Animals - Killeen ISD
... – Invented by reptiles; Allows for fully living on land – Embryo protected within membranes & shell – Mammals take this a step further by keeping embryo inside the mother (but same idea!) ...
... – Invented by reptiles; Allows for fully living on land – Embryo protected within membranes & shell – Mammals take this a step further by keeping embryo inside the mother (but same idea!) ...
Photosynthesis - Cloudfront.net
... atrium near septum, receives signal from SA node. - The AV node then signals the ventricles to contract - It does this with the aid of special large fibers, called the bundle of His, which terminate in smaller Purkinje Fibers - This allows both ventricles to contract simultaneously and very quickly. ...
... atrium near septum, receives signal from SA node. - The AV node then signals the ventricles to contract - It does this with the aid of special large fibers, called the bundle of His, which terminate in smaller Purkinje Fibers - This allows both ventricles to contract simultaneously and very quickly. ...
Bioenergetics and Cardiorespiratory Unit Test Review Chapter 3
... -Complete Oxygen recovery happens within several minutes of stopping activity. ...
... -Complete Oxygen recovery happens within several minutes of stopping activity. ...
ST120 Respiratory System
... and conditions of the respiratory system including signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options. Demonstrate knowledge of medical terminology related to the respiratory system verbally and in the written form. ...
... and conditions of the respiratory system including signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options. Demonstrate knowledge of medical terminology related to the respiratory system verbally and in the written form. ...
NeoReviewsPlus 2008 - American Academy of Pediatrics
... times more potent than norepinephrine and 100 times more potent than angiotensin I. It acts within seconds after an acute dose, but is degraded within minutes. It acts on the arterioles to cause an increase in total peripheral resistance, and on the veins to augment venous return to the heart. It in ...
... times more potent than norepinephrine and 100 times more potent than angiotensin I. It acts within seconds after an acute dose, but is degraded within minutes. It acts on the arterioles to cause an increase in total peripheral resistance, and on the veins to augment venous return to the heart. It in ...
Microsoft PowerPoint - file [jen pro \350ten\355]
... produce about 300 – 400 litres CO2 per day (~ 15 – 20 mol/d) and this amount may be higher, e.g., with the increase in physical activity. Molecules of carbon dioxide are nonpolar. They freely diffuse across plasma membranes. In tissues, capillary blood CO2 content increases by 40 – 50 ml CO2 / l. Th ...
... produce about 300 – 400 litres CO2 per day (~ 15 – 20 mol/d) and this amount may be higher, e.g., with the increase in physical activity. Molecules of carbon dioxide are nonpolar. They freely diffuse across plasma membranes. In tissues, capillary blood CO2 content increases by 40 – 50 ml CO2 / l. Th ...
Physiology # 2 Dr. Ahmad Dwari Qaisar A. Maaya`h
... Factors that affect GFR 1- Decrease (↓) in the Glomerular capillary filtration coefficient (↓) GFR. (e.g.: chronic uncontrolled hypertension, DM, or chronic kidney disease). So, the filtration membranes are of no efficient filtration of the plasma. 2- Increase (↑) in the Bowman's capsule hydro ...
... Factors that affect GFR 1- Decrease (↓) in the Glomerular capillary filtration coefficient (↓) GFR. (e.g.: chronic uncontrolled hypertension, DM, or chronic kidney disease). So, the filtration membranes are of no efficient filtration of the plasma. 2- Increase (↑) in the Bowman's capsule hydro ...
EVEN/ODD
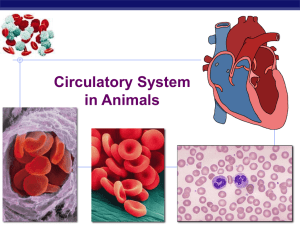
... i. thinner walls than arteries because the pressure of blood is lower in veins ii. they have small flaps in veins keep blood flowing in 1 direction c. Capillaries – thin blood vessels that connect arteries to veins i. very thin walls ii. every tissue has these next to it iii. nutrients, oxygen, and ...
... i. thinner walls than arteries because the pressure of blood is lower in veins ii. they have small flaps in veins keep blood flowing in 1 direction c. Capillaries – thin blood vessels that connect arteries to veins i. very thin walls ii. every tissue has these next to it iii. nutrients, oxygen, and ...
Ch_20_lecture_presentation
... lipids (fatty acids, cholesterol, glycerides), carbohydrates (primarily glucose), and amino acids ...
... lipids (fatty acids, cholesterol, glycerides), carbohydrates (primarily glucose), and amino acids ...
Regents Biology
... likes trees to smaller and smaller arteries At their narrowest vessels are capillaries where materials can be exchanged between cells and the blood Blood flows from small capillaries to small veins which meet up with other small veins to form large veins ...
... likes trees to smaller and smaller arteries At their narrowest vessels are capillaries where materials can be exchanged between cells and the blood Blood flows from small capillaries to small veins which meet up with other small veins to form large veins ...
Ninth Lecture 9. Respiratory system
... Summary of previous lectures In the previous lectures we talked about the basic elements of the medical word: word root, combining form, suffix, and prefix. The meaning of a word is determined by how these elements are combined. Detailed information about suffixes is mentioned. Suffix linking and su ...
