Cardiovascular System, Respiratory System
... Respiratory system Embryology: development of the face, nasal cavity, sinuses and respiratory system. Anatomy: nasal cavity and sinuses, pharynx, larynx, thoracic wall and diaphragm, thoracic cavity with the topography of the mediastinum, main tracheae and bronchia, pleural cavities, lungs, surface ...
... Respiratory system Embryology: development of the face, nasal cavity, sinuses and respiratory system. Anatomy: nasal cavity and sinuses, pharynx, larynx, thoracic wall and diaphragm, thoracic cavity with the topography of the mediastinum, main tracheae and bronchia, pleural cavities, lungs, surface ...
Document
... Hemoglobin – oxygen-carrying protein the function of hemoglobin is to attract oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules to increase the carrying capacity of blood (plasma also carries these gases but not in adequate quantities) Biconcave shape – 30% more surface area ...
... Hemoglobin – oxygen-carrying protein the function of hemoglobin is to attract oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules to increase the carrying capacity of blood (plasma also carries these gases but not in adequate quantities) Biconcave shape – 30% more surface area ...
Body Systems Web Unit Worksheets
... 3. Make a chart (or print the Blood Chart) and beside each job, write which type of blood cell does that job. Carry oxygen or food to your lungs Find germs Eat foreign things in your body Take carbon dioxide or waste away Kill infections 4. BONUS: Blood is made up of four parts (red blood ...
... 3. Make a chart (or print the Blood Chart) and beside each job, write which type of blood cell does that job. Carry oxygen or food to your lungs Find germs Eat foreign things in your body Take carbon dioxide or waste away Kill infections 4. BONUS: Blood is made up of four parts (red blood ...
Concepts and functions - Pécsi Tudományegyetem
... body with a web-like network of capillaries connecting them. Arteries use vessel size, controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, to move blood by pressure; veins use one-way valves controlled by muscle contractions. Arteries are strong, elastic vessels adapted for carrying blood away from the he ...
... body with a web-like network of capillaries connecting them. Arteries use vessel size, controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, to move blood by pressure; veins use one-way valves controlled by muscle contractions. Arteries are strong, elastic vessels adapted for carrying blood away from the he ...
4. Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration PDF File
... This type of respiration can only be used for short bursts. Examples of sport that require anaerobic respiration are: 100m sprinting and Netball. Interval training is an anaerobic training method. A lot of games activities will require both types of respiration: Aerobic to keep playing for a long pe ...
... This type of respiration can only be used for short bursts. Examples of sport that require anaerobic respiration are: 100m sprinting and Netball. Interval training is an anaerobic training method. A lot of games activities will require both types of respiration: Aerobic to keep playing for a long pe ...
Control of Respiration
... called the apneustic center is the major source of this output, whereas an area of the upper pons called the pneumotaxic center modulates the activity of the apneustic center. Another cutoff signal for inspiration comes from pulmonary stretch receptors, which lie in the airway smooth-muscle layer an ...
... called the apneustic center is the major source of this output, whereas an area of the upper pons called the pneumotaxic center modulates the activity of the apneustic center. Another cutoff signal for inspiration comes from pulmonary stretch receptors, which lie in the airway smooth-muscle layer an ...
MD0542 1-1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE 542 The
... a. The veins of the systemic blood circulatory system bring oxygen-poor blood from all parts of the body to the right atrium of the heart. From the right atrium, the blood flows into the right ventricle of the heart. Upon contraction of the right ventricle, blood is forced into the pulmonary arch. T ...
... a. The veins of the systemic blood circulatory system bring oxygen-poor blood from all parts of the body to the right atrium of the heart. From the right atrium, the blood flows into the right ventricle of the heart. Upon contraction of the right ventricle, blood is forced into the pulmonary arch. T ...
The Human Body: An Orientation
... Nutrients and wastes pass between blood and cells via the interstitial fluid ...
... Nutrients and wastes pass between blood and cells via the interstitial fluid ...
Student Background Information 1C
... Observing carefully, attempt to arrange the lung layers in the correct order. Each part of the respiratory system is designed for the specific job it does and you can often guess what the job is by observing – you will be surprised at what you can do when you take time to observe and think about wha ...
... Observing carefully, attempt to arrange the lung layers in the correct order. Each part of the respiratory system is designed for the specific job it does and you can often guess what the job is by observing – you will be surprised at what you can do when you take time to observe and think about wha ...
Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE
... to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps blood through a circuit that includes arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins. One important circuit is the pulmonary circuit, where there is an exchange of gases within the alveoli of the lungs. The right side of the human heart received deo ...
... to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps blood through a circuit that includes arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins. One important circuit is the pulmonary circuit, where there is an exchange of gases within the alveoli of the lungs. The right side of the human heart received deo ...
Respiration
... The main transport pigment is hemoglobin (are proteins) Each molecule of hemoglobin binds 4 molecules of oxygen in the lungs (high concentration) and releases them in the tissues where oxygen is low Myoglobin is another iron-containing respiratory, which is a ...
