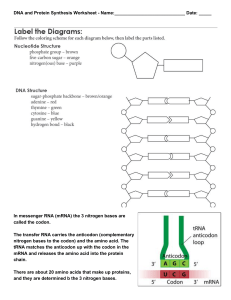
03 - summer worksheet
... compounds suggested in the “types” column (choose from car4bohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). ...
... compounds suggested in the “types” column (choose from car4bohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). ...
CLINICAL CASE (UREA CYCLE)
... Oral therapy was started by administering a combination of essential amino acids (including arginine) at a dose of 1.1g/kg/d. By the seventh day, his plasma NH4+ level was 40 uM, and he appeared clinically well. Learning objectives: Explain ...
... Oral therapy was started by administering a combination of essential amino acids (including arginine) at a dose of 1.1g/kg/d. By the seventh day, his plasma NH4+ level was 40 uM, and he appeared clinically well. Learning objectives: Explain ...
Proteins - Northern Highlands
... All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids that are relevant to the chemical make-up of mammalian proteins. Amino Acids Consist of a carboxylic acid (-COOH) and an amino (-NH2) functional group attached to an α-carbon. Distinct R-groups that distinguish one a ...
... All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids that are relevant to the chemical make-up of mammalian proteins. Amino Acids Consist of a carboxylic acid (-COOH) and an amino (-NH2) functional group attached to an α-carbon. Distinct R-groups that distinguish one a ...
Biomolecules Review
... 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? alanine–lysine–aspartic acid 17. What is denaturation of protein? What c ...
... 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? alanine–lysine–aspartic acid 17. What is denaturation of protein? What c ...
Amino acids and protein (lect 3%2c 2015)
... forms a covalent peptide bond with α-amino group of another amino acid (with the side chain R2) by removal of a molecule of water. The result is : Dipeptide ( i.e. Two amino acids linked by one peptide bond). By the same way, the dipeptide can then forms a second peptide bond with a third amino acid ...
... forms a covalent peptide bond with α-amino group of another amino acid (with the side chain R2) by removal of a molecule of water. The result is : Dipeptide ( i.e. Two amino acids linked by one peptide bond). By the same way, the dipeptide can then forms a second peptide bond with a third amino acid ...
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates Polarity: Polar Functions: Store
... Efficient energy-storage molecules, with more than double the energy per gram than carbohydrates (but this energy is less accessible to cells than in CHOs) – long term energy accessed after CHOs are used up Insulate against heat loss, protective cushion for major organs, component of cell membranes, ...
... Efficient energy-storage molecules, with more than double the energy per gram than carbohydrates (but this energy is less accessible to cells than in CHOs) – long term energy accessed after CHOs are used up Insulate against heat loss, protective cushion for major organs, component of cell membranes, ...
Chem 464 Biochemistry
... 10. (10 points) Histones are proteins found in eukariotic cell nuclei, tightly bound to DNA which has many negatively charged phosphate groups. The pI of histones is very high, about 10.8, What amino acid residues must be present in relatively large numbers in histones? In what way do these residues ...
... 10. (10 points) Histones are proteins found in eukariotic cell nuclei, tightly bound to DNA which has many negatively charged phosphate groups. The pI of histones is very high, about 10.8, What amino acid residues must be present in relatively large numbers in histones? In what way do these residues ...
All amino acids participate in these reactions at some
... All amino acids participate in these reactions at some point in their catabolism *** This is false; serine and threonine are not transaminated ¾ they are oxidatively deaminated (release NH3) by a dehydratase enzyme to form pyruvate and propionyl coA respectively. The first step in the catabolism of ...
... All amino acids participate in these reactions at some point in their catabolism *** This is false; serine and threonine are not transaminated ¾ they are oxidatively deaminated (release NH3) by a dehydratase enzyme to form pyruvate and propionyl coA respectively. The first step in the catabolism of ...
Quiz Chapter 5 Organic Molecules
... Directions: Each group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of numbered phrases or sentences. For each numbered phrase or sentence, select the one heading that is most closely related to it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Each heading may be used ...
... Directions: Each group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of numbered phrases or sentences. For each numbered phrase or sentence, select the one heading that is most closely related to it and fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. Each heading may be used ...
2012-ISB-symposium
... proteins to aid in understanding of the factors responsible for certain portions of the protein structure being strongly detected in tandem mass spectrometry while others are detected weakly or not at all. ...
... proteins to aid in understanding of the factors responsible for certain portions of the protein structure being strongly detected in tandem mass spectrometry while others are detected weakly or not at all. ...
Lecture 2
... Amino acids can be classified (sometimes roughly) into groups based on the chemical properties of the R groups and their internal functional groups. The main classifications are: polar vs. non polar, hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic, aromatic vs. aliphatic, charged vs. non-charged. Hydrophilic (charged, ...
... Amino acids can be classified (sometimes roughly) into groups based on the chemical properties of the R groups and their internal functional groups. The main classifications are: polar vs. non polar, hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic, aromatic vs. aliphatic, charged vs. non-charged. Hydrophilic (charged, ...
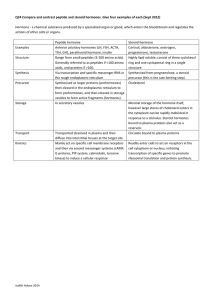
Q24 Compare and contrast peptide and steroid hormones. Give four
... TSH, GH), parathyroid hormone, insulin progesterone, testosterone Structure Range from small peptides (3-‐200 amino acids). Highly lipid soluble; consist of three cyclohexal Generally referred to as peptides if ...
... TSH, GH), parathyroid hormone, insulin progesterone, testosterone Structure Range from small peptides (3-‐200 amino acids). Highly lipid soluble; consist of three cyclohexal Generally referred to as peptides if ...
Week 2
... Protein Complex Structures - Cryo-Electron Microscopy is becoming an increasingly common way of measuring structures of large protein complexes ...
... Protein Complex Structures - Cryo-Electron Microscopy is becoming an increasingly common way of measuring structures of large protein complexes ...
amino acid letter codes
... differs from Aspartate by its amide nitrogen (AsN = "N"). [Not used very often are the letters B (either D or N) and Z (either E or Q)]. Q Gln "Q-tamine" ...
... differs from Aspartate by its amide nitrogen (AsN = "N"). [Not used very often are the letters B (either D or N) and Z (either E or Q)]. Q Gln "Q-tamine" ...
Soon you will learn what HIV requires to come to life…
... We would like to understand the forces that stabilize secondary and tertiary structure (i.e. what determines a protein structure)? ...
... We would like to understand the forces that stabilize secondary and tertiary structure (i.e. what determines a protein structure)? ...
Eledoisin peptide
... Solubility: It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Eledoisin in sterile 18M-cm H2O not less than 100ug/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. Purity/Purification: Greater than 98.0% as determined by: (a) Analysis by RP-HPLC. (b) Anion-exchange FPLC. (c) Analysis ...
... Solubility: It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Eledoisin in sterile 18M-cm H2O not less than 100ug/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. Purity/Purification: Greater than 98.0% as determined by: (a) Analysis by RP-HPLC. (b) Anion-exchange FPLC. (c) Analysis ...