RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
Virtual Labs: Class Set Building DNA, transcription, translation
... Answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. During transcription, RNA is developed from a strand of DNA. List the base pairs used to make RNA. 2. What is the name of the DNA strand used in transcription? 3. Where does transcription occur? 4. Where does translation occur? 5. Name the RN ...
... Answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. During transcription, RNA is developed from a strand of DNA. List the base pairs used to make RNA. 2. What is the name of the DNA strand used in transcription? 3. Where does transcription occur? 4. Where does translation occur? 5. Name the RN ...
Athena, Jen and Natalie`s Powerpt
... mRNA reading frame is read in codons Codon: a sequence of 3 nucleotides AUG: the first codon recognized The start codon codes for methionine Whose tRNA enters the P-site tRNA: single stranded nucleic acid It’s shaped like a clover and here’s what happens ...
... mRNA reading frame is read in codons Codon: a sequence of 3 nucleotides AUG: the first codon recognized The start codon codes for methionine Whose tRNA enters the P-site tRNA: single stranded nucleic acid It’s shaped like a clover and here’s what happens ...
protein synthesis (simplified)
... The bases are complementary • DNA has two strands. • The strands are stuck together by the complementary bases. • Adenine to Thymine A-T • Cytosine to Guanine C-G ...
... The bases are complementary • DNA has two strands. • The strands are stuck together by the complementary bases. • Adenine to Thymine A-T • Cytosine to Guanine C-G ...
Gene expression
... • nucleotide sequence encoded by a gene that remains present within the final mature RNA product of that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. • This is the expressed genetic material… the light is turned on. ...
... • nucleotide sequence encoded by a gene that remains present within the final mature RNA product of that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. • This is the expressed genetic material… the light is turned on. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... • An expressed gene is one that is transcribed into RNA • Not all genes are expressed by every cell • How does an organism know when to “turn on” or “turn off” a gene? ...
... • An expressed gene is one that is transcribed into RNA • Not all genes are expressed by every cell • How does an organism know when to “turn on” or “turn off” a gene? ...
Topic 7 The Discovery of DNA & Its Roles
... cell is the ribosome Amino acids are carried to the growing ...
... cell is the ribosome Amino acids are carried to the growing ...
Proteins
... hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase ...
... hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase ...
gene expression - Aurora City Schools
... an anticodon). This process is called initiation. 2 tRNAs can fit at one time. 3. ribosome moves down and matches next codon. 4. Amino acids form peptide bond and protein continues to grow, 1 amino acid at a time. This process is called elongation. 5. ribosome reaches stop codon, mRNA, tRNAs, protei ...
... an anticodon). This process is called initiation. 2 tRNAs can fit at one time. 3. ribosome moves down and matches next codon. 4. Amino acids form peptide bond and protein continues to grow, 1 amino acid at a time. This process is called elongation. 5. ribosome reaches stop codon, mRNA, tRNAs, protei ...
Study Guide to Chapter 5 Ð DNA
... ______________________ a) transcription b) translation, in which a DNA serves as a template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is cal ...
... ______________________ a) transcription b) translation, in which a DNA serves as a template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is cal ...
BIO CH 13 Test Review
... “stop” codons, which end translation. 18. Ribosomes use the sequence of codons in mRNA to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains. 19. The decoding of an mRNA message into a protein is a process known as translation. 20. Each tRNA molecule carries just one kind of amino acid. In addition, each ...
... “stop” codons, which end translation. 18. Ribosomes use the sequence of codons in mRNA to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains. 19. The decoding of an mRNA message into a protein is a process known as translation. 20. Each tRNA molecule carries just one kind of amino acid. In addition, each ...
Chapter 17 - Denton ISD
... 1) __________- initiator tRNA attaches at AUG (start) codon. (prokaryotes also have something called the _____________________ about 10 base pairs before AUG to distinguish start from other AUG combinations.) This is followed by the attaching of the small and large ribosomal subunits. 2) ___________ ...
