In Vitro Selection of Metabolite-Dependent Self-Cleaving
... Similar to enzymes, many RNAs have catalytic properties, such as peptide bond formation and self-cleaving. Many self-cleaving ribozymes have already been found in viral, bacterial, and mammalian genomes. However, only the glmS ribozyme, found in Gram-positive bacteria, has been found to self-cleave ...
... Similar to enzymes, many RNAs have catalytic properties, such as peptide bond formation and self-cleaving. Many self-cleaving ribozymes have already been found in viral, bacterial, and mammalian genomes. However, only the glmS ribozyme, found in Gram-positive bacteria, has been found to self-cleave ...
DNA
... 1. DNA unwinds 2. DNA HELICASE enzyme unzips the weak hydrogen bonds between base pairs 3. Complementary RNA PRIMERS are added to the DNA to begin copying. 4. DNA POLYMERASE enzyme matches up DNA nucleotides to 3’-5’ end continuously(“leading strand”) and later the RNA primers are replaced with DNA ...
... 1. DNA unwinds 2. DNA HELICASE enzyme unzips the weak hydrogen bonds between base pairs 3. Complementary RNA PRIMERS are added to the DNA to begin copying. 4. DNA POLYMERASE enzyme matches up DNA nucleotides to 3’-5’ end continuously(“leading strand”) and later the RNA primers are replaced with DNA ...
DNA replication - Understanding Evolution
... Students will understand that 1) molecular mechanisms that preserve the fidelity of the genetic sequence have been favored by natural selection, 2) some entities, such as HIV, lack some of these mechanisms and so have a higher rate of mutation and evolution, and 3) many challenges posed to medical s ...
... Students will understand that 1) molecular mechanisms that preserve the fidelity of the genetic sequence have been favored by natural selection, 2) some entities, such as HIV, lack some of these mechanisms and so have a higher rate of mutation and evolution, and 3) many challenges posed to medical s ...
Carbohydrate Tutorial
... Role of DNA 3. While you are growing you need DNA to produce more _____________. 4. As an adult you also need DNA to : a. b. c. The Cell 5. DNA directs the entire operation by issuing instructions to make things you need such as __________________. 6. DNA allows organisms to make _______________ of ...
... Role of DNA 3. While you are growing you need DNA to produce more _____________. 4. As an adult you also need DNA to : a. b. c. The Cell 5. DNA directs the entire operation by issuing instructions to make things you need such as __________________. 6. DNA allows organisms to make _______________ of ...
Building DNA -Hemoglobin Gene
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is one of the two types of nucleic acids found in organisms and viruses. The structure of DNA determines which proteins particular cells will make. The general structure of DNA was determined in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick. The model of DNA that they constructe ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is one of the two types of nucleic acids found in organisms and viruses. The structure of DNA determines which proteins particular cells will make. The general structure of DNA was determined in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick. The model of DNA that they constructe ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Test
... Transcription occurs in the nucleus. The code from DNA is transferred via complementary base pairs to mRNA. ...
... Transcription occurs in the nucleus. The code from DNA is transferred via complementary base pairs to mRNA. ...
Protein Synthesis
... As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA, it untwists the double helix and separates the strands RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the mRNA molecule ...
... As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA, it untwists the double helix and separates the strands RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the mRNA molecule ...
DNA Replication Simulation WKST
... As you pulled the strands apart, you may have noticed the ends were still wound around each other. If there was nothing to release this tension, it would continue to tangle up the DNA. To demonstrate this, pull on two origins of replication on your string and notice what happens between the replica ...
... As you pulled the strands apart, you may have noticed the ends were still wound around each other. If there was nothing to release this tension, it would continue to tangle up the DNA. To demonstrate this, pull on two origins of replication on your string and notice what happens between the replica ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... The Genetic Code • Triplet code every 3 bases of mRNA codes for 1 amino acid – Each 3 letter (nucleotide) unit of mRNA is called a ...
