IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to
... 2. Polypeptide contains many amino acids and if there are very many amino acids one can call it protein C. Proteins have molecular weights > several thousand and have 3-4 levels of structure 1. Primary Structure (1°) sequence of amino acids connected by peptide bo n d s 2. Secondary Structure (2°) l ...
... 2. Polypeptide contains many amino acids and if there are very many amino acids one can call it protein C. Proteins have molecular weights > several thousand and have 3-4 levels of structure 1. Primary Structure (1°) sequence of amino acids connected by peptide bo n d s 2. Secondary Structure (2°) l ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 18. __Amino_____ and ______carboxyl__ functional groups are contained within an amino acid. 19. The carbonyl functional group when located on the end of the compound is called ___carbonyl end (Aldehyde)____________. ...
... 18. __Amino_____ and ______carboxyl__ functional groups are contained within an amino acid. 19. The carbonyl functional group when located on the end of the compound is called ___carbonyl end (Aldehyde)____________. ...
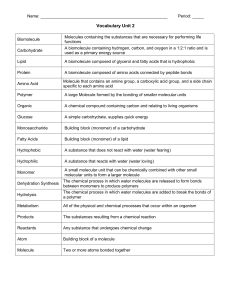
Name: Period: _____ Vocabulary Unit 2 Biomolecule Molecules
... Molecules containing the substances that are necessary for performing life functions ...
... Molecules containing the substances that are necessary for performing life functions ...
Chapter 14 Proteins
... ◦ Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ◦ Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ◦ Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. ◦ Polypeptide: ...
... ◦ Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ◦ Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ◦ Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. ◦ Polypeptide: ...
Macromolecules - Issaquah Connect
... 24. A peptide bond is always formed between the ____ group of one _____ and the _____ group of the next. (amino, amino acid, carboxyl) 25. Using a structural formula diagram, show how a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids. 26. Discuss one type of interaction that can occur between the R g ...
... 24. A peptide bond is always formed between the ____ group of one _____ and the _____ group of the next. (amino, amino acid, carboxyl) 25. Using a structural formula diagram, show how a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids. 26. Discuss one type of interaction that can occur between the R g ...
Macromolecules 2: Proteins and Nucleic Acids Amino Acids differ
... • Sometimes a single functional PROTEIN is made of several POLYPEPTIDES that work together as a unit ...
... • Sometimes a single functional PROTEIN is made of several POLYPEPTIDES that work together as a unit ...
answers to study guide
... made of 3 fatty acids and a glycerol saturated fatty acid no C-C double bonds unsaturated fatty acid one or more C- C double bonds hydrogenation – what it does decreases# of C-C double bonds increases # of H atoms at room temp, goes from oil to solid saturated fatty acid vs. unsaturated fatty acid s ...
... made of 3 fatty acids and a glycerol saturated fatty acid no C-C double bonds unsaturated fatty acid one or more C- C double bonds hydrogenation – what it does decreases# of C-C double bonds increases # of H atoms at room temp, goes from oil to solid saturated fatty acid vs. unsaturated fatty acid s ...
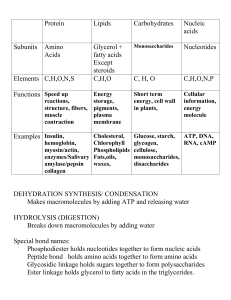
Macromolecules chart
... Makes macromolecules by adding ATP and releasing water HYDROLYSIS (DIGESTION) Breaks down macromolecules by adding water Special bond names: Phosphodiester holds nucleotides together to form nucleic acids Peptide bond holds amino acids together to form amino acids Glycosidic linkage holds sugars tog ...
... Makes macromolecules by adding ATP and releasing water HYDROLYSIS (DIGESTION) Breaks down macromolecules by adding water Special bond names: Phosphodiester holds nucleotides together to form nucleic acids Peptide bond holds amino acids together to form amino acids Glycosidic linkage holds sugars tog ...
Midterm IV Key
... Instructions: The exam consists of 20 multiple choice (3 points each) and 6 short answer questions (40 points). Indicate your answers to the multiple choice questions by writing the letter choice in the space provided in the answer sheet, below. Write your short answers in the space provided. Answer ...
... Instructions: The exam consists of 20 multiple choice (3 points each) and 6 short answer questions (40 points). Indicate your answers to the multiple choice questions by writing the letter choice in the space provided in the answer sheet, below. Write your short answers in the space provided. Answer ...
Test 1
... 2. (10 points) Some proteins contain added chemical groups or cofactors that give them added chemical reactivity. One such cofactor is NAD+ or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Our body cannot synthesize this cofactor so it must be obtained in our diet as the vitamin riboflavin. Below is the struct ...
