DNA - eTutorWorld
... a. How many bases are there in this DNA structure ? _________ b. These two long strands are in the shape of a ________________ helix. c. What type of bondings are seen in DNA double helix ?__________________ d. Name purines and Pyrimidines . _____________,______________,_______________,_____________ ...
... a. How many bases are there in this DNA structure ? _________ b. These two long strands are in the shape of a ________________ helix. c. What type of bondings are seen in DNA double helix ?__________________ d. Name purines and Pyrimidines . _____________,______________,_______________,_____________ ...
DNA replication limits…
... billion nucleotides to its daughter cells. Finally, consider the fact that in life (literally), nothing is perfect. While most DNA replicates with fairly high fidelity, mistakes do happen, with polymerase enzymes sometimes inserting the wrong nucleotide or too many or too few nucleotides into a sequ ...
... billion nucleotides to its daughter cells. Finally, consider the fact that in life (literally), nothing is perfect. While most DNA replicates with fairly high fidelity, mistakes do happen, with polymerase enzymes sometimes inserting the wrong nucleotide or too many or too few nucleotides into a sequ ...
Genetics Objectives 15
... genes on the same chromosome can be separated during meiosis. The closer the genes are to each other, the less likely that a crossing over event will occur between them, and the more closely linked they are. Morgan (108 base pairs): the unit of length for one crossing over to happen every time Centi ...
... genes on the same chromosome can be separated during meiosis. The closer the genes are to each other, the less likely that a crossing over event will occur between them, and the more closely linked they are. Morgan (108 base pairs): the unit of length for one crossing over to happen every time Centi ...
Notes
... DNA is a nucleic acid macromolecule made of nucleotides joined into long strands by covalent bonds. It is located in the ___________________________________________________ cells and the ___________________________________________________ cells. ...
... DNA is a nucleic acid macromolecule made of nucleotides joined into long strands by covalent bonds. It is located in the ___________________________________________________ cells and the ___________________________________________________ cells. ...
Name
... Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing. DNA unwinds The DNA of the daughter strands winds with together with its parent strand. ...
... Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing. DNA unwinds The DNA of the daughter strands winds with together with its parent strand. ...
Chapter 11 Content Mastery - Mecca Hosting Client Sites on rhode
... When the DNA ladder replicates, or copies itself, the ladder breaks apart. You can think of the attach to free nucleotides apart, are ladder of the sides two or, ,ipping.Wh"n the breaking apart as "ipp", the sides"ofthe ladder, and two copies of the DNA are formed. The copies are ...
... When the DNA ladder replicates, or copies itself, the ladder breaks apart. You can think of the attach to free nucleotides apart, are ladder of the sides two or, ,ipping.Wh"n the breaking apart as "ipp", the sides"ofthe ladder, and two copies of the DNA are formed. The copies are ...
DNA Study guide
... 2. Be sure to know the four types of nucleotides and how they pair together. 3. Know the importance of Franklin, Watson, and Crick. 4. Be able to diagram DNA replication until two identical strands of DNA are created, similar to previous homework assignments. 5. Know the role the various enzymes pla ...
... 2. Be sure to know the four types of nucleotides and how they pair together. 3. Know the importance of Franklin, Watson, and Crick. 4. Be able to diagram DNA replication until two identical strands of DNA are created, similar to previous homework assignments. 5. Know the role the various enzymes pla ...
Document
... DNA ligase joins the two Okazaki fragments with phosphodiester bonds to produce a continuous chain Each new DNA molecule is rewound by helicase. Each molecule is identical ...
... DNA ligase joins the two Okazaki fragments with phosphodiester bonds to produce a continuous chain Each new DNA molecule is rewound by helicase. Each molecule is identical ...
Summer 2007
... DNA/RNA, Protein Synthesis and Mutations - REVIEW I. Understand all vocabulary. II. Understand Cell Reproduction III. Understand the scientific process involved in establishing DNA as the heredity ...
... DNA/RNA, Protein Synthesis and Mutations - REVIEW I. Understand all vocabulary. II. Understand Cell Reproduction III. Understand the scientific process involved in establishing DNA as the heredity ...
DNA RNA - wrightbiology
... B. The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. C. Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA. D. Copies of DNA molecules are made. 2. In eukaryotes, DNA C. is located in the ribosomes. A. is located in the nucleus. B. floats freely in the cytoplasm. D. is circular. 3. Which of the ...
