Name
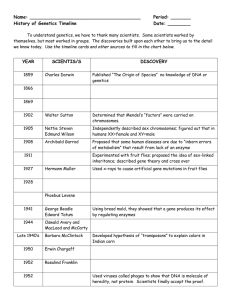
... themselves, but most worked in groups. The discoveries built upon each other to bring us to the detail we know today. Use the timeline cards and other sources to fill in the chart below. ...
... themselves, but most worked in groups. The discoveries built upon each other to bring us to the detail we know today. Use the timeline cards and other sources to fill in the chart below. ...
RNA - PowerSchool Learning (Haiku)
... sequences of mRNA, tRNA, and amino acids, which changes the structure of the protein, which changes its function, which results in a different trait? ...
... sequences of mRNA, tRNA, and amino acids, which changes the structure of the protein, which changes its function, which results in a different trait? ...
The brain and spinal cord comprise the central nervous system
... • Barr Body – concept of X-Chromosome Inactivation and Dosage Compensation • Nondisjunction of autosomes (example Down Syndrome) and Sex Chromosomes • In utero detection methods for genetic defects: Amniocentesis, Chorionic villi sampling • Exceptions to the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Concep ...
... • Barr Body – concept of X-Chromosome Inactivation and Dosage Compensation • Nondisjunction of autosomes (example Down Syndrome) and Sex Chromosomes • In utero detection methods for genetic defects: Amniocentesis, Chorionic villi sampling • Exceptions to the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Concep ...
Biology - The Roblesite
... ________________, which lets the enzyme recognize the start of a gene. 13. When mRNA is being assembled, it grows in the ________to __________direction. 14. These numbers are based on the position of ____________atoms in the ________________molecules, which, along with phosphate groups, comprise the ...
... ________________, which lets the enzyme recognize the start of a gene. 13. When mRNA is being assembled, it grows in the ________to __________direction. 14. These numbers are based on the position of ____________atoms in the ________________molecules, which, along with phosphate groups, comprise the ...
DNA & Heredity
... and Cytosine paired with Guanine (Chargaff’s Rule) Rosalind Franklin – in 1952 took x-ray photographs of DNA. Watson and Crick – in 1953 were credited with the discovery of the structure of DNA Sydney Brenner- in 1960 found the existence of RNA Walter Gilbert and Team- in 1977 found a way to read th ...
... and Cytosine paired with Guanine (Chargaff’s Rule) Rosalind Franklin – in 1952 took x-ray photographs of DNA. Watson and Crick – in 1953 were credited with the discovery of the structure of DNA Sydney Brenner- in 1960 found the existence of RNA Walter Gilbert and Team- in 1977 found a way to read th ...
Student work sheets for Power Point Slides
... 15) An anticodon consists of three base pairs which are opposite to the base pairs in the mRNA. Slide 4 16) Describe what you see from this slide. Slide 5 17) During transcription process, the complimentary RNA is read from the 5’ end to the 3’ end of the RNA strand. 18) One of the DNA strand is kno ...
... 15) An anticodon consists of three base pairs which are opposite to the base pairs in the mRNA. Slide 4 16) Describe what you see from this slide. Slide 5 17) During transcription process, the complimentary RNA is read from the 5’ end to the 3’ end of the RNA strand. 18) One of the DNA strand is kno ...
Wednesday Sept 22, 2010 Bio 111 Dr. Ellen Yerger
... • Individual chains in cells • Aka “single-stranded”: ssRNA • Chains generally from 505000 nucleotides • Distributed throughout the cell ...
... • Individual chains in cells • Aka “single-stranded”: ssRNA • Chains generally from 505000 nucleotides • Distributed throughout the cell ...
Capsid Virus Lysogenic Infection B acteriophage Prophage Lytic
... Single-celled organism without a membranebound nucleus ...
... Single-celled organism without a membranebound nucleus ...
Molecular Genetics - Southmoreland School District
... Chromosomal and Genetic Mutations A mutation is any permanent transmissible change of genetic material. Many different types of mutations can occur. They can either affect a few nucleotides (point mutations) or affect large portions of DNA (chromosomal mutations). These will ultimately affect the sh ...
... Chromosomal and Genetic Mutations A mutation is any permanent transmissible change of genetic material. Many different types of mutations can occur. They can either affect a few nucleotides (point mutations) or affect large portions of DNA (chromosomal mutations). These will ultimately affect the sh ...
RNA - Montville.net
... sequences of mRNA, tRNA, and amino acids, which changes the structure of the protein, which changes its function, which results in a different trait? ...
... sequences of mRNA, tRNA, and amino acids, which changes the structure of the protein, which changes its function, which results in a different trait? ...
Genetics
... This helix is referred to as chromatin during interphase of the cell cyce & as chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. In the double helix, complemetary strands match-up in a specific way. Think of it as a latter that got sawed down the middle. When you put it together again, each step conne ...
... This helix is referred to as chromatin during interphase of the cell cyce & as chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. In the double helix, complemetary strands match-up in a specific way. Think of it as a latter that got sawed down the middle. When you put it together again, each step conne ...
Name
... 5.) Measure and cut out two 2 meter lengths of string. Tape down one length of the string at both ends onto your work area. 6.) Start from the end of the taped down string, place a Sugar, then a Phosphate, alternating with the sugars and phosphates, and then tape the 12 Sugars and 12 Phosphates on e ...
... 5.) Measure and cut out two 2 meter lengths of string. Tape down one length of the string at both ends onto your work area. 6.) Start from the end of the taped down string, place a Sugar, then a Phosphate, alternating with the sugars and phosphates, and then tape the 12 Sugars and 12 Phosphates on e ...
Entry Test Sample for MS in Bioinformatics Program Weightage Distribution:
... A. Each of R, S, X and Y is adjacent to W. B. X is adjacent to Y. C. Each of R and S is adjacent to Z. Which of the following is a pair of countries that can be the same color? A. R and S B. S and W C. W and X D. X and Y 3. Many surveys _____ out the idea that effective communication is essential fo ...
... A. Each of R, S, X and Y is adjacent to W. B. X is adjacent to Y. C. Each of R and S is adjacent to Z. Which of the following is a pair of countries that can be the same color? A. R and S B. S and W C. W and X D. X and Y 3. Many surveys _____ out the idea that effective communication is essential fo ...
Wednesday Sept 22, 2010 Bio 111 Dr. Ellen Yerger
... • Individual chains in cells • Aka “single-stranded”: ssRNA • Chains generally from 505000 nucleotides • Distributed throughout the cell ...
... • Individual chains in cells • Aka “single-stranded”: ssRNA • Chains generally from 505000 nucleotides • Distributed throughout the cell ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.























