
Amino Acids and Healthy Muscle - SEA
... promotion of our body muscles. In particular, the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) which cannot be produced in our living body are called “essential amino acids”. Human beings should take BCAAs (valine, leucine and isoleucine) through meal (and / or supplement if needed) in considering the balance ...
... promotion of our body muscles. In particular, the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) which cannot be produced in our living body are called “essential amino acids”. Human beings should take BCAAs (valine, leucine and isoleucine) through meal (and / or supplement if needed) in considering the balance ...
Macromolecules 9-3
... c. Four Levels of Protein Structure i. Primary 1. Sequence of amino acids in the protein a. Determined by the structure of the DNA sequence in the nucleus! b. Every three letters in DNA codes for an amino acid c. These amino acids form chains to make proteins ii. Secondary 1. The folding and/or coil ...
... c. Four Levels of Protein Structure i. Primary 1. Sequence of amino acids in the protein a. Determined by the structure of the DNA sequence in the nucleus! b. Every three letters in DNA codes for an amino acid c. These amino acids form chains to make proteins ii. Secondary 1. The folding and/or coil ...
Chemistry of Proteins Model Making
... Proteins are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in m ...
... Proteins are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in m ...
NAME
... 1. Check with the other groups in the class. What other variants of the gene exist? How similar or dissimilar were their DNA sequence? ...
... 1. Check with the other groups in the class. What other variants of the gene exist? How similar or dissimilar were their DNA sequence? ...
Rice Krispie Treats
... 1. Check with the other groups in the class. What other variants of the gene exist? How similar or dissimilar were their DNA sequence? ...
... 1. Check with the other groups in the class. What other variants of the gene exist? How similar or dissimilar were their DNA sequence? ...
Structural Genomics - University of Houston
... pK1 and pK2 respectively pKR is for R group pK’s pK1 2.2 while pK2 9.4 ...
... pK1 and pK2 respectively pKR is for R group pK’s pK1 2.2 while pK2 9.4 ...
Protein structure - Manning`s Science
... joins with the OH from the carboxyl group. This forms a water molecule. The Nitrogen atom them combines with the carbon atom forming a peptide bond. ...
... joins with the OH from the carboxyl group. This forms a water molecule. The Nitrogen atom them combines with the carbon atom forming a peptide bond. ...
QUIZ #1 - Introduction, Water, pH, buffers, Amino Acids, Proteins
... c. When the pH = pI, the amino acid is at its greatest buffering capacity d. When the pH = pI, the pK of each ionizable group is unchanged 14. Concerning buffers, which of the following is true? a. Strong acid and bases are good buffers b. Buffers cause dramatic pH changes c. The -NH2 / -NH3+ pair i ...
... c. When the pH = pI, the amino acid is at its greatest buffering capacity d. When the pH = pI, the pK of each ionizable group is unchanged 14. Concerning buffers, which of the following is true? a. Strong acid and bases are good buffers b. Buffers cause dramatic pH changes c. The -NH2 / -NH3+ pair i ...
Proteins - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 1. amino acids consist of a central or alpha carbon; bound to that carbon is a hydrogen atom, an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a variable side group (R group) • the R group determines the identity and much of the chemical properties of the amino acid ...
... 1. amino acids consist of a central or alpha carbon; bound to that carbon is a hydrogen atom, an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a variable side group (R group) • the R group determines the identity and much of the chemical properties of the amino acid ...
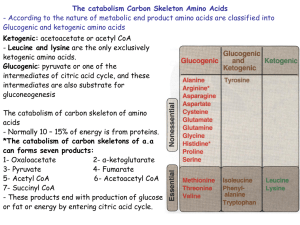
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... carboxyl groups of each amino acid are adjacent to each other, they can be combined by undergoing a dehydration reaction which results in the formation of a peptide bond. Amino acids in a polypeptide (protein) are linked by peptide bonds that begin with the N-terminal with a free amino group and end ...
... carboxyl groups of each amino acid are adjacent to each other, they can be combined by undergoing a dehydration reaction which results in the formation of a peptide bond. Amino acids in a polypeptide (protein) are linked by peptide bonds that begin with the N-terminal with a free amino group and end ...
