bacteriophage
... are ‘male-specific’ phages, since they infect the cell by attaching to the tips of the pili specified by the F plasmid As the replication cycle proceeds, one of the phage proteins that is produced is able to bind to the single-stranded DNA and divert it into the production of phage particles by targ ...
... are ‘male-specific’ phages, since they infect the cell by attaching to the tips of the pili specified by the F plasmid As the replication cycle proceeds, one of the phage proteins that is produced is able to bind to the single-stranded DNA and divert it into the production of phage particles by targ ...
1 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... b. contains 13-bp inverted repeat at the termini (TIR) c. forms a two-element system d. first cloned from the waxy locus e. moves via cut-and-paste (gain-and-loss) mechanism 6. Many transposons in plants are inactive, but can be activated. Which mechanism has not been shown to make a major contribut ...
... b. contains 13-bp inverted repeat at the termini (TIR) c. forms a two-element system d. first cloned from the waxy locus e. moves via cut-and-paste (gain-and-loss) mechanism 6. Many transposons in plants are inactive, but can be activated. Which mechanism has not been shown to make a major contribut ...
Repair of Damaged DNA
... causes incorporation of an incorrect base during replication • DNA glycosylases hydrolyze base-sugar N-glycosidic bonds • Deaminated bases are then removed and replaced ...
... causes incorporation of an incorrect base during replication • DNA glycosylases hydrolyze base-sugar N-glycosidic bonds • Deaminated bases are then removed and replaced ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... • very extended and tangled during interphase • condensed into discrete chromosomes during mitosis ...
... • very extended and tangled during interphase • condensed into discrete chromosomes during mitosis ...
Notes
... 5. The message is decoded into protein by anticodons on tRNA that are complementary the codons of mRNA. ...
... 5. The message is decoded into protein by anticodons on tRNA that are complementary the codons of mRNA. ...
AP Biology Ch. 12 Reading Guide – Molecular Biology of the Gene
... 6. What is transformation and why is it possible to do this with different organisms? ...
... 6. What is transformation and why is it possible to do this with different organisms? ...
the nucleic acids - Y11-Biology-SG
... the two strands together are the H bonds that form between complementary bases. ...
... the two strands together are the H bonds that form between complementary bases. ...
Exam 2
... P selectively labels nucleotides (via phosphate group) but not proteins because P is in nucleic acid but not protein. 35S elements selectively labels proteins but not nucleic acids because S is in protein but not nucleic acids. Thus, the location of the DNA and proteins could be independently follow ...
... P selectively labels nucleotides (via phosphate group) but not proteins because P is in nucleic acid but not protein. 35S elements selectively labels proteins but not nucleic acids because S is in protein but not nucleic acids. Thus, the location of the DNA and proteins could be independently follow ...
DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis - Social Circle City Schools
... Process of DNA Replication • Enzymes (RNA polymerase) “unzips” molecule of DNA at the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases. • Nitrogen bases that are floating around in the nucleus base pair with the unzipped DNA to make 2 new strands: – Each new strand contains an original strand and a new s ...
... Process of DNA Replication • Enzymes (RNA polymerase) “unzips” molecule of DNA at the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases. • Nitrogen bases that are floating around in the nucleus base pair with the unzipped DNA to make 2 new strands: – Each new strand contains an original strand and a new s ...
Transcription And Translation
... referred to as the SENSE or TEMPLATE strand. The complimentary DNA strand that is not used is referred to as the NONSENSE strand. Only a very small part of the genome is copied. April 20, 2001 ...
... referred to as the SENSE or TEMPLATE strand. The complimentary DNA strand that is not used is referred to as the NONSENSE strand. Only a very small part of the genome is copied. April 20, 2001 ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... The fact that there is a problem maintaining the very ends of eukaryotic chromosomes during replication has to do with 1. the fact that eukaryotic chromosomes are linear. 2. the inability of DNA polymerases to initiate synthesis without a primer. 3. the restriction that DNA synthesis must occur in a ...
... The fact that there is a problem maintaining the very ends of eukaryotic chromosomes during replication has to do with 1. the fact that eukaryotic chromosomes are linear. 2. the inability of DNA polymerases to initiate synthesis without a primer. 3. the restriction that DNA synthesis must occur in a ...
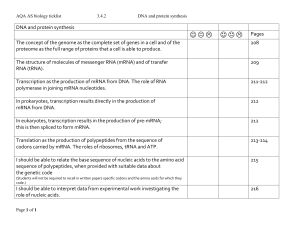
doc 3.4.2 protein synthesis checklist
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
HigH-THrougHpuT dna sequencing
... always paired with its complementary base on the opposing strand. A on one strand is paired with T on the other strand, T with A, G with C, and C with G. Variations of the nucleotide sequence are a normal feature of DNA. However, if these changes affect the way a gene functions, they can result in d ...
... always paired with its complementary base on the opposing strand. A on one strand is paired with T on the other strand, T with A, G with C, and C with G. Variations of the nucleotide sequence are a normal feature of DNA. However, if these changes affect the way a gene functions, they can result in d ...
