Unit 4
... The two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each functions as a template for synthesis of a new complementary strand. The experiment was using the culturing of bacteria. 10. Describe the process of DNA replication, and explain the role of helicase, single strand binding protein, DNA poly ...
... The two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each functions as a template for synthesis of a new complementary strand. The experiment was using the culturing of bacteria. 10. Describe the process of DNA replication, and explain the role of helicase, single strand binding protein, DNA poly ...
DNA Replication
... • The Instructions for your growth is in the DNA • As a multicellular organism, you need instructions in every cell. • Before MITOSIS and MEIOSIS, your DNA copies itself so that each new cell has an exact copy INTERPHASE ...
... • The Instructions for your growth is in the DNA • As a multicellular organism, you need instructions in every cell. • Before MITOSIS and MEIOSIS, your DNA copies itself so that each new cell has an exact copy INTERPHASE ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... 7.) Why is the percentage of cytosine always the same as the percentage of guanine? - they always pair with each other 8.) Describe the role of histones and nucleosomes in chromosome structure. - nucleosomes are composed of DNA wound around histones ...
... 7.) Why is the percentage of cytosine always the same as the percentage of guanine? - they always pair with each other 8.) Describe the role of histones and nucleosomes in chromosome structure. - nucleosomes are composed of DNA wound around histones ...
Mock Exam 3 Chapters 14-18 Anthony Todd http
... c. MIH which inhibits the formation of Mullerian ducts so male development can continue d. A and B are correct e. B and C are correct Use the following information for Questions 15 and 16: A dominant sex-linked gene B produces white bars on black chickens. A clutch of chickens has equal numbers of b ...
... c. MIH which inhibits the formation of Mullerian ducts so male development can continue d. A and B are correct e. B and C are correct Use the following information for Questions 15 and 16: A dominant sex-linked gene B produces white bars on black chickens. A clutch of chickens has equal numbers of b ...
Unit4 DNA and Protein Syn
... Bio EOC Review Topics for DNA and Protein Synthesis o DNA: structure - What are the parts of a nucleotide? sugar, acid, N-bases (and be able to identify these parts on a diagram) A-T / T-A / C-G / G-C (complementary N-base pairing between 2 strands in DNA molecule) types of bonds that hold the DNA m ...
... Bio EOC Review Topics for DNA and Protein Synthesis o DNA: structure - What are the parts of a nucleotide? sugar, acid, N-bases (and be able to identify these parts on a diagram) A-T / T-A / C-G / G-C (complementary N-base pairing between 2 strands in DNA molecule) types of bonds that hold the DNA m ...
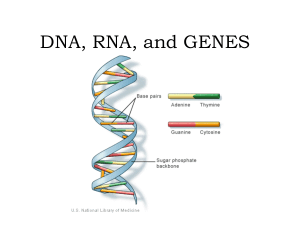
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
... molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
Unit4 DNA and Protein Syn
... Bio EOC Review Topics for DNA and Protein Synthesis o DNA: structure - What are the parts of a nucleotide? sugar, acid, N-bases (and be able to identify these parts on a diagram) A-T / T-A / C-G / G-C (complementary N-base pairing between 2 strands in DNA molecule) types of bonds that hold the DNA m ...
... Bio EOC Review Topics for DNA and Protein Synthesis o DNA: structure - What are the parts of a nucleotide? sugar, acid, N-bases (and be able to identify these parts on a diagram) A-T / T-A / C-G / G-C (complementary N-base pairing between 2 strands in DNA molecule) types of bonds that hold the DNA m ...
Fill-in-Notes - Pearland ISD
... DNA codes for RNA, which guides ___________________ From Genes to Genetic expression (The central dogma of molecular biology) _____->_____->____________->__________-> __________________ Answer the following questions as you watch the video ...
... DNA codes for RNA, which guides ___________________ From Genes to Genetic expression (The central dogma of molecular biology) _____->_____->____________->__________-> __________________ Answer the following questions as you watch the video ...
Chapter 10
... 6. Both DNA and RNA consist of a long chain of nucleotides. DNA however, contains the base thymine. RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. DNA is double-stranded; RNA is a single-stranded. DNA has a deoxyribose sugar; RNA has a ribose sugar. 7. Messenger RNA carries protein assembly instructions, ...
... 6. Both DNA and RNA consist of a long chain of nucleotides. DNA however, contains the base thymine. RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. DNA is double-stranded; RNA is a single-stranded. DNA has a deoxyribose sugar; RNA has a ribose sugar. 7. Messenger RNA carries protein assembly instructions, ...
Molecular Genetics
... deoxyribose), a phosphate group and 1 of 4 bases. A small section of DNA. These occur because DNA is replicated in the 5’ to 3’ direction and on the other strand must be made up in short sections (the Okazaki fragments). The site that a repressor protein can bind to prevent transcription One or more ...
... deoxyribose), a phosphate group and 1 of 4 bases. A small section of DNA. These occur because DNA is replicated in the 5’ to 3’ direction and on the other strand must be made up in short sections (the Okazaki fragments). The site that a repressor protein can bind to prevent transcription One or more ...
DNA: Structure, Function, and Replication
... James ● Figured out that the sugar-phosphate backbone is on the outside, and the Mid nitrogen base pairings are on the inside Watson 1950’s and Francis ● Watson & Crick’s model explained Chargaff’s rules (A=T; C=G) ● Based on their model, they came up with a mechanism for replication Crick ● Semicon ...
