Quantitative Analysis of the Kinetics of End
... structure. The ATP concentration is maintained at high levels so that each DNA-bound RecA monomer is functioning at its kcat. The kcat employed is that observed in the presence of longer random sequence ssDNA molecules. Under conditions used in this series of experiments, the kcat for ATP hydrolysis ...
... structure. The ATP concentration is maintained at high levels so that each DNA-bound RecA monomer is functioning at its kcat. The kcat employed is that observed in the presence of longer random sequence ssDNA molecules. Under conditions used in this series of experiments, the kcat for ATP hydrolysis ...
Comparative genomics of unintrogressed Campylobacter coli clades 2 and 3
... found in poultry and ruminants, whereas C. coli colonizes pigs more frequently. Nevertheless, C. coli is also found in poultry, and it has been suggested that the populations circulating in these animal species are different [12]. Phylogenetic analyses by Sheppard et al. [13,14] have shown that C. c ...
... found in poultry and ruminants, whereas C. coli colonizes pigs more frequently. Nevertheless, C. coli is also found in poultry, and it has been suggested that the populations circulating in these animal species are different [12]. Phylogenetic analyses by Sheppard et al. [13,14] have shown that C. c ...
Document
... …appears to be able to replicate itself… …is not a bacteria! …is smaller than a virus? …is not a virus! …contains genetic information! …structurally like the “guts”of a virus! ...
... …appears to be able to replicate itself… …is not a bacteria! …is smaller than a virus? …is not a virus! …contains genetic information! …structurally like the “guts”of a virus! ...
Organization and Integration of Large-scale Datasets for
... Mycoplasma pneumoniae, one of the smallest known self-replicating organisms, is a promising model organism in systems biology when aiming to assess understanding of an entire living cell. One of the key steps towards this goal is the design of mathematical models that describe the cellular processes ...
... Mycoplasma pneumoniae, one of the smallest known self-replicating organisms, is a promising model organism in systems biology when aiming to assess understanding of an entire living cell. One of the key steps towards this goal is the design of mathematical models that describe the cellular processes ...
Organization and Integration of Large
... Mycoplasma pneumoniae, one of the smallest known self-replicating organisms, is a promising model organism in systems biology when aiming to assess understanding of an entire living cell. One of the key steps towards this goal is the design of mathematical models that describe the cellular processes ...
... Mycoplasma pneumoniae, one of the smallest known self-replicating organisms, is a promising model organism in systems biology when aiming to assess understanding of an entire living cell. One of the key steps towards this goal is the design of mathematical models that describe the cellular processes ...
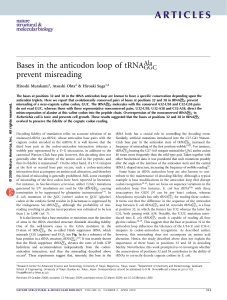
ARTICLES
... canonical Watson-Click base pair, however, this decoding does not generally alter the identity of the amino acid in the peptide, and thus its fidelity is maintained1. On the other hand, if a U G mispair at the first or second base pair occurs, such a codon-anticodon interaction does accompany an ami ...
... canonical Watson-Click base pair, however, this decoding does not generally alter the identity of the amino acid in the peptide, and thus its fidelity is maintained1. On the other hand, if a U G mispair at the first or second base pair occurs, such a codon-anticodon interaction does accompany an ami ...
Biomolecules
... • **In proteins, the specific order of amino acid monomers in a polypeptide interacts with the environment to determine the overall shape of the protein. ...
... • **In proteins, the specific order of amino acid monomers in a polypeptide interacts with the environment to determine the overall shape of the protein. ...
From Sequence to Structure
... isolation, or the cellular function it performs as part of an assemblage or complex with other molecules, or the phenotype it produces in the cell or organism. Major examples of the biochemical functions of proteins include binding; catalysis; operating as molecular switches; and serving as structur ...
... isolation, or the cellular function it performs as part of an assemblage or complex with other molecules, or the phenotype it produces in the cell or organism. Major examples of the biochemical functions of proteins include binding; catalysis; operating as molecular switches; and serving as structur ...
Multiple Lines of Evidence Localize Signaling
... thaliana), we integrated a quantitative mass spectrometry analysis of highly enriched and prefractionated samples with a number of confirmatory biochemical and cell biology approaches. This approach identified 42 proteins, 27 of which were novel, more than doubling the number of confirmed outer memb ...
... thaliana), we integrated a quantitative mass spectrometry analysis of highly enriched and prefractionated samples with a number of confirmatory biochemical and cell biology approaches. This approach identified 42 proteins, 27 of which were novel, more than doubling the number of confirmed outer memb ...
