p-5-wwu_wp3_talk-wagenknecht-kolkenbrock
... biodegradability and the multitude of reactions that they catalyse. As an example, enzymes may be employed to change the properties of a polysaccharide in a desired way, thus making it more suitable for a particular industrial application. The first step in such a process, however, is the selection ...
... biodegradability and the multitude of reactions that they catalyse. As an example, enzymes may be employed to change the properties of a polysaccharide in a desired way, thus making it more suitable for a particular industrial application. The first step in such a process, however, is the selection ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most common mechanism for termination is the formation of a hairpin structure In proka ...
... Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most common mechanism for termination is the formation of a hairpin structure In proka ...
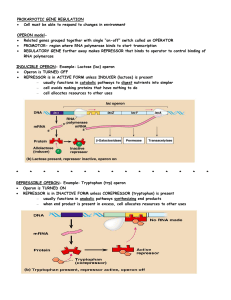
PROKARYOTIC GENE REGULATION
... LEVELS OF DNA PACKING REGULATE GENE EXPRESSION DNA packaged in chromatin fibers- regulates access to DNA by RNA ...
... LEVELS OF DNA PACKING REGULATE GENE EXPRESSION DNA packaged in chromatin fibers- regulates access to DNA by RNA ...
Nucleic acid recognition from prokaryotes to eukaryotes: Case
... Part (2) Recognition of the 3' pre-mRNA splice site. Almost all human genes contain intervening noncoding introns that must be removed by pre-mRNA splicing. The 3' splice site is marked by consensus sequences, yet variations of these sequences allow specific splice site regulation. Structures of the ...
... Part (2) Recognition of the 3' pre-mRNA splice site. Almost all human genes contain intervening noncoding introns that must be removed by pre-mRNA splicing. The 3' splice site is marked by consensus sequences, yet variations of these sequences allow specific splice site regulation. Structures of the ...
control of gene expression
... Sigma factors Different sigma factors recognize different promoters thus, the availability of sigma factors can regulate the transcription of genes associated with these promoters. The availability of sigma factors can be used to regulate sets of genes. E.g., a group of genes whose product is rarely ...
... Sigma factors Different sigma factors recognize different promoters thus, the availability of sigma factors can regulate the transcription of genes associated with these promoters. The availability of sigma factors can be used to regulate sets of genes. E.g., a group of genes whose product is rarely ...
CS 262—Lecture 1 Notes • 4-‐5 HWs, 3 late days • (Optional
... o As such, DNA is double stranded • DNA must be read from 5’ to 3’ end • RNA usually single-‐stranded o Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA • Gene transcription: Transcription factors recognize binding sites in ...
... o As such, DNA is double stranded • DNA must be read from 5’ to 3’ end • RNA usually single-‐stranded o Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA • Gene transcription: Transcription factors recognize binding sites in ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... condensed even during interphase • Barr bodies are X chromosomes condensed into heterochromatin • Telomeres, centromeres also heterochromatin • euchromatin is chromatin that is not condensed and can be transcribed ...
... condensed even during interphase • Barr bodies are X chromosomes condensed into heterochromatin • Telomeres, centromeres also heterochromatin • euchromatin is chromatin that is not condensed and can be transcribed ...
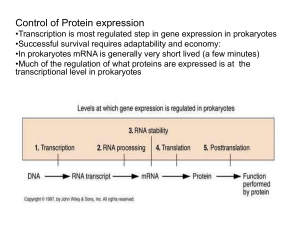
Control of Gene Expression
... Alternative RNA splicing Produces different mRNAs from the same transcript Results in the production of more than one polypeptide from the same gene and ...
... Alternative RNA splicing Produces different mRNAs from the same transcript Results in the production of more than one polypeptide from the same gene and ...
Lecture TandT
... from DNA to RNA to Protein – DNA functions as the inherited directions for a cell or organism. ...
... from DNA to RNA to Protein – DNA functions as the inherited directions for a cell or organism. ...
omic glossary
... the expression, localizations, functions, and interactions of the proteins expressed in the body and the determination of their role in physiological and pathophysiological functions. ...