Revealing the Genetic Code
... Gene = sequence of nucleotides (bases) Protein = sequence of amino acids Sequence of bases determines sequence of amino acids (protein’s primary structure) Protein’s primary structure determines its secondary & tertiary (3D) structures Protein’s 3D structure determines its function!! ...
... Gene = sequence of nucleotides (bases) Protein = sequence of amino acids Sequence of bases determines sequence of amino acids (protein’s primary structure) Protein’s primary structure determines its secondary & tertiary (3D) structures Protein’s 3D structure determines its function!! ...
Amino Acid R (neutral form) -NH3 -CO2H Side chain Glycine, Gly
... Goal: Our goal in this activity is to apply what we learned about amino acids and the primary structure of proteins and begin to consider how proteins fold into the 3-dimensional structures that we observe in our bodies. This activity will specifically investigate the chemistry of amino acid side ch ...
... Goal: Our goal in this activity is to apply what we learned about amino acids and the primary structure of proteins and begin to consider how proteins fold into the 3-dimensional structures that we observe in our bodies. This activity will specifically investigate the chemistry of amino acid side ch ...
Altering enzyme activities using chemical modification Claire Louise
... ways of inserting these non-canonical amino acids: either by genetic incorporation or by post-translational modification. Major advances in engineering new enzyme activities have been made by site-directed mutagenesis and directed evolution, however these methods are restricted to the use of the twe ...
... ways of inserting these non-canonical amino acids: either by genetic incorporation or by post-translational modification. Major advances in engineering new enzyme activities have been made by site-directed mutagenesis and directed evolution, however these methods are restricted to the use of the twe ...
Ch 3
... o Enzyme catalysis o Defense o Transport o Support o Motion o Regulation o Storage • Proteins are polymers – Composed of 1 or more long, unbranched chains – Each chain is a polypeptide – Amino acids are monomers • Amino acid structure – Central carbon atom – Amino group – Carboxyl group – Single hyd ...
... o Enzyme catalysis o Defense o Transport o Support o Motion o Regulation o Storage • Proteins are polymers – Composed of 1 or more long, unbranched chains – Each chain is a polypeptide – Amino acids are monomers • Amino acid structure – Central carbon atom – Amino group – Carboxyl group – Single hyd ...
Bi 12 Biological Molecules Current.pptx
... ¨ generally quite large. A long polymer chain of amino acid subunits linked end to end by a peptide bond ...
... ¨ generally quite large. A long polymer chain of amino acid subunits linked end to end by a peptide bond ...
Traffic Lights Biological Cpds
... because glucose can be added or removed easily and they have little or no osmotic effect in cells because they are insoluble. 15. Cellulose and chitin are similar structural polysaccharides with the alternating isomers allowing cross linking between chains (by hydrogen bonds), forming microfibrils ( ...
... because glucose can be added or removed easily and they have little or no osmotic effect in cells because they are insoluble. 15. Cellulose and chitin are similar structural polysaccharides with the alternating isomers allowing cross linking between chains (by hydrogen bonds), forming microfibrils ( ...
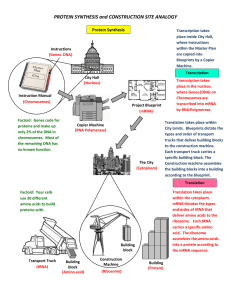
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
Proteins2[1]
... • Many proteins contain two or more polypeptide chains • Each chain forms a three-dimensional structure called subunit • It is the 3D arrangement of different subunits of a protein ...
... • Many proteins contain two or more polypeptide chains • Each chain forms a three-dimensional structure called subunit • It is the 3D arrangement of different subunits of a protein ...
DNA Template for Protein Transcription Directions: 1) Use the DNA
... Directions: 1) Use the DNA template (above) to find the corresponding piece of mRNA. (Remember you have to identify the starting point in the strand first. The start CODON is?) 2) Once you have identified the starting point, transcribe the mRNA for that gene segment. 3) Use the mRNA sequence to perf ...
... Directions: 1) Use the DNA template (above) to find the corresponding piece of mRNA. (Remember you have to identify the starting point in the strand first. The start CODON is?) 2) Once you have identified the starting point, transcribe the mRNA for that gene segment. 3) Use the mRNA sequence to perf ...


















![Proteins2[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008291804_1-fc4b593e0423ea377f021b9f7071accd-300x300.png)