Role of adiponectin in the regulation of carbohydrate and lipid
... REGULATION OF ADIPONECTIN GENE EXPRESSION Regulation of adiponectin gene expression remains to be elucidated. Several studies have shown that adiponectin is induced during adipocyte differentiation and its secretion is stimulated by insulin (1, 4, 16). It has also been observed that IGF-1 ...
... REGULATION OF ADIPONECTIN GENE EXPRESSION Regulation of adiponectin gene expression remains to be elucidated. Several studies have shown that adiponectin is induced during adipocyte differentiation and its secretion is stimulated by insulin (1, 4, 16). It has also been observed that IGF-1 ...
53 - Lab Times
... att-sequences. Once cloned into this Gateway entry clone vector, DNA segments can be rapidly transferred into diverse Gateway expression vectors via a similar Clonasebased reaction. In recent years, a couple of labs have established extensive collections of ORF clones created by Gateway cloning cont ...
... att-sequences. Once cloned into this Gateway entry clone vector, DNA segments can be rapidly transferred into diverse Gateway expression vectors via a similar Clonasebased reaction. In recent years, a couple of labs have established extensive collections of ORF clones created by Gateway cloning cont ...
Structure-Based Prediction of Asparagine and Aspartate
... which is essential for the development of a drug candidate into a marketed product. Therapeutic proteins may degrade via asparagine (Asn) deamidation and aspartate (Asp) isomerization, but the factors responsible for such degradation remain poorly understood. We studied the structural properties of ...
... which is essential for the development of a drug candidate into a marketed product. Therapeutic proteins may degrade via asparagine (Asn) deamidation and aspartate (Asp) isomerization, but the factors responsible for such degradation remain poorly understood. We studied the structural properties of ...
Identification and characterization of novel interaction
... C-terminal domain of the α subunit of the RNA polymerase C-terminal domain of the α subunit of the RNA polymerase Adenosindiphosphate Ampicillin Adenosinmomophosphate Ammoniumperoxodisulfate Adenosintriphosphate Bacillus base pair bovine serum albumin casamino acids cyclic Adenosinmomophosphate Cata ...
... C-terminal domain of the α subunit of the RNA polymerase C-terminal domain of the α subunit of the RNA polymerase Adenosindiphosphate Ampicillin Adenosinmomophosphate Ammoniumperoxodisulfate Adenosintriphosphate Bacillus base pair bovine serum albumin casamino acids cyclic Adenosinmomophosphate Cata ...
Recycling of vitamin B12 and NAD+ within the Pdu
... the intermediate propionaldehyde formed in the first step of 1,2-PD degradation in order to mitigate its toxicity and prevent DNA damage. Several sequentially-acting metabolic enzymes, ...
... the intermediate propionaldehyde formed in the first step of 1,2-PD degradation in order to mitigate its toxicity and prevent DNA damage. Several sequentially-acting metabolic enzymes, ...
IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SYNAPTONEMAL
... Meiosis consists of two successive cell divisions, meiosis I and II. After premeiotic S-phase, during the prophase of meiosis I, a series of chromatin rearrangements takes place by which homologous chromosomes condense, pair, recombine and segregate; the result is that at meiosis I diploid cells div ...
... Meiosis consists of two successive cell divisions, meiosis I and II. After premeiotic S-phase, during the prophase of meiosis I, a series of chromatin rearrangements takes place by which homologous chromosomes condense, pair, recombine and segregate; the result is that at meiosis I diploid cells div ...
The Major Component of the Paraflagellar Rod of Trypanosoma
... similarity to the intermediate filament proteins (solubility properties, amino acid composition, and high degree of helicity), the PFR protein does not belong in this class of cytoskeletal proteins. The PFR protein is coded for by two tandemly linked genes of identical nucleotide sequence. Both gene ...
... similarity to the intermediate filament proteins (solubility properties, amino acid composition, and high degree of helicity), the PFR protein does not belong in this class of cytoskeletal proteins. The PFR protein is coded for by two tandemly linked genes of identical nucleotide sequence. Both gene ...
The Plant Cell
... There is little evidence for the function of the MATE genes in eukaryotes beyond the sequence similarities with other family members. The function of the yeast ERC1 MATE gene has been inferred from the ethionine resistance phenotype conferred when ERC1 is expressed from a multicopy plasmid (Shiomi e ...
... There is little evidence for the function of the MATE genes in eukaryotes beyond the sequence similarities with other family members. The function of the yeast ERC1 MATE gene has been inferred from the ethionine resistance phenotype conferred when ERC1 is expressed from a multicopy plasmid (Shiomi e ...