... B. The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. C. Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA. D. Copies of DNA molecules are made. 2. In eukaryotes, DNA C. is located in the ribosomes. A. is located in the nucleus. B. floats freely in the cytoplasm. D. is circular. 3. Which of the ...
Ch.22Pt.2_000
... function of different types of nucleic acids •Draw the basic structure of nucleosides and nucleotides •Explain the primary structure of nucleic acids and compare it to protein structure •Describe the structural properties of the DNA double helix •Draw the steps involved in DNA replication •Compare & ...
... function of different types of nucleic acids •Draw the basic structure of nucleosides and nucleotides •Explain the primary structure of nucleic acids and compare it to protein structure •Describe the structural properties of the DNA double helix •Draw the steps involved in DNA replication •Compare & ...
Biology
... f. make and interpret scientific graphs and diagrams g. teach someone else the concepts discussed h. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. summarize the experiments leading to the discovery of DNA as the genetic material 2. diagram and label ...
... f. make and interpret scientific graphs and diagrams g. teach someone else the concepts discussed h. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each student that is able to: 1. summarize the experiments leading to the discovery of DNA as the genetic material 2. diagram and label ...
DNA history and structure KS
... • Replicate = to copy • Enzyme = a chemical that makes a reaction go faster • DNA replicates with the help of an enzymes ...
... • Replicate = to copy • Enzyme = a chemical that makes a reaction go faster • DNA replicates with the help of an enzymes ...
Name - Mission Hills High School
... Or www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/DNA To review click on DNA replication. Proceed through it. 1. How many base pairs are in the human chromosomes? __________________ Now choose Protein synthesis by clicking on it. 1. What happened? __________________________________________________ 2. Match. What base p ...
... Or www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/DNA To review click on DNA replication. Proceed through it. 1. How many base pairs are in the human chromosomes? __________________ Now choose Protein synthesis by clicking on it. 1. What happened? __________________________________________________ 2. Match. What base p ...
Introduction to DNA webquest: Name http://learn.genetics.utah.
... B. Go back and Click onto “what is a gene” ...
... B. Go back and Click onto “what is a gene” ...
Genetic Exchange - Pennsylvania State University
... Self-replicative recombination •Transposon or IS self-replicates copy to splice into DNA at a specific target sequences. • Endonuclease activity cuts target sequence, leaving single strand overhanging ends. •Transposon is ligated to ends. • Gaps are filled by DNA polymerase to yield a target sequen ...
... Self-replicative recombination •Transposon or IS self-replicates copy to splice into DNA at a specific target sequences. • Endonuclease activity cuts target sequence, leaving single strand overhanging ends. •Transposon is ligated to ends. • Gaps are filled by DNA polymerase to yield a target sequen ...
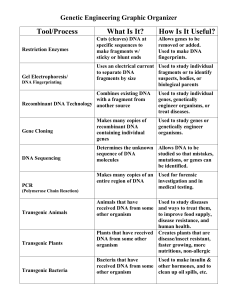
DNA Technology Tools Graphic Organizer KEY
... Makes many copies of an Used for forensic entire region of DNA investigation and in medical testing. Animals that have Used to study diseases received DNA from some and ways to treat them, other organism to improve food supply, disease resistance, and human health. Plants that have received Creates ...
... Makes many copies of an Used for forensic entire region of DNA investigation and in medical testing. Animals that have Used to study diseases received DNA from some and ways to treat them, other organism to improve food supply, disease resistance, and human health. Plants that have received Creates ...
Name: Biology TEST Review DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
... __3__ The base ____ pairs with adenine in RNA. __6__ Nucleotides lining up along the template strand according to base pairing rules helps to ____ genetic material stored in the DNA during replication. __9__ The process that converts DNA to RNA and occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells is ____. ...
... __3__ The base ____ pairs with adenine in RNA. __6__ Nucleotides lining up along the template strand according to base pairing rules helps to ____ genetic material stored in the DNA during replication. __9__ The process that converts DNA to RNA and occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells is ____. ...
Chapter 19 – Molecular Genetic Analysis and Biotechnology
... – Yeast artificial chromosomes – Yeast origin of replication, centromere, telomeres – ~600kb – 1,000kb ...
... – Yeast artificial chromosomes – Yeast origin of replication, centromere, telomeres – ~600kb – 1,000kb ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.