... The Genetic Code • Triplet code every 3 bases of mRNA codes for 1 amino acid – Each 3 letter (nucleotide) unit of mRNA is called a ...
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis-New
... bonded best with guanine (G). • DNA forms a double-helix shape, with two spiraled polynucleotide strands bonded down the middle. ...
... bonded best with guanine (G). • DNA forms a double-helix shape, with two spiraled polynucleotide strands bonded down the middle. ...
Part 4 Transcription
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
Chapter 20 DNA Metabolism Gene: A segment of DNA or RNA that
... The DnaA-complex denatures the Origin forming an Open Complex. Then DnaB aids the binding of DnaC (a helicase) which unwinds the DNA bidirectionally. Topoisomerase II and single-strand DNA binding proteins cause 1000s of BP to be unwound. Initiation is the only point of regulation of replication but ...
... The DnaA-complex denatures the Origin forming an Open Complex. Then DnaB aids the binding of DnaC (a helicase) which unwinds the DNA bidirectionally. Topoisomerase II and single-strand DNA binding proteins cause 1000s of BP to be unwound. Initiation is the only point of regulation of replication but ...
Slide 1
... DNA Replication and Repair During cell division in eukaryotic cells, the replicated genetic material in the nucleus is _____ ________________________________________. It is important that each _________________has an ___________of the parent cell’s DNA. ...
... DNA Replication and Repair During cell division in eukaryotic cells, the replicated genetic material in the nucleus is _____ ________________________________________. It is important that each _________________has an ___________of the parent cell’s DNA. ...
Cell Division
... • The chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose rodlike appearance. A new nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes. ...
... • The chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose rodlike appearance. A new nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes. ...
Journey Into dna
... Which two scientists used Rosalind Franklin’s photo 51 to piece together the first accurate model of DNA? The structure of DNA resembles a _____________ ______________. DNA bases: Name the base for each abbreviation: T= A= C= G= A always pairs up with _____________. C always pairs up with __________ ...
... Which two scientists used Rosalind Franklin’s photo 51 to piece together the first accurate model of DNA? The structure of DNA resembles a _____________ ______________. DNA bases: Name the base for each abbreviation: T= A= C= G= A always pairs up with _____________. C always pairs up with __________ ...
Document
... along a template strand in a 3 to 5 direction. Therefore, the newly made lagging strand is synthesized in short pieces in the direction away from the replication fork. C22. The leading strand is primed once, at the origin, and then DNA polymerase III makes it continuously in the direction of the r ...
... along a template strand in a 3 to 5 direction. Therefore, the newly made lagging strand is synthesized in short pieces in the direction away from the replication fork. C22. The leading strand is primed once, at the origin, and then DNA polymerase III makes it continuously in the direction of the r ...
DNA - Biology at the Rural
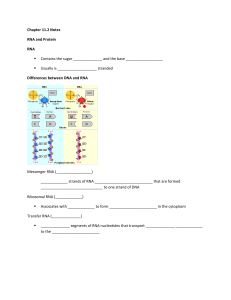
... “Working Copy” of DNA’s instructions to make proteins 13. What is the structure of RNA? Single stranded made of nucleotides (A,U,C,G); contains “ribose” as the sugar ...
... “Working Copy” of DNA’s instructions to make proteins 13. What is the structure of RNA? Single stranded made of nucleotides (A,U,C,G); contains “ribose” as the sugar ...
DNA Structure and Function
... along the gene briefly binding nucleotides to DNA (only about 10 nucleotides at a time), as the RNA nucleotides join together in a making a single complimentary strand • At Termination the mRNA moves out of nucleus, detaches and DNA recoils ...
... along the gene briefly binding nucleotides to DNA (only about 10 nucleotides at a time), as the RNA nucleotides join together in a making a single complimentary strand • At Termination the mRNA moves out of nucleus, detaches and DNA recoils ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.