – The resistance increases as vessel diameter decreases. • This will lead to less gas reaching the alveoli for exchange. • As airway resistance rises, breathing movements become more strenuous ...
... • Gas flow is inversely proportional to resistance – The resistance increases as vessel diameter decreases. • This will lead to less gas reaching the alveoli for exchange. • As airway resistance rises, breathing movements become more strenuous ...
File
... • Ganglia (bunched nerve cells) located in each of the body segments serve to connect the nerve cord with the peripheral nerves, which branch out to remote areas of the earthworm. • This aids in the process of regulation, since the nerve impulses are directed in specific pathways from the receptor o ...
... • Ganglia (bunched nerve cells) located in each of the body segments serve to connect the nerve cord with the peripheral nerves, which branch out to remote areas of the earthworm. • This aids in the process of regulation, since the nerve impulses are directed in specific pathways from the receptor o ...
Human Body Review - Effingham County Schools
... function is to break down food into the nutrients needed to be absorbed into the blood? ...
... function is to break down food into the nutrients needed to be absorbed into the blood? ...
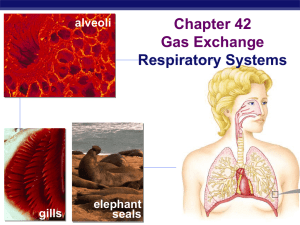
Chapter 14 & 13- Respiration and Immunity
... – Functional units of the respiratory system – Minute sacs where oxygen diffuses from the air into the blood ...
... – Functional units of the respiratory system – Minute sacs where oxygen diffuses from the air into the blood ...
Chapter 23 - Anatomy Freaks
... – Bronchial arteries provide oxygenated systemic blood to lung tissue. They arise from the aorta & run along the branching bronchi. Part of this now deoxygenated blood exits through the bronchial veins to the azygous (drains chest muscles); part merges with blood of alveolar capillaries and returns ...
... – Bronchial arteries provide oxygenated systemic blood to lung tissue. They arise from the aorta & run along the branching bronchi. Part of this now deoxygenated blood exits through the bronchial veins to the azygous (drains chest muscles); part merges with blood of alveolar capillaries and returns ...
Respiration, Circulation & Excretion PowerPoint
... stretch as you inhale and return to their original size as you exhale. • The alveoli still contain a small amount of air after you exhale. ...
... stretch as you inhale and return to their original size as you exhale. • The alveoli still contain a small amount of air after you exhale. ...
molecular physiology
... Renal blood flow Renal blood vessels To perform its function, kidneys are abundantly supplied with blood vessels. Although they constitute less than 0.5% of the total body mass but they receive 20-25% of the resting cardiac output via the renal artery. Renal artery enter the kidney at the pelvis and ...
... Renal blood flow Renal blood vessels To perform its function, kidneys are abundantly supplied with blood vessels. Although they constitute less than 0.5% of the total body mass but they receive 20-25% of the resting cardiac output via the renal artery. Renal artery enter the kidney at the pelvis and ...
Chapter 25
... 25.6 Animals must dispose of nitrogenous wastes • Metabolism produces nitrogenous wastes from the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids • Most aquatic animals dispose of their nitrogenous wastes as ammonia ...
... 25.6 Animals must dispose of nitrogenous wastes • Metabolism produces nitrogenous wastes from the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids • Most aquatic animals dispose of their nitrogenous wastes as ammonia ...
Olfactory Epithelium
... In the lung, the combining of O2 with hemoglobin makes the hemoglobin more acidic and reduces its ability to bind CO2. Additionally, the excess hydrogen ions released because of the greater acidity of hemoglobin become bound to bicarbonate ions, forming carbonic acid. Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes th ...
... In the lung, the combining of O2 with hemoglobin makes the hemoglobin more acidic and reduces its ability to bind CO2. Additionally, the excess hydrogen ions released because of the greater acidity of hemoglobin become bound to bicarbonate ions, forming carbonic acid. Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes th ...
Document
... • Mrs. D has type A blood and is Rh+. So, she has A+ blood. What antigens (ID markers) are carried on her blood? • Mrs. D’s husband has type A- blood. What does this ...
... • Mrs. D has type A blood and is Rh+. So, she has A+ blood. What antigens (ID markers) are carried on her blood? • Mrs. D’s husband has type A- blood. What does this ...
Blood, a more in-depth examination
... – Term for removed blood when composition is unaltered • May be fractionated or separated – Plasma » 46%–63% of blood volume – Hematocrit (or packed cell volume [PCV]) » Percentage of whole blood contributed by formed elements (99% of which are red blood cells) » Average 47% for male (range 40%–54%) ...
... – Term for removed blood when composition is unaltered • May be fractionated or separated – Plasma » 46%–63% of blood volume – Hematocrit (or packed cell volume [PCV]) » Percentage of whole blood contributed by formed elements (99% of which are red blood cells) » Average 47% for male (range 40%–54%) ...
Topic 17: OXYGEN UPTAKE AND TRANSPORT
... Air capillary lungs (fig. 42.25); these lungs lack alveoli but instead have thousands of rigid tubes called air capillaries (or parabronchi) that run the length of the lung. The volume of the lungs never changes. Instead, the lungs are connected to a series of ventilatory structures known as air sac ...
... Air capillary lungs (fig. 42.25); these lungs lack alveoli but instead have thousands of rigid tubes called air capillaries (or parabronchi) that run the length of the lung. The volume of the lungs never changes. Instead, the lungs are connected to a series of ventilatory structures known as air sac ...
Negative Feedback
... move in the opposite direction (so as to return the value toward the correct level) – it is called negative feedback Let’s look at BP again: ...
... move in the opposite direction (so as to return the value toward the correct level) – it is called negative feedback Let’s look at BP again: ...
D - VCOMcc
... B. Cerebral arterioles and arteries show disproportionately myogenic responses with arteries having a greater proportionate response than arterioles. C. Decreased K+o occurs when many action potentials are locally generated. D. NO comes from endothelium, neuronal and glial components. E. pH increase ...
... B. Cerebral arterioles and arteries show disproportionately myogenic responses with arteries having a greater proportionate response than arterioles. C. Decreased K+o occurs when many action potentials are locally generated. D. NO comes from endothelium, neuronal and glial components. E. pH increase ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.