Respiratory and Circulation Systems of the Human Body
... Mouth/Oral Cavity- Oxygen/air can also enter through your Mouth but it is not filtered. Your Mouth opens up into your Oral Cavity. Sinus- A cavity in the bones of your skull that helps moisten and heat the air that you breath. Pharynx/Throat- Gathers air from your Nasal and Oral Cavities and passes ...
... Mouth/Oral Cavity- Oxygen/air can also enter through your Mouth but it is not filtered. Your Mouth opens up into your Oral Cavity. Sinus- A cavity in the bones of your skull that helps moisten and heat the air that you breath. Pharynx/Throat- Gathers air from your Nasal and Oral Cavities and passes ...
The Human Body: Systems Working Together
... body. Organ systems include the nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system. What is the role of the endocrine system in the body? • A. It gets rid of wastes that the body produces. • B. It uses electrical signals to control body functions. • C. It uses chemical messages to control body ...
... body. Organ systems include the nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system. What is the role of the endocrine system in the body? • A. It gets rid of wastes that the body produces. • B. It uses electrical signals to control body functions. • C. It uses chemical messages to control body ...
Excretion and osmoregulation in earthworm
... form and tissues remain healthy • Leeches were used hundreds of years in medicine to take blood out of patients whose diseases were mistakenly believed to be caused by excess blood • Freshwater leeches live as external parasites and suck their blood • Earthworms are a source of food for numerous ani ...
... form and tissues remain healthy • Leeches were used hundreds of years in medicine to take blood out of patients whose diseases were mistakenly believed to be caused by excess blood • Freshwater leeches live as external parasites and suck their blood • Earthworms are a source of food for numerous ani ...
Primary Function of the Lung
... cells), and the cells. Inside the cell, cellular respiration generates energy (ATP), using O2 and glucose and producing waste CO2. ...
... cells), and the cells. Inside the cell, cellular respiration generates energy (ATP), using O2 and glucose and producing waste CO2. ...
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... thoracic walls, a rise in O2 level, and a decrease in CO2 and H+ levels; while normal breathing is stimulated by relaxing of the lungs and thoracic walls, a decrease in O2 level, and a rise in CO2 and H+ levels. ...
... thoracic walls, a rise in O2 level, and a decrease in CO2 and H+ levels; while normal breathing is stimulated by relaxing of the lungs and thoracic walls, a decrease in O2 level, and a rise in CO2 and H+ levels. ...
module 3 3.1.1 exchange surfaces
... and has 2 stacks of thin lamellae which lie on top of each other like pages in a book. • The lamellae need to be kept apart by water to prevent them sticking together. • The upper and lower surface of each lamellae have projections called gill plates, these increase the surface area further. ...
... and has 2 stacks of thin lamellae which lie on top of each other like pages in a book. • The lamellae need to be kept apart by water to prevent them sticking together. • The upper and lower surface of each lamellae have projections called gill plates, these increase the surface area further. ...
Body System Show 3
... ones are organs of excretion and which ones are organs of elimination? • Lungs, skin, kidneys- excretion • Large Intestine/ anus- elimination ...
... ones are organs of excretion and which ones are organs of elimination? • Lungs, skin, kidneys- excretion • Large Intestine/ anus- elimination ...
active vocabulary - Минусинский медицинский техникум
... When infection occurs, inflammation results, and part of this defensive reaction involves antibodies and antitoxins. They are present in the blood and help overcome the microorganisms concerned. Some of these antibodies and antitoxins can remain in the blood for life and prevent any repetition of th ...
... When infection occurs, inflammation results, and part of this defensive reaction involves antibodies and antitoxins. They are present in the blood and help overcome the microorganisms concerned. Some of these antibodies and antitoxins can remain in the blood for life and prevent any repetition of th ...
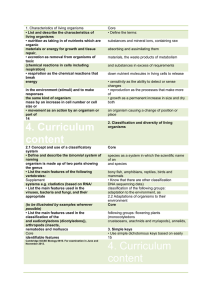
1. Characteristics of living organisms Core • List and describe the
... Supplement microscope in the plant cell and in the animal 2. Levels of organisation • Relate the structure of the following to their • ciliated cells – in respiratory tract • xylem vessels – conduction and support • red blood cells – transport • tissue as a group of cells with similar ...
... Supplement microscope in the plant cell and in the animal 2. Levels of organisation • Relate the structure of the following to their • ciliated cells – in respiratory tract • xylem vessels – conduction and support • red blood cells – transport • tissue as a group of cells with similar ...
Animal Form and Function
... produces the characteristic “lub-dup” sounds of the heart. Hydrostatic pressure created by the heart forces blood to move through the arteries. As blood reaches the capillaries, however, blood pressure drops dramatically and approaches zero in the venules. Blood continues to move through the veins, ...