... the expression, localizations, functions, and interactions of the proteins expressed in the body and the determination of their role in physiological and pathophysiological functions. ...
PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... Principal Type of RNA (1) There are 5 types you need to know about All have a role in the control of gene expression Not all are intermediate “central dogma” codes however 1) mRNA -Messenger RNA (<2000bp) is the direct coding intermediate for the production of proteins. Passes through various steps ...
... Principal Type of RNA (1) There are 5 types you need to know about All have a role in the control of gene expression Not all are intermediate “central dogma” codes however 1) mRNA -Messenger RNA (<2000bp) is the direct coding intermediate for the production of proteins. Passes through various steps ...
Gene Expression
... _________________ of RNA to the language of proteins. The instructions for building a protein are written as a series of _______ nucleotide sequences called __________. 2. Translation 2nd step: The protein making machinery, called the ___________, reads the mRNA sequence and translates it into the _ ...
... _________________ of RNA to the language of proteins. The instructions for building a protein are written as a series of _______ nucleotide sequences called __________. 2. Translation 2nd step: The protein making machinery, called the ___________, reads the mRNA sequence and translates it into the _ ...
Powerpoint
... GENE is a section of a DNA molecule that contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
... GENE is a section of a DNA molecule that contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
The Central Dogma of Biology Classroom Copy
... functional product. It was first proposed in 1958 by Francis Crick, one of the discoverers of the structure of DNA. The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information, from DNA to RNA, to make a functional protein also known as a polypeptide. DNA contains the information ...
... functional product. It was first proposed in 1958 by Francis Crick, one of the discoverers of the structure of DNA. The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information, from DNA to RNA, to make a functional protein also known as a polypeptide. DNA contains the information ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... – All under the control of the same promoter region – Thus these genes are transcribed all together into one continuous mRNA strand: polycistronic mRNA • Proteins are then synthesized from that mRNA ...
... – All under the control of the same promoter region – Thus these genes are transcribed all together into one continuous mRNA strand: polycistronic mRNA • Proteins are then synthesized from that mRNA ...
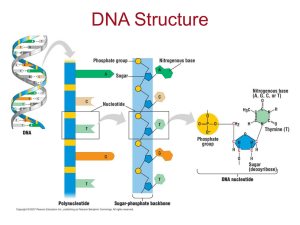
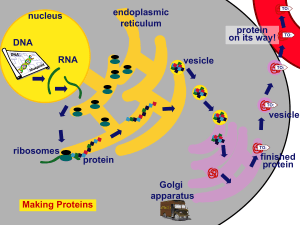
Protein Synthesis
... The ribosome is made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All cells need proteins, DNA, and ribosomes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes have ribosomes. ...
... The ribosome is made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All cells need proteins, DNA, and ribosomes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes have ribosomes. ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... complementary to the DNA base pairs. The enzyme used is RNA polymerase ...
... complementary to the DNA base pairs. The enzyme used is RNA polymerase ...
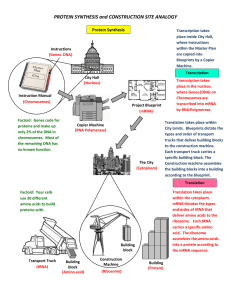
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The C ...
... where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The C ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... from digestion by nucleases and phosphatases as it exits nucleus and role in the initiation of translation 2. Poly A tail added to 3 end. Tail consists of ~200 A nucleotides and keeps the mRNA stable 3. Eukaryotic DNA gene contains coding regions (EXONS) and non-coding regions (INTRONS). Splicing u ...
... from digestion by nucleases and phosphatases as it exits nucleus and role in the initiation of translation 2. Poly A tail added to 3 end. Tail consists of ~200 A nucleotides and keeps the mRNA stable 3. Eukaryotic DNA gene contains coding regions (EXONS) and non-coding regions (INTRONS). Splicing u ...
Protein Synth Notes GO New
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
Eukaryotic Gene Control
... • Poly A tail and methyl G cap resist mRNA degradation in the cytoplasm until translation has ...
... • Poly A tail and methyl G cap resist mRNA degradation in the cytoplasm until translation has ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.