Body chemicals
... Steroids are also classed as lipids, but have a different structure based on four interconnected carbon rings. They are insoluble in water and include cholesterol and sex hormones such as testosterone and oestrogen. Proteins Proteins are made from atoms of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. For ...
... Steroids are also classed as lipids, but have a different structure based on four interconnected carbon rings. They are insoluble in water and include cholesterol and sex hormones such as testosterone and oestrogen. Proteins Proteins are made from atoms of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. For ...
Biochemistry File - Northwest ISD Moodle
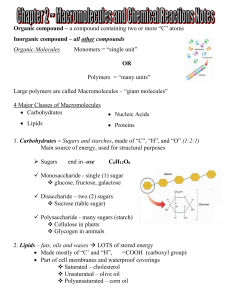
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
Biochemistry Lecture 4 9/6/01
... – First H+ released from aa is much more easily given up than second H+ ...
... – First H+ released from aa is much more easily given up than second H+ ...
chp4_5_hw_review_worksheet
... As mentioned (in class), generally “plain” hydrocarbons are not found in living cells. There are usually other groups of atoms attached somewhere on the molecule. There are certain groups of atoms that are frequently attached to the organic molecules we will be studying, and these are called functio ...
... As mentioned (in class), generally “plain” hydrocarbons are not found in living cells. There are usually other groups of atoms attached somewhere on the molecule. There are certain groups of atoms that are frequently attached to the organic molecules we will be studying, and these are called functio ...
Carbon Compounds In Cells
... • Rigid backbone of four fused-together carbon rings • Cholesterol - most ...
... • Rigid backbone of four fused-together carbon rings • Cholesterol - most ...
g. ¶I - wwphs
... stretches of amino acids coil, and other regions form sheets or ioops Comes in two slightly different forms, alpha and beta; two of each form make up one hemoglobin molecule in humans Airoteins that transport attached cholesterol, triglycerides, and phospholipids The type of covalent bond linking on ...
... stretches of amino acids coil, and other regions form sheets or ioops Comes in two slightly different forms, alpha and beta; two of each form make up one hemoglobin molecule in humans Airoteins that transport attached cholesterol, triglycerides, and phospholipids The type of covalent bond linking on ...
Pulsatílla praténsis
... Amino acids are one of the physiologically important groups of compounds, taking part in synthesis of specific tissue proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, fats, hormones and other compounds necessary for living organisms. They are capable of maintaining normal function of organs and systems at extreme ...
... Amino acids are one of the physiologically important groups of compounds, taking part in synthesis of specific tissue proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, fats, hormones and other compounds necessary for living organisms. They are capable of maintaining normal function of organs and systems at extreme ...
THE CENTRAL DOGMA THE CENTRAL DOGMA
... Formation of Secondary Structure • The most stable and common forms are αhelix and β-sheet structures • Maximize hydrogen bonds between αaminos and α-carbonyls of peptide bonds • Maximize electrostatic interactions between R-groups • Minimize steric clashes between R-groups ...
... Formation of Secondary Structure • The most stable and common forms are αhelix and β-sheet structures • Maximize hydrogen bonds between αaminos and α-carbonyls of peptide bonds • Maximize electrostatic interactions between R-groups • Minimize steric clashes between R-groups ...
Evidence of Evolution Fossils Provide Evidence FOSSIL: The
... FOSSIL: The _____________ or mineralized remains (bone, petrified tree, tooth, or shell) or ______________ of an organism that lived long ago. Three Major Points • Earth is about _________ billion years old. • Organisms have inhabited the earth for most of its history. • All organisms living today _ ...
... FOSSIL: The _____________ or mineralized remains (bone, petrified tree, tooth, or shell) or ______________ of an organism that lived long ago. Three Major Points • Earth is about _________ billion years old. • Organisms have inhabited the earth for most of its history. • All organisms living today _ ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... ____________________ 5. These are the individual subunits that make up DNA and RNA. ____________________ 6. What is a long chain of amino acids called? ____________________ 7. What sugar does DNA contain? ____________________ 8. When the pH is greater than 7, it is called this. ____________________ ...
... ____________________ 5. These are the individual subunits that make up DNA and RNA. ____________________ 6. What is a long chain of amino acids called? ____________________ 7. What sugar does DNA contain? ____________________ 8. When the pH is greater than 7, it is called this. ____________________ ...
A little less conjugation, a little more accuracy
... proceed at all of the accessible reactive sites on a protein and can lead to a mixture of products that often possess different properties. When a homogenous conjugate is required, a different synthetic strategy is needed — one that offers precise control over the site at which modification occurs. ...
... proceed at all of the accessible reactive sites on a protein and can lead to a mixture of products that often possess different properties. When a homogenous conjugate is required, a different synthetic strategy is needed — one that offers precise control over the site at which modification occurs. ...
R–groups
... A. Primary Structure—the unique sequence of amino acids, type sequence and number; determines the other three structures It is held together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl group of one amino acid with the amino group of another amino acid B. Secondary Structure― regular repeated coiling and f ...
... A. Primary Structure—the unique sequence of amino acids, type sequence and number; determines the other three structures It is held together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl group of one amino acid with the amino group of another amino acid B. Secondary Structure― regular repeated coiling and f ...
PEPTIDE BONDS AND POLYPEPTIDES OLIGOPEPTIDE
... •hydrolysis of protein (usually in 6N HCl at 110°) •hydrolysate (amino acids) is separated by ion exchange chromatography a column of beads that separates molecules on the basis of charge there are cation exchange (-) columns and anion exchange (+) columns •amount of each amino acid is then quantita ...
... •hydrolysis of protein (usually in 6N HCl at 110°) •hydrolysate (amino acids) is separated by ion exchange chromatography a column of beads that separates molecules on the basis of charge there are cation exchange (-) columns and anion exchange (+) columns •amount of each amino acid is then quantita ...
The Synthesis of Proteins
... consisting of three bases that selects specific amino acids and “escorts” them to the growing protein chain so that they join at just the proper position. ...
... consisting of three bases that selects specific amino acids and “escorts” them to the growing protein chain so that they join at just the proper position. ...
Slide 1
... acid has different properties, and this in turn means that proteins can have a wide range of properties ...
... acid has different properties, and this in turn means that proteins can have a wide range of properties ...
A1983RE63700001
... courtyard of the Cavendish Physics Laboratory), I got nowhere in my crosses. Finally, in desperation l took the train down to London every morning to do the crosses in William Hayes’s lab at the Hammersmith Hospital, with the help of Hayes’s associate, Royston Clowes, And within a week or so, I had ...
... courtyard of the Cavendish Physics Laboratory), I got nowhere in my crosses. Finally, in desperation l took the train down to London every morning to do the crosses in William Hayes’s lab at the Hammersmith Hospital, with the help of Hayes’s associate, Royston Clowes, And within a week or so, I had ...
chapter3_part2
... Proteins are the most diverse biological molecule (structural, nutritious, enzyme, transport, communication, and defense proteins) ...
... Proteins are the most diverse biological molecule (structural, nutritious, enzyme, transport, communication, and defense proteins) ...