... 1) __________- initiator tRNA attaches at AUG (start) codon. (prokaryotes also have something called the _____________________ about 10 base pairs before AUG to distinguish start from other AUG combinations.) This is followed by the attaching of the small and large ribosomal subunits. 2) ___________ ...
GENE-SILENCING IN THE BRAIN IN VIVO USING siRNA
... to traditional gene-silencing approaches. We developed and applied non-viral delivery of RNAi in the brain. First, enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)-targeting short interfering RNA (siRNA), was administered, using 1- or 2-week osmotic minipumps, into the dorsal third ventricle of eGFP-expres ...
... to traditional gene-silencing approaches. We developed and applied non-viral delivery of RNAi in the brain. First, enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)-targeting short interfering RNA (siRNA), was administered, using 1- or 2-week osmotic minipumps, into the dorsal third ventricle of eGFP-expres ...
Transcription
... promoter) Elongation~ RNA polymerase continues unwinding DNA and adding nucleotides to the 3’ end Termination~ RNA polymerase reaches terminator sequence ...
... promoter) Elongation~ RNA polymerase continues unwinding DNA and adding nucleotides to the 3’ end Termination~ RNA polymerase reaches terminator sequence ...
lesson x - MisterSyracuse.com
... 2. What tells RNA polymerase to start or stop? 3. What tells DNA polymerase to start or stop? New Learning: (30 minutes) 1. What we need to find out is how genes are controlled. We don’t want them on all the time, but we don’t want them off all the time, either. 2. In prokaryotes, things called oper ...
... 2. What tells RNA polymerase to start or stop? 3. What tells DNA polymerase to start or stop? New Learning: (30 minutes) 1. What we need to find out is how genes are controlled. We don’t want them on all the time, but we don’t want them off all the time, either. 2. In prokaryotes, things called oper ...
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly ...
... to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly ...
No Slide Title
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) leaves the nucleus, binds to the amino acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) leaves the nucleus, binds to the amino acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
Protein Synthesis
... Proteins are responsible for most of the differences in organisms that we see. EX: height, curly or straight hair, etc. ...
... Proteins are responsible for most of the differences in organisms that we see. EX: height, curly or straight hair, etc. ...
A substance formed by the chemical joining of two or more
... nucleus to other parts of the cell ...
... nucleus to other parts of the cell ...
Reviewing Key Concepts Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Section Review 12-3
... 5. Each tRNA molecule contains three unpaired bases, called the , which ensure that amino acids are added in the correct sequence. ...
... 5. Each tRNA molecule contains three unpaired bases, called the , which ensure that amino acids are added in the correct sequence. ...
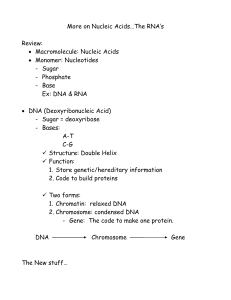
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... from DNA and carry those instructions to the ribosome/ “workbench” 3. tRNA: [“t” = transfer] - structure: upside down hair-pin loop or upside down “t”. - function: locate and transfer the correct amino acid to the mRNA on the rRNA (ribosome) and place them in the correct order and location. Differen ...
... from DNA and carry those instructions to the ribosome/ “workbench” 3. tRNA: [“t” = transfer] - structure: upside down hair-pin loop or upside down “t”. - function: locate and transfer the correct amino acid to the mRNA on the rRNA (ribosome) and place them in the correct order and location. Differen ...
Bio 313 worksheet 14 - Iowa State University
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
DNA/RNA.lecture
... C. Overview: information flow & gene expression II. Transcription A. Structure 1. nucleotide differences 2. RNA 3. short B. When does this happen? C. 3 main kinds of RNA 1. messenger RNAs (mRNA) 2. Other 2 types of RNA - protein-producing machinery a. transfer RNAs (tRNA) b. ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) D. ...
... C. Overview: information flow & gene expression II. Transcription A. Structure 1. nucleotide differences 2. RNA 3. short B. When does this happen? C. 3 main kinds of RNA 1. messenger RNAs (mRNA) 2. Other 2 types of RNA - protein-producing machinery a. transfer RNAs (tRNA) b. ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) D. ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.