2-BuildingBlocks
... molecules. These non-covalent bonds involve the AA side chains. Selecting from those listed in the box, which type(s) of amino acids would: A. form ionic bonds with negatively charged DNA. _________ B. form hydrogen bonds with water. __________ C. help hold together two water-soluble proteins.______ ...
... molecules. These non-covalent bonds involve the AA side chains. Selecting from those listed in the box, which type(s) of amino acids would: A. form ionic bonds with negatively charged DNA. _________ B. form hydrogen bonds with water. __________ C. help hold together two water-soluble proteins.______ ...
Midterm for Bio98B A1 (1) Enzymes accelerate reactions by
... in a buffer at 25oC. Enzyme is then added and the reaction is allowed to proceed to equilibrium, whereupon, the concentrations of A and B are found to be 1.5 x 10-5 M and 4.5 x 10-4 M, respectively. Calculate Keq for the reaction, the starting concentration of A, and the value of ΔGo for this reacti ...
... in a buffer at 25oC. Enzyme is then added and the reaction is allowed to proceed to equilibrium, whereupon, the concentrations of A and B are found to be 1.5 x 10-5 M and 4.5 x 10-4 M, respectively. Calculate Keq for the reaction, the starting concentration of A, and the value of ΔGo for this reacti ...
Proteins - chem.uwec.edu
... When this reaction is done in a test tube acid chorides or and acid anhydrides are used instead of the carboxylic acid. a. This is done to make the reaction more favorable. ...
... When this reaction is done in a test tube acid chorides or and acid anhydrides are used instead of the carboxylic acid. a. This is done to make the reaction more favorable. ...
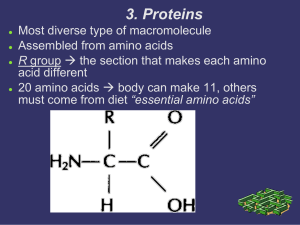
3. Proteins
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
hwk- pg-331 - WordPress.com
... 1. In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the key steps in the initiation of translation are the association an initiator methionine-tRNA with the small ribosomal subunit. The complex binds the mRNA at the 5' cap and scans for the AUG start codon. The large ribosomal subunit then binds, completing the ...
... 1. In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the key steps in the initiation of translation are the association an initiator methionine-tRNA with the small ribosomal subunit. The complex binds the mRNA at the 5' cap and scans for the AUG start codon. The large ribosomal subunit then binds, completing the ...
Synthesis of Phosphopeptides Containing O
... catalyze the transfer of phosphate from high-energy nucleoside triphosphate. Major proteins in bones, teeth, eggs, and milk are highly phosphorylated. Preparation of phosphopeptides related to sequences of phosphoproteins is important for the study of their properties. Enzymatic methods for the synt ...
... catalyze the transfer of phosphate from high-energy nucleoside triphosphate. Major proteins in bones, teeth, eggs, and milk are highly phosphorylated. Preparation of phosphopeptides related to sequences of phosphoproteins is important for the study of their properties. Enzymatic methods for the synt ...
Nutrients and the structure of macromolecules File
... is partly how fats get their name i.e. C18 or C12 (Lorenzo’s Oil). 2. These chains can also be saturated with Hydrogen molecules so there are only single bonds between carbon atoms Or……… They can be unsaturated and have double bonds between the carbons in the fatty acid chain. 4. The glycerol molecu ...
... is partly how fats get their name i.e. C18 or C12 (Lorenzo’s Oil). 2. These chains can also be saturated with Hydrogen molecules so there are only single bonds between carbon atoms Or……… They can be unsaturated and have double bonds between the carbons in the fatty acid chain. 4. The glycerol molecu ...
Molecole per la vita
... Triglycerides are lipids that are obtained by means of the esterification reaction between glycerol and fatty acids and form the fatty tissues of animals and plants. Triglycerides may be saturated or unsaturated depending on whether the hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids contain double bonds or n ...
... Triglycerides are lipids that are obtained by means of the esterification reaction between glycerol and fatty acids and form the fatty tissues of animals and plants. Triglycerides may be saturated or unsaturated depending on whether the hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids contain double bonds or n ...
Name - MsOttoliniBiology
... wall – plants), glycogen (energy storage – animals) Examples: Fats (triglycerides) Oils Waxes Phospholipids ...
... wall – plants), glycogen (energy storage – animals) Examples: Fats (triglycerides) Oils Waxes Phospholipids ...
C - Eric Hamber Secondary
... C10. PRIMARY, SECONDARY, TERTIARY & QUATERNARY STRUCTURE Primary Structure: This simple chain is called the primary structure of a protein. It is simply the order of amino acids. Secondary Structure: - Hydrogen bonds form between the H on the Amino group and the =O in the acid group of close amino a ...
... C10. PRIMARY, SECONDARY, TERTIARY & QUATERNARY STRUCTURE Primary Structure: This simple chain is called the primary structure of a protein. It is simply the order of amino acids. Secondary Structure: - Hydrogen bonds form between the H on the Amino group and the =O in the acid group of close amino a ...
