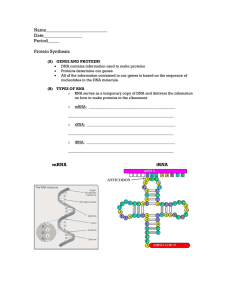
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
From Gene to Protein
... • 4 nucleotide bases cannot independently code for 20 different AA • Pairs of bases would only account for 16 AA • Triplet bases would give us 64 possible AA that could be coded, exceeding the required amount necessary ...
... • 4 nucleotide bases cannot independently code for 20 different AA • Pairs of bases would only account for 16 AA • Triplet bases would give us 64 possible AA that could be coded, exceeding the required amount necessary ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
... Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
HANDOUT: CH 17 pt 1 Study
... a) What is the purpose of the mRNA codon: AUG? b) What is the purpose of the 3 triplets that do not code for an amino acid? 8) Complete the chart below summarizing the changes made to a pre-mRNA molecule in eukaryotes. (HINT: see notes!) mRNA end Description of modification ...
... a) What is the purpose of the mRNA codon: AUG? b) What is the purpose of the 3 triplets that do not code for an amino acid? 8) Complete the chart below summarizing the changes made to a pre-mRNA molecule in eukaryotes. (HINT: see notes!) mRNA end Description of modification ...
Gene Expression Vocabulary
... 7. Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that acts as a “start” signal for transcription 8. Terminator: a sequence of bases that tells the RNA polymerase to stop adding nucleotides 9. Messenger RNA: carries hereditary information from DNA and delivers it to the site of translation 10. Transfer RNA: a ...
... 7. Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that acts as a “start” signal for transcription 8. Terminator: a sequence of bases that tells the RNA polymerase to stop adding nucleotides 9. Messenger RNA: carries hereditary information from DNA and delivers it to the site of translation 10. Transfer RNA: a ...
Chapter 7 Biology
... • Scientists whom are famed to have discovered the double helix structure of DNA ...
... • Scientists whom are famed to have discovered the double helix structure of DNA ...
Biology Ch 10 How Proteins are Made
... • Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules deliver the proper amino acids to the ribosome • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • tRNA molecules have an anti-codon that matches the codon • The delivered AA attaches to the chain adding to the polymer (protein) ...
... • Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules deliver the proper amino acids to the ribosome • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • tRNA molecules have an anti-codon that matches the codon • The delivered AA attaches to the chain adding to the polymer (protein) ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
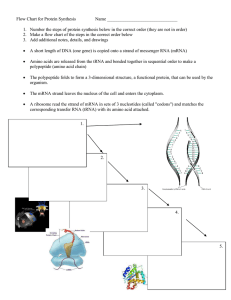
Flow Chart for Protein Synthesis
... 1. Number the steps of protein synthesis below in the correct order (they are not in order) 2. Make a flow chart of the steps in the correct order below 3. Add additional notes, details, and drawings ...
... 1. Number the steps of protein synthesis below in the correct order (they are not in order) 2. Make a flow chart of the steps in the correct order below 3. Add additional notes, details, and drawings ...
Nucleic Acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for ...
... _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for ...
Control of Gene Expression
... Complementary strands bind to one another Gene sequence may allow formation of a ...
... Complementary strands bind to one another Gene sequence may allow formation of a ...
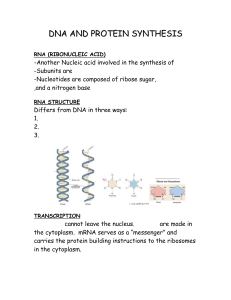
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... bases in mRNA into the amino acids of a protein. 1 Codon = 3 nucleotides on mRNA 1 Codon = Some codons are redundant (can be used again to give the same amino acid) RESULT OF TRANSLATION ...
... bases in mRNA into the amino acids of a protein. 1 Codon = 3 nucleotides on mRNA 1 Codon = Some codons are redundant (can be used again to give the same amino acid) RESULT OF TRANSLATION ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.