... produces the characteristic “lub-dup” sounds of the heart. Hydrostatic pressure created by the heart forces blood to move through the arteries. As blood reaches the capillaries, however, blood pressure drops dramatically and approaches zero in the venules. Blood continues to move through the veins, ...
Forensic Science
... presence of drugs and poisons in body fluids, tissues, and organs. •Toxicologists not only work in crime laboratories and medical examiners’ offices, but may also reach into hospital laboratories and health facilities to identify a drug overdose or monitor the intake of drugs. •A major branch of for ...
... presence of drugs and poisons in body fluids, tissues, and organs. •Toxicologists not only work in crime laboratories and medical examiners’ offices, but may also reach into hospital laboratories and health facilities to identify a drug overdose or monitor the intake of drugs. •A major branch of for ...
Anatomy Workbook - Wright Wonders
... Functional classification is based upon the amount of movement available and structural classification is based on the presence / absence of a synovial cavity (a space between the articulating bones) and the kind of tissue that bonds the bones together. Fixed or fibrous joints A fibrous joint has n ...
... Functional classification is based upon the amount of movement available and structural classification is based on the presence / absence of a synovial cavity (a space between the articulating bones) and the kind of tissue that bonds the bones together. Fixed or fibrous joints A fibrous joint has n ...
Lung Volumes and Capacities
... oxygen uptake in the lungs and carbon dioxide production can differ from elimination in the lungs, but within a short time these imbalances automatically produce changes in diffusion gradients in the lungs and tissues that reestablish steady-state balances. The amounts of oxygen consumed by cells an ...
... oxygen uptake in the lungs and carbon dioxide production can differ from elimination in the lungs, but within a short time these imbalances automatically produce changes in diffusion gradients in the lungs and tissues that reestablish steady-state balances. The amounts of oxygen consumed by cells an ...
My Body - Rocky River
... intestines, stomach, and you esophagus. When you’re eating food it doesn’t just go from your mouth to your stomach. It has a very complicated system. The digestive system has the Important job of digesting your food. As soon as the food reaches you’re mouth salvia appears in your mouth. It may seem ...
... intestines, stomach, and you esophagus. When you’re eating food it doesn’t just go from your mouth to your stomach. It has a very complicated system. The digestive system has the Important job of digesting your food. As soon as the food reaches you’re mouth salvia appears in your mouth. It may seem ...
1 category question correct answer your answer
... A) Glycogen metabolism traps glucose within liver cells and increases storage of glucose in the form of glycogen. These processes decrease blood glucose levels. A) Glycogen metabolism traps glucose within liver cells and increases storage of glucose in the form of glycogen. These processes decrease ...
... A) Glycogen metabolism traps glucose within liver cells and increases storage of glucose in the form of glycogen. These processes decrease blood glucose levels. A) Glycogen metabolism traps glucose within liver cells and increases storage of glucose in the form of glycogen. These processes decrease ...
Fundamental Principles of Gas Exchangers
... can maintain high O2-to-CO2 exchange ratio in relation to their body mass can generate high and stable tissue-fluid gas concentrations under different environmental conditions and metabolic states. Ecologically, they are the most successful ones. Predator avoidance, survival, and self-perpetuation m ...
... can maintain high O2-to-CO2 exchange ratio in relation to their body mass can generate high and stable tissue-fluid gas concentrations under different environmental conditions and metabolic states. Ecologically, they are the most successful ones. Predator avoidance, survival, and self-perpetuation m ...
the body in motion
... muscle to shorten, lengthen or remain the same length. This is known as muscle contraction. In those cases where movement results the repeated contraction shortens the muscles’ length. The tendons of the shortened muscle pull on the bones in the direction of the contraction and this produces movemen ...
... muscle to shorten, lengthen or remain the same length. This is known as muscle contraction. In those cases where movement results the repeated contraction shortens the muscles’ length. The tendons of the shortened muscle pull on the bones in the direction of the contraction and this produces movemen ...
file - Athens Academy
... The Abdominal Cavity The liver, the largest organ in the abdominal cavity, has a multitude of functions, most of which are underappreciated. For example, in the fetus, blood cell production takes place in the liver as well as the bone marrow. In the adult, the liver: ...
... The Abdominal Cavity The liver, the largest organ in the abdominal cavity, has a multitude of functions, most of which are underappreciated. For example, in the fetus, blood cell production takes place in the liver as well as the bone marrow. In the adult, the liver: ...
Circulation and Gas Exchange
... MOIST membranes Close spacing of gas and blood for easy diffusion High surface area-to-volume ratio An animal’s respiratory surfaces must be large enough to provide oxygen and expel carbon dioxide for the entire body ...
... MOIST membranes Close spacing of gas and blood for easy diffusion High surface area-to-volume ratio An animal’s respiratory surfaces must be large enough to provide oxygen and expel carbon dioxide for the entire body ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.