Document
... Gene – a section of DNA controlling the making of specific proteins Proteins – substances that determine our physical appearance Amino acid – a chain of these make up a protein Replication – the copying of a DNA molecule mRNA – a chemical used to read the DNA in the nucleus which takes the ...
... Gene – a section of DNA controlling the making of specific proteins Proteins – substances that determine our physical appearance Amino acid – a chain of these make up a protein Replication – the copying of a DNA molecule mRNA – a chemical used to read the DNA in the nucleus which takes the ...
Molecular genetics of bacteria
... – Replication is bidirectional – In each direction, there is a replication fork. – Bacterial DNA is circular, so there is one Origin and one terminus ...
... – Replication is bidirectional – In each direction, there is a replication fork. – Bacterial DNA is circular, so there is one Origin and one terminus ...
forensic science
... Remember: Each chromosome is a very long DNA molecule that contains many genes. The DNA controls the production of proteins within a cell. Gene: A segment of DNA that is part of a chromosome that is responsible for inherited traits such as eye ...
... Remember: Each chromosome is a very long DNA molecule that contains many genes. The DNA controls the production of proteins within a cell. Gene: A segment of DNA that is part of a chromosome that is responsible for inherited traits such as eye ...
ANSWER KEY BIO SOL Review 16 - DNA - RNA
... carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape c. DNA d. cell size 12. (2003-9) Which of the followi ...
... carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape c. DNA d. cell size 12. (2003-9) Which of the followi ...
BIO SOL Review 16
... carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape c. DNA d. cell size 12. (2003-9) Which of the followi ...
... carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape c. DNA d. cell size 12. (2003-9) Which of the followi ...
Replication
... significantly, since DNA strands must be separated at ambient conditions at which the double helix is very stable, a special molecular motor, called helicase moves along DNA and separates the complementary strands consuming the ATP energy, of course. Special small proteins, called SSB (for single-st ...
... significantly, since DNA strands must be separated at ambient conditions at which the double helix is very stable, a special molecular motor, called helicase moves along DNA and separates the complementary strands consuming the ATP energy, of course. Special small proteins, called SSB (for single-st ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Trisomy 21, or Down syndrome, occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement of 46 chromosomes plus one (extra) chromosome #21. Such individuals therefore have 47 chromosomes. While there is impaired fertility of both sexes, females are more likely to be fertile than males. Assume that ...
... Trisomy 21, or Down syndrome, occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement of 46 chromosomes plus one (extra) chromosome #21. Such individuals therefore have 47 chromosomes. While there is impaired fertility of both sexes, females are more likely to be fertile than males. Assume that ...
DNA Notes - Firelands Local Schools
... DNA – DNA REGULATES ALL CELLULAR ACTIVITY BY REGULATING PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. – DNA IS A SELF-REPLICATING MOLECULE WHICH GETS PASSED ON FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT. ...
... DNA – DNA REGULATES ALL CELLULAR ACTIVITY BY REGULATING PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. – DNA IS A SELF-REPLICATING MOLECULE WHICH GETS PASSED ON FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT. ...
Vocabulary List
... for RNA) and a nitrogen base (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 5. Nitrogenous Bases – the parts of DNA and RNA that pair (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 6. DNA Replication – the process of making another copy of the genetic code by a semi-conservative process. Occurs within the nucleus 7 ...
... for RNA) and a nitrogen base (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 5. Nitrogenous Bases – the parts of DNA and RNA that pair (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 6. DNA Replication – the process of making another copy of the genetic code by a semi-conservative process. Occurs within the nucleus 7 ...
DNA Structure powerpoint
... • Why is DNA wrapped so tightly? • How are DNA, proteins, and traits related? ...
... • Why is DNA wrapped so tightly? • How are DNA, proteins, and traits related? ...
DNA
... DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
... DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
DNA Structure and Replication Integrated Science 4
... The percentages of corresponding bases was equal in almost any sample of DNA regardless of the organism from which it came. 9. Describe the basic structure of a DNA molecule (pg. 357-358) double helix – a pair of twisted strands bonded together by nitrogenous bases ...
... The percentages of corresponding bases was equal in almost any sample of DNA regardless of the organism from which it came. 9. Describe the basic structure of a DNA molecule (pg. 357-358) double helix – a pair of twisted strands bonded together by nitrogenous bases ...
Specification
... and a base, where the bases are Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine). The term genetic code refers in this context to the sequence of bases on the DNA molecule. DNA replication comprises unwinding the DNA molecule, breaking the bonds between the strands, replication, and repackaging. Candidates shou ...
... and a base, where the bases are Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine). The term genetic code refers in this context to the sequence of bases on the DNA molecule. DNA replication comprises unwinding the DNA molecule, breaking the bonds between the strands, replication, and repackaging. Candidates shou ...
DNA versus RNA Notes File
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
Unit 2 – Genetics Content Map
... Unit Essential Question: What makes organisms unique? GPS Standard(s): SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. A. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. B. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. C. Using Mendel’s laws, ex ...
... Unit Essential Question: What makes organisms unique? GPS Standard(s): SB2. Students will analyze how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. A. Distinguish between DNA and RNA. B. Explain the role of DNA in storing and transmitting cellular information. C. Using Mendel’s laws, ex ...
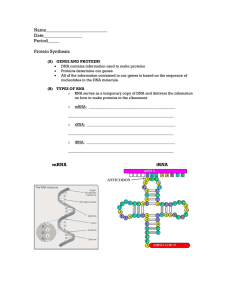
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
DNA
... o Watson, Crick and Franklin received Nobel Prize in Medicine. Gene Definition: a short, active section of DNA, which contains the instructions (code) for building all proteins. The code (directions for building the protein) is the order of bases on DNA. Each chromosome is made up of many hundre ...
... o Watson, Crick and Franklin received Nobel Prize in Medicine. Gene Definition: a short, active section of DNA, which contains the instructions (code) for building all proteins. The code (directions for building the protein) is the order of bases on DNA. Each chromosome is made up of many hundre ...
15.3 Gene Technologies in Detail
... Tools to Manipulate Genes II. Gel Electrophoresis= The process by which electrically charged DNA particles suspended in gel move through the gel because of an electric charge. a. The DNA forms “lanes.” b. Used to compare DNA, such as that of a suspect or a victim. ...
... Tools to Manipulate Genes II. Gel Electrophoresis= The process by which electrically charged DNA particles suspended in gel move through the gel because of an electric charge. a. The DNA forms “lanes.” b. Used to compare DNA, such as that of a suspect or a victim. ...
DNA Sequencing
... in-vitro DNA synthesis using ‘terminators’, use of dideoxinucleotides that do not permit chain elongation after their integration DNA synthesis using deoxy- and dideoxynucleotides that results in termination of synthesis at specific nucleotides Requires a primer, DNA polymerase, a template, a ...
... in-vitro DNA synthesis using ‘terminators’, use of dideoxinucleotides that do not permit chain elongation after their integration DNA synthesis using deoxy- and dideoxynucleotides that results in termination of synthesis at specific nucleotides Requires a primer, DNA polymerase, a template, a ...
key
... 1. A critical feature of cloning plasmids is the presence of a selectable marker such as antibiotic (or ampicillin or …) resistance. 2. Northern blotting is a technique in which RNA is fractionated on a gel, and transferred to a membrane. The RNA attached to the membrane is incubated with a labeled ...
... 1. A critical feature of cloning plasmids is the presence of a selectable marker such as antibiotic (or ampicillin or …) resistance. 2. Northern blotting is a technique in which RNA is fractionated on a gel, and transferred to a membrane. The RNA attached to the membrane is incubated with a labeled ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.