... Summary of previous lectures In the previous lectures we talked about the basic elements of the medical word: word root, combining form, suffix, and prefix. The meaning of a word is determined by how these elements are combined. Detailed information about suffixes is mentioned. Suffix linking and su ...
CHAPTER 53: RESPIRATION
... in the brain. It sends signals to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract. This process is ultimately not under direct conscious control, you cannot asphyxiate yourself by holding your breath. The speed and depth of breathing is dependent on the level of CO2 in the blood. Chemoreceptors se ...
... in the brain. It sends signals to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract. This process is ultimately not under direct conscious control, you cannot asphyxiate yourself by holding your breath. The speed and depth of breathing is dependent on the level of CO2 in the blood. Chemoreceptors se ...
History of the Circulatory System
... little doors of the veins’ and proposed that they ‘delay the blood and so prevent the whole of it flowing to the feet…and collecting there’.4 But it was William Harvey (1578-1657) who finally deconstructed the false views of the cardiovascular system. His, “De Motu Cordis”, a short book dedicated to ...
... little doors of the veins’ and proposed that they ‘delay the blood and so prevent the whole of it flowing to the feet…and collecting there’.4 But it was William Harvey (1578-1657) who finally deconstructed the false views of the cardiovascular system. His, “De Motu Cordis”, a short book dedicated to ...
Posterior cardinal veins
... liquid part of the blood to suspended the other components of the blood with in it, including food particles, hormones and waste products from the cells to the liver and kidneys. Rohu fishes blood is approximately 2% of their body weight. ...
... liquid part of the blood to suspended the other components of the blood with in it, including food particles, hormones and waste products from the cells to the liver and kidneys. Rohu fishes blood is approximately 2% of their body weight. ...
Transport System in Mammals
... Oedema may also be associated with kidney or liver disease, or with restricted body movement. At the arterial end of a capillary, blood is under pressure. This forces fluid and small molecules normally found in plasma out through the capillary walls into the intercellular spaces, forming tissue flui ...
... Oedema may also be associated with kidney or liver disease, or with restricted body movement. At the arterial end of a capillary, blood is under pressure. This forces fluid and small molecules normally found in plasma out through the capillary walls into the intercellular spaces, forming tissue flui ...
here - TurkoTek
... - In our bodies,our pipes can change their diameters,meaning they can change their resistance, meaning they can change flow. - Autoregulation- keeps oxygen constant even when metabolic rate changes. * Anytime, flow is from higher to lower pressure. * --- Circulation’s function is to bring all tissue ...
... - In our bodies,our pipes can change their diameters,meaning they can change their resistance, meaning they can change flow. - Autoregulation- keeps oxygen constant even when metabolic rate changes. * Anytime, flow is from higher to lower pressure. * --- Circulation’s function is to bring all tissue ...
Travel Brochure of the Body Systems
... peristalsis, amylase, hydrochloric acid, pepsin, lipase, bile, E. coli, acidic pH ...
... peristalsis, amylase, hydrochloric acid, pepsin, lipase, bile, E. coli, acidic pH ...
DIVERSITY NOTES
... 1. Capitalize 1st letter of genus name 2. Underline genus and species names 3. 1st use of name must be written out in each paragraph 4. After 1st use - abbreviate genus name to 1st letter: H. sapiens F. domesticus ...
... 1. Capitalize 1st letter of genus name 2. Underline genus and species names 3. 1st use of name must be written out in each paragraph 4. After 1st use - abbreviate genus name to 1st letter: H. sapiens F. domesticus ...
Heart Dissection Lab File
... Front or Ventral Side of the Heart 1. Locate the following chambers of the heart from this surface: Left atria - upper chamber to your right Left ventricle - lower chamber to your right Right atria - upper chamber to your left Right ventricle - lower chamber to your left 2. While the heart ...
... Front or Ventral Side of the Heart 1. Locate the following chambers of the heart from this surface: Left atria - upper chamber to your right Left ventricle - lower chamber to your right Right atria - upper chamber to your left Right ventricle - lower chamber to your left 2. While the heart ...
The Powerpoint - helpmemrr.com
... and the interstitial fluid occurs across the thin walls of capillaries • At any given time, only about 5-10% of the body’s capillaries have blood flowing through them. • Capillaries in the brain, heart, kidneys, and liver are usually filled to capacity, but in many other sites, the blood supply vari ...
... and the interstitial fluid occurs across the thin walls of capillaries • At any given time, only about 5-10% of the body’s capillaries have blood flowing through them. • Capillaries in the brain, heart, kidneys, and liver are usually filled to capacity, but in many other sites, the blood supply vari ...
Blood - Images
... • Mrs. D has type A blood and is Rh+. So, she has A+ blood. What antigens (ID markers) are carried on her blood? • Mrs. D’s husband has type A- blood. What does this ...
... • Mrs. D has type A blood and is Rh+. So, she has A+ blood. What antigens (ID markers) are carried on her blood? • Mrs. D’s husband has type A- blood. What does this ...
Chapter 21 - Coastal Bend College
... increases BP below the level of the heart & decreases BP above the level of the heart. ...
... increases BP below the level of the heart & decreases BP above the level of the heart. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.



![Microsoft PowerPoint - file [jen pro \350ten\355]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016060961_1-556381e0739da94672054efd0d08e475-300x300.png)