... James ● Figured out that the sugar-phosphate backbone is on the outside, and the Mid nitrogen base pairings are on the inside Watson 1950’s and Francis ● Watson & Crick’s model explained Chargaff’s rules (A=T; C=G) ● Based on their model, they came up with a mechanism for replication Crick ● Semicon ...
DNA
... • naturally exist in bacterial cells • Often provide bacteria with genetic advantages – antibiotic resistance ...
... • naturally exist in bacterial cells • Often provide bacteria with genetic advantages – antibiotic resistance ...
7 - DNA.notebook
... DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid A code in a cell's hereditary material; It contains information for an organism‛s growth and function. • DNA is shaped like a spiral staircase called a "double helix" • Its shape is made up of the sides of the ladder and the rungs (steps). - Sides of the ladder = Deoxyribo ...
... DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid A code in a cell's hereditary material; It contains information for an organism‛s growth and function. • DNA is shaped like a spiral staircase called a "double helix" • Its shape is made up of the sides of the ladder and the rungs (steps). - Sides of the ladder = Deoxyribo ...
Genetics Lecture I
... 5a~ students know the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and proteins 5b~ students know how to apply base-pairing rules to explain precise copying of DNA during semiconservative replication and the transcription of information from DNA into RNA ...
... 5a~ students know the general structures and functions of DNA, RNA, and proteins 5b~ students know how to apply base-pairing rules to explain precise copying of DNA during semiconservative replication and the transcription of information from DNA into RNA ...
The Chemistry of Inheritance
... Leading and Lagging Strand Synthesis • DNA polymerase can only add to a free 3´ OH. • The two template strands are antiparallel. • Therefore, only one of the strands can provide a template for continuous 5´ to 3´ new strand synthesis. The strand synthesized from this template is called the leading ...
... Leading and Lagging Strand Synthesis • DNA polymerase can only add to a free 3´ OH. • The two template strands are antiparallel. • Therefore, only one of the strands can provide a template for continuous 5´ to 3´ new strand synthesis. The strand synthesized from this template is called the leading ...
Nucleic Acids What are they
... Model proposed by Watson & Crick, 1953 Two sugar-phosphate strands, next to each other, but running in opposite directions. Specific Hydrogen bonds occur among bases from one chain to the other: A---T ...
... Model proposed by Watson & Crick, 1953 Two sugar-phosphate strands, next to each other, but running in opposite directions. Specific Hydrogen bonds occur among bases from one chain to the other: A---T ...
What is a protein? - Hicksville Public Schools
... DNA-PROTEIN CONNECTION • Genes contain coded information • This information is used to make proteins that are required for it’s shape and function. ...
... DNA-PROTEIN CONNECTION • Genes contain coded information • This information is used to make proteins that are required for it’s shape and function. ...
Genetics
... 12. A winding shape, similar to a spiral; the DNA molecule has a double-helix shape, which is two helixes twisted around each other. 13. The process used to make genetically identical copies of an organism. 14. An organism's physical feature, determined by a gene. Down 1. Substance within the cell b ...
... 12. A winding shape, similar to a spiral; the DNA molecule has a double-helix shape, which is two helixes twisted around each other. 13. The process used to make genetically identical copies of an organism. 14. An organism's physical feature, determined by a gene. Down 1. Substance within the cell b ...
1 Questions: Concept Check 11.1 1. How did Griffith`s experiments
... Sickle cell anemia is caused by the hemoglobin variant Hb S. In this variant, the hydrophobic amino acid valine takes the place of hydrophilic glutamic acid at the sixth amino acid position of the HBB polypeptide chain. This substitution creates a hydrophobic spot on the outside of the protein struc ...
... Sickle cell anemia is caused by the hemoglobin variant Hb S. In this variant, the hydrophobic amino acid valine takes the place of hydrophilic glutamic acid at the sixth amino acid position of the HBB polypeptide chain. This substitution creates a hydrophobic spot on the outside of the protein struc ...
ppt - Faculty
... Nucleotides have to be assembled and available in the nucleus, along with energy to make bonds between nucleotides. DNA helicase enzymes unzip the DNA helix by breaking the H-bonds between bases. Once the polymerases have opened the DNA, an area known as the replication bubble forks (always initiate ...
... Nucleotides have to be assembled and available in the nucleus, along with energy to make bonds between nucleotides. DNA helicase enzymes unzip the DNA helix by breaking the H-bonds between bases. Once the polymerases have opened the DNA, an area known as the replication bubble forks (always initiate ...
Unit 6 Review: Answer Key - East Providence High School
... 9. One DNA strand is coped by mRNA during transcription DNA Translation 10. mRNA gets read by tRNA and produces an amino acid 11. Chains of amino acids form genes which give instructions to produce proteins. 12. The AUG codon codes for start/methionine Mutations 13. Substitutions: point mutation ins ...
... 9. One DNA strand is coped by mRNA during transcription DNA Translation 10. mRNA gets read by tRNA and produces an amino acid 11. Chains of amino acids form genes which give instructions to produce proteins. 12. The AUG codon codes for start/methionine Mutations 13. Substitutions: point mutation ins ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.