Glucosamine-Induced Insulin Resistance in Primary Rat
... 142g/day (Felig, Marliss et al. 1969; Gottstein 1979). The second reason for regulating glucose concentration is that glucose is toxic. The amount of glucose in the bloodstream is tightly regulated by actions of insulin and glucagon during fed and fasting states (Flakoll PJ 2000). Insulin, a hormon ...
... 142g/day (Felig, Marliss et al. 1969; Gottstein 1979). The second reason for regulating glucose concentration is that glucose is toxic. The amount of glucose in the bloodstream is tightly regulated by actions of insulin and glucagon during fed and fasting states (Flakoll PJ 2000). Insulin, a hormon ...
Cyclic-‐di-‐AMP: another second messenger enters the fray
... The DAC domain bears no amino acid or structural similarity to the c-‐di-‐ GMP cyclase GGDEF domain (Pfam00990). The observation that evolutionarily unrelated proteins have evolved for the synthesis ...
... The DAC domain bears no amino acid or structural similarity to the c-‐di-‐ GMP cyclase GGDEF domain (Pfam00990). The observation that evolutionarily unrelated proteins have evolved for the synthesis ...
New peptide and gene coding for same
... al., Biochemistry 18, 5294-5299, 1979), and enriched for poly (A)+ RNA (mRNA) with an oligo (dT) cellulose column. The poly (A) RNA were used to prepare a cDNA library according to the Okayama-Berg method (Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 161-170, 1982). The library was screened with a mixture of probes consisti ...
... al., Biochemistry 18, 5294-5299, 1979), and enriched for poly (A)+ RNA (mRNA) with an oligo (dT) cellulose column. The poly (A) RNA were used to prepare a cDNA library according to the Okayama-Berg method (Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 161-170, 1982). The library was screened with a mixture of probes consisti ...
Interactions of TCA cycle enzymes and of the CcpA
... carbon sources and NADP . Excess of α-ketoglutarate can be applied to amino acid anabolism, since αketoglutarate is the precursor molecule of glutamate. No interaction was detected between Mdh and CitZ by SPR even in the presence of the corresponding metabolites. This result was surprising, because ...
... carbon sources and NADP . Excess of α-ketoglutarate can be applied to amino acid anabolism, since αketoglutarate is the precursor molecule of glutamate. No interaction was detected between Mdh and CitZ by SPR even in the presence of the corresponding metabolites. This result was surprising, because ...
A systems biology approach sheds new light on the regulation of
... In my years in Birmingham I had the pleasure to meet many friends and co-workers. I would like to thank them for being there to support me and I am sorry if I cannot mention all of them in this page. However, they will always be in my thoughts. The most special thanks are for my supervisor, Dr Franc ...
... In my years in Birmingham I had the pleasure to meet many friends and co-workers. I would like to thank them for being there to support me and I am sorry if I cannot mention all of them in this page. However, they will always be in my thoughts. The most special thanks are for my supervisor, Dr Franc ...
Attachment 1 - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... that the transferred gene is stably integrated into the plant genome as a single copy at one insertion site, and is inherited in subsequent generations according to predicted patterns of inheritance. There was no transfer of bacterial antibiotic resistance marker genes in this modification. The EPSP ...
... that the transferred gene is stably integrated into the plant genome as a single copy at one insertion site, and is inherited in subsequent generations according to predicted patterns of inheritance. There was no transfer of bacterial antibiotic resistance marker genes in this modification. The EPSP ...
Distinct C-terminal Amino Acid Sequence Motifs Serve
... me, a strong work ethic that has allowed me to excel in my studies. I can never express enough gratitude towards these individuals, and everyone who has helped me reach this point. All of the data presented in this thesis was generated by Howard Teresinski and a portion of this thesis is published i ...
... me, a strong work ethic that has allowed me to excel in my studies. I can never express enough gratitude towards these individuals, and everyone who has helped me reach this point. All of the data presented in this thesis was generated by Howard Teresinski and a portion of this thesis is published i ...
Genetic tools for manipulating Acinetobacter baumannii genome: an
... as a temperature-sensitive replicon. The vector must also carry a selectable marker, usually an antibiotic resistance gene. Sometimes integration vectors also contain oriT so that the construct can be transferred to other bacteria by conjugation. This is especially helpful when the other transfer me ...
... as a temperature-sensitive replicon. The vector must also carry a selectable marker, usually an antibiotic resistance gene. Sometimes integration vectors also contain oriT so that the construct can be transferred to other bacteria by conjugation. This is especially helpful when the other transfer me ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.