CONFOUNDING PHYLOGENETIC TREES
... -Despite instability in clones of E. coli, some PAIs have been part of genome for millions of years -these features suggest that PAIs are derived from transposons that have become fixed in the genome leading to speciation -because the transfer of islands are often relatively recent events in evoluti ...
... -Despite instability in clones of E. coli, some PAIs have been part of genome for millions of years -these features suggest that PAIs are derived from transposons that have become fixed in the genome leading to speciation -because the transfer of islands are often relatively recent events in evoluti ...
Nucleotide is composed of a ribose sugar, a base and a phosphate
... • DNA polymerase III – main DNApol involved in replication (catalysis the incorporates of the nucleotides into the growing DNA strand) • DNA polymerase II – DNA repair and a minor role in replication • DNA polymerase I – DNA repair and SOS responses. Fills gap from removed RNA primer in lagging stra ...
... • DNA polymerase III – main DNApol involved in replication (catalysis the incorporates of the nucleotides into the growing DNA strand) • DNA polymerase II – DNA repair and a minor role in replication • DNA polymerase I – DNA repair and SOS responses. Fills gap from removed RNA primer in lagging stra ...
CfE Higher Biology
... moves along the strand DNA polymerase moves along the 3’ end continuously adding nucleotides. This strand is called the leading strand. ...
... moves along the strand DNA polymerase moves along the 3’ end continuously adding nucleotides. This strand is called the leading strand. ...
DNA Structure and DNA Replication
... ► Due to Chargaff’s discovery, we now understand why DNA is able to copy itself without making _________ or __________ the order of nucleotides. ► This explains why each new cell is able to always receive an __________ ________ of the __________ cells DNA. How Replication Works ► To begin replicatio ...
... ► Due to Chargaff’s discovery, we now understand why DNA is able to copy itself without making _________ or __________ the order of nucleotides. ► This explains why each new cell is able to always receive an __________ ________ of the __________ cells DNA. How Replication Works ► To begin replicatio ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 14. When a plant fertilizes itself, it is called ______________. 15. What is it called when cells are copied with half the number of chromosomes? 16. What factors have an influence on your traits? 17. Why do sex-linked disorders occur more often in males? 18. Three bases code for one ______. 19. Wha ...
... 14. When a plant fertilizes itself, it is called ______________. 15. What is it called when cells are copied with half the number of chromosomes? 16. What factors have an influence on your traits? 17. Why do sex-linked disorders occur more often in males? 18. Three bases code for one ______. 19. Wha ...
GENETICS 603 Outline and Key Topics for Lecture 1 DNA
... DNA in which two strands, running in opposite directions, were held together by Hydrogen bonds between the base pairs A and T, and G and C. The base pairs are in the center of the molecule like the steps of a spiral staircase, with the phosphate-sugar (deoxyribose) backbones of the two strands formi ...
... DNA in which two strands, running in opposite directions, were held together by Hydrogen bonds between the base pairs A and T, and G and C. The base pairs are in the center of the molecule like the steps of a spiral staircase, with the phosphate-sugar (deoxyribose) backbones of the two strands formi ...
Only One Strand of DNA Is Translated
... centrifuged on a CsCl gradient. DNA-RNA hybrids are denser than DNA-DNA hybrids (RNA nucleotides have an extra oxygen atom in their ribose sugars and are heavier), so that the cytosine-rich T7 DNA strand with bound poly-UG was denser than the other T7 DNA strand, which binds far less RNA. In this fa ...
... centrifuged on a CsCl gradient. DNA-RNA hybrids are denser than DNA-DNA hybrids (RNA nucleotides have an extra oxygen atom in their ribose sugars and are heavier), so that the cytosine-rich T7 DNA strand with bound poly-UG was denser than the other T7 DNA strand, which binds far less RNA. In this fa ...
Vocabulary Glossary - CTAE Resource Network
... 10. Gel Electrophoresis: Technique to separate protein molecules of various sizes by moving them through a block of gel 11. Introns: Non-coding segments of DNA interrupting a gene-coding sequence 12. Marker DNA: Gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome which can be used to identify ...
... 10. Gel Electrophoresis: Technique to separate protein molecules of various sizes by moving them through a block of gel 11. Introns: Non-coding segments of DNA interrupting a gene-coding sequence 12. Marker DNA: Gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome which can be used to identify ...
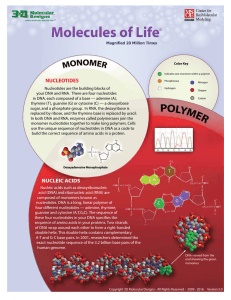
Nucleic Acids Placemat
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
Carbohydrate Tutorial
... Role of DNA 3. While you are growing you need DNA to produce more _____________. 4. As an adult you also need DNA to : a. b. c. The Cell 5. DNA directs the entire operation by issuing instructions to make things you need such as __________________. 6. DNA allows organisms to make _______________ of ...
... Role of DNA 3. While you are growing you need DNA to produce more _____________. 4. As an adult you also need DNA to : a. b. c. The Cell 5. DNA directs the entire operation by issuing instructions to make things you need such as __________________. 6. DNA allows organisms to make _______________ of ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.