... 2. (10 points) Some proteins contain added chemical groups or cofactors that give them added chemical reactivity. One such cofactor is NAD+ or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Our body cannot synthesize this cofactor so it must be obtained in our diet as the vitamin riboflavin. Below is the struct ...
Import Settings
... C) constant pKs no matter what aqueous environment they are found in D) different pKs in peptides as compared to the free amino acids E) polar functional groups 19. Asx refers to A) a negatively charged aspartic acid B) a positively charged asparagine C) a dipeptide containing both aspartic acid and ...
... C) constant pKs no matter what aqueous environment they are found in D) different pKs in peptides as compared to the free amino acids E) polar functional groups 19. Asx refers to A) a negatively charged aspartic acid B) a positively charged asparagine C) a dipeptide containing both aspartic acid and ...
Core Concept Cheat Sheet
... ! Functional group: The specific atom or group of atoms that confers a particular chemical property on a biomolecule. ! Organic Compounds: Molecules containing covalently bonded carbon backbones are called organic compounds. ! Hydrolysis: Cleavage of a bond, such as an anhydride or peptide bond, by ...
... ! Functional group: The specific atom or group of atoms that confers a particular chemical property on a biomolecule. ! Organic Compounds: Molecules containing covalently bonded carbon backbones are called organic compounds. ! Hydrolysis: Cleavage of a bond, such as an anhydride or peptide bond, by ...
Faculty of Science Department of science Chemistry of
... Monosaccharide structures and stereochemistry. Aldoses and ketoses. Nomenclature. Fischer projection formula. Cyclic hemiacetal formation. Hawarth formula. Furanoses and pyranoses. The anomeric effect. Reactions and methods of synthesis. ...
... Monosaccharide structures and stereochemistry. Aldoses and ketoses. Nomenclature. Fischer projection formula. Cyclic hemiacetal formation. Hawarth formula. Furanoses and pyranoses. The anomeric effect. Reactions and methods of synthesis. ...
No Slide Title
... The amino acid composition of a peptide chain is determined by its complete hydrolysis followed by the quantitative analysis of the liberated amino acids. Acid hydrolysis (6 N HCl) at 120 oC for 10 to 100 h destroys Trp and partially destroys Ser, Thr, and Tyr. ...
... The amino acid composition of a peptide chain is determined by its complete hydrolysis followed by the quantitative analysis of the liberated amino acids. Acid hydrolysis (6 N HCl) at 120 oC for 10 to 100 h destroys Trp and partially destroys Ser, Thr, and Tyr. ...
macromolecule_sheets
... 2. How does the number of H atoms in a carbohydrate compare to the number of oxygen atoms? 3. What is the simplest type of carbohydrate? 4. What two functional groups are found in monosaccharides? 5. Name three common monosaccharides and give the molecular formula for each. 6. What suffix is commonl ...
... 2. How does the number of H atoms in a carbohydrate compare to the number of oxygen atoms? 3. What is the simplest type of carbohydrate? 4. What two functional groups are found in monosaccharides? 5. Name three common monosaccharides and give the molecular formula for each. 6. What suffix is commonl ...
Introduction- Amino acid protection and deprotection is particularly
... intermediate in organic synthesis there is variety of reagent for conversion of amino acid to amino acid ester (2). Amino acid protection and deprotection is also used in peptide synthesis of amino acid in solid and solution phase synthesis , the advantage of solution phase synthesis is to isolate a ...
... intermediate in organic synthesis there is variety of reagent for conversion of amino acid to amino acid ester (2). Amino acid protection and deprotection is also used in peptide synthesis of amino acid in solid and solution phase synthesis , the advantage of solution phase synthesis is to isolate a ...
PT2009-1 Overcoming Peptide Problems by Design.indd
... peptide for the intended purpose. Consequently, when we receive an order for a peptide or set of peptides, the sequences are analysed using predictive algorithms to determine if there is likely to be any problem with peptide assembly or solubility [1,2]. The sequences are also examined for sequence- ...
... peptide for the intended purpose. Consequently, when we receive an order for a peptide or set of peptides, the sequences are analysed using predictive algorithms to determine if there is likely to be any problem with peptide assembly or solubility [1,2]. The sequences are also examined for sequence- ...
Chapter 6: Biochemistry
... A. contain many carbon atoms B. they are polymers (long chains of small molecules) C. condensation reactions make monomers into polymers ...
... A. contain many carbon atoms B. they are polymers (long chains of small molecules) C. condensation reactions make monomers into polymers ...