... The main transport pigment is hemoglobin (are proteins) Each molecule of hemoglobin binds 4 molecules of oxygen in the lungs (high concentration) and releases them in the tissues where oxygen is low Myoglobin is another iron-containing respiratory, which is a ...
AP resp
... body inward The openings are called spiracles. The trachea are extensively branched into tracheoles which takes air directly to individual cells. ...
... body inward The openings are called spiracles. The trachea are extensively branched into tracheoles which takes air directly to individual cells. ...
6b Resp System II-BreathingGasExch
... *Perfusion is the ability of blood to flow through tissues. ...
... *Perfusion is the ability of blood to flow through tissues. ...
How Air Moves In and Out of the Lung
... . Which of the statements below gives the best definition of gas exchange? :d) exchanging oxygen for carbon dioxide in the lung alveoli. 10. Which of the following help the lungs to be such good gas exchange organs? (Choose at least 4). They have a large surface area. The air in the alveoli and bloo ...
... . Which of the statements below gives the best definition of gas exchange? :d) exchanging oxygen for carbon dioxide in the lung alveoli. 10. Which of the following help the lungs to be such good gas exchange organs? (Choose at least 4). They have a large surface area. The air in the alveoli and bloo ...
O 2
... a partial pressure of gas of 100 mmHg; the breakers at right show the conditions after equilibration, when the gas has dissolved in the water until the gas’s partial pressure in both media are equal. (a) After equilibration, the concentration of O2 in water is much less than its concentration in air ...
... a partial pressure of gas of 100 mmHg; the breakers at right show the conditions after equilibration, when the gas has dissolved in the water until the gas’s partial pressure in both media are equal. (a) After equilibration, the concentration of O2 in water is much less than its concentration in air ...
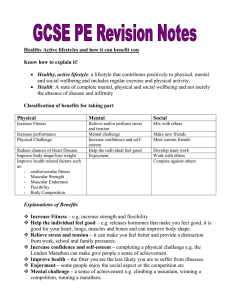
GCSE Revision bookle..
... To improve or work aerobically a person needs to work between 60%-80% of their maximum heart rate. To work more anaerobically a person needs to work at above 80% of there Maximum heart rate. E.g. a 20 year old would have a maximum heart rate of 200 bpm. To improve their target heart they need to wor ...
... To improve or work aerobically a person needs to work between 60%-80% of their maximum heart rate. To work more anaerobically a person needs to work at above 80% of there Maximum heart rate. E.g. a 20 year old would have a maximum heart rate of 200 bpm. To improve their target heart they need to wor ...
chapter 1
... 12. Eosinophils are granulocytic white blood cells that help protect the body from irritants that cause allergies. They are also capable of phagocytosis. Basophils also function in allergic reactions. They secrete a number of important chemicals, such as heparin, which help prevent the formation of ...
... 12. Eosinophils are granulocytic white blood cells that help protect the body from irritants that cause allergies. They are also capable of phagocytosis. Basophils also function in allergic reactions. They secrete a number of important chemicals, such as heparin, which help prevent the formation of ...
Biology
... Drinking reduces blood osmolarity to set point ADH Increased permeability Pituitary gland Distal tubule ...
... Drinking reduces blood osmolarity to set point ADH Increased permeability Pituitary gland Distal tubule ...
Pressure
... vessels, lymphatics, and nerves enter the lungs. • Each lung is enclosed by a double-layered serous membrane, called the pleura. The visceral pleura is firmly attached to the surface of the lung. At the hilum, the visceral pleura is continuous with the parietal pleura that lines the wall of the thor ...
... vessels, lymphatics, and nerves enter the lungs. • Each lung is enclosed by a double-layered serous membrane, called the pleura. The visceral pleura is firmly attached to the surface of the lung. At the hilum, the visceral pleura is continuous with the parietal pleura that lines the wall of the thor ...
Gas Exchange
... • PO2 and PCO2 vary within the circulatory system – Blue and red vessels – Lungs: high O2, low CO2 – Body tissues: low O2, high CO2 ...
... • PO2 and PCO2 vary within the circulatory system – Blue and red vessels – Lungs: high O2, low CO2 – Body tissues: low O2, high CO2 ...
42 BIOLOGY 1. Circulation in the Animal Kingdom
... Blood flows through only 5–10% of the body’s capillaries at any given time Capillaries in major organs are usually filled to capacity Blood supply varies in many other sites Two mechanisms regulate distribution of blood in capillary beds Constriction or dilation of arterioles that supply c ...
... Blood flows through only 5–10% of the body’s capillaries at any given time Capillaries in major organs are usually filled to capacity Blood supply varies in many other sites Two mechanisms regulate distribution of blood in capillary beds Constriction or dilation of arterioles that supply c ...
UNIT 8 NOTES - Adirondack Central School District
... Those of you going on to college for anything in the medical field will have to take a course called A&P, Anatomy and Physiology. This is where you learn how you are built and how you work. Depending on where you go to school some of you may use cats in your lab to dissect, and others will have cada ...
... Those of you going on to college for anything in the medical field will have to take a course called A&P, Anatomy and Physiology. This is where you learn how you are built and how you work. Depending on where you go to school some of you may use cats in your lab to dissect, and others will have cada ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.