List of molecular weight for each amino acid:
... center peaks tell you about the charge state of the peptide samples? Based on this, what is the average molecular mass (in Daltons) of the peptides corresponding to peak 804.4? 2. (2 pts) We then generated the tandem MS/MS spectrum of this peptide. We know that most MS/MS fragment ions are single ch ...
... center peaks tell you about the charge state of the peptide samples? Based on this, what is the average molecular mass (in Daltons) of the peptides corresponding to peak 804.4? 2. (2 pts) We then generated the tandem MS/MS spectrum of this peptide. We know that most MS/MS fragment ions are single ch ...
4.1_Proteins_Amino_Acids_2011
... chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is called phi (ϕ). By convention, an R group is often used to denote an amin ...
... chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is called phi (ϕ). By convention, an R group is often used to denote an amin ...
Biochemistry Study Guide – Exam 1
... Peptide formation, peptide bond structure Protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quartenary ...
... Peptide formation, peptide bond structure Protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quartenary ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... base sequence of this ssDNA? Remember: AT and GC and use Thymine instead of Uracil when converting back to DNA. ...
... base sequence of this ssDNA? Remember: AT and GC and use Thymine instead of Uracil when converting back to DNA. ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... base sequence of this ssDNA? Remember: AT and GC and use Thymine instead of Uracil when converting back to DNA. ...
... base sequence of this ssDNA? Remember: AT and GC and use Thymine instead of Uracil when converting back to DNA. ...
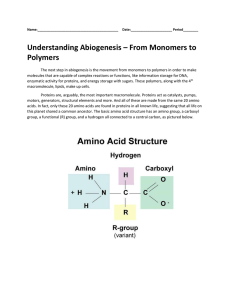
2.3 Carbon Compounds
... Amino acids are the monomers of proteins. Each amino acid has three distinct parts: an amino group, an R group, and a carboxyl group. An amino group has the formula –NH2, a carboxyl group is –COOH, and the R group varies from one amino acid to another. Two amino acids are joined in a chemical reacti ...
... Amino acids are the monomers of proteins. Each amino acid has three distinct parts: an amino group, an R group, and a carboxyl group. An amino group has the formula –NH2, a carboxyl group is –COOH, and the R group varies from one amino acid to another. Two amino acids are joined in a chemical reacti ...
Biomolecules Worksheet
... 5). All enzymes and proteins are chains of specific amino acids, but in order for them to perform their specific tasks, they must also have the correct 3D shape. a) There are a number of structural levels in a protein, describe what is meant by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. ...
... 5). All enzymes and proteins are chains of specific amino acids, but in order for them to perform their specific tasks, they must also have the correct 3D shape. a) There are a number of structural levels in a protein, describe what is meant by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. ...
Notes Guide Part 2
... Primary structure- Form a __________________ of amino acids. Secondary structure- ______________________________ the chain of amino acids. Tertiary Structure- Fold the chain ________________________________. Quaternary Structure- Bring _____ to ________ amino acid subunits together. ...
... Primary structure- Form a __________________ of amino acids. Secondary structure- ______________________________ the chain of amino acids. Tertiary Structure- Fold the chain ________________________________. Quaternary Structure- Bring _____ to ________ amino acid subunits together. ...
Characterisation of glycogenic and ketogenic metabolic pathways
... WP 1: Characterisation of glycogenic and ketogenic metabolic pathways following diets of industrial refined proteins Background: The use of whey protein as a source of amino acids and its effect on reducing risks of diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes [6,7] is the focus of ongoing re ...
... WP 1: Characterisation of glycogenic and ketogenic metabolic pathways following diets of industrial refined proteins Background: The use of whey protein as a source of amino acids and its effect on reducing risks of diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes [6,7] is the focus of ongoing re ...
Proteins
... _enzyme____ 9) Give a more specific name for a protein in your digestive system that speeds hydrolysis of lipids. ___lipase __________ 10) What happens to the structure of a protein as it is heated to a high temperature? What effect does this have on its function? ____The three dimensional structure ...
... _enzyme____ 9) Give a more specific name for a protein in your digestive system that speeds hydrolysis of lipids. ___lipase __________ 10) What happens to the structure of a protein as it is heated to a high temperature? What effect does this have on its function? ____The three dimensional structure ...
Bio/CS 251 Bioinformatics
... The Oxygen atom attracts electrons much more forcefully than does a Hydrogen atom. In this way, oxygen is a strongly electronegative atom. As a result the O-H bond is said to be polarized, such that one of the atoms has a partial negative charge, and the other a partial positive charge. Molecules, s ...
... The Oxygen atom attracts electrons much more forcefully than does a Hydrogen atom. In this way, oxygen is a strongly electronegative atom. As a result the O-H bond is said to be polarized, such that one of the atoms has a partial negative charge, and the other a partial positive charge. Molecules, s ...