Epigenetics and Inheritance
... or near. The work was coined by Conrad Waddington in the early 1940s to explain “the causal interactions between genes and their products, which bring the phenotype into being”. ...
... or near. The work was coined by Conrad Waddington in the early 1940s to explain “the causal interactions between genes and their products, which bring the phenotype into being”. ...
Advance Molecular Biology (LS6421, 1999)
... (2). X-linked variegation is caused by the random inactivation of one chromosome in each precursor cell (n-1 rule). (3). X-inactivation center (Xic) is a cis-acting locus that contains the information necessary to inactivate all copies of X chromosomes but one. (4). Xic has an element(s) for countin ...
... (2). X-linked variegation is caused by the random inactivation of one chromosome in each precursor cell (n-1 rule). (3). X-inactivation center (Xic) is a cis-acting locus that contains the information necessary to inactivate all copies of X chromosomes but one. (4). Xic has an element(s) for countin ...
DNA Replication - Texas Tech University
... Regulation of Transcription in Euks. Promoters can be affected by regulatory proteins bound 1000’s of bp’s away Require several transcription factors Chromatin packaging can help regulation of transcription ...
... Regulation of Transcription in Euks. Promoters can be affected by regulatory proteins bound 1000’s of bp’s away Require several transcription factors Chromatin packaging can help regulation of transcription ...
组蛋白甲基化
... addition of acetyl groups; some transcriptional coactivators have HAT activity. A deacetylase is an enzyme that removes acetyl groups from proteins. Histone deacetyltransferase (HDAC) enzymes remove acetyl groups from histones; they may be associated with repressors of transcription. ...
... addition of acetyl groups; some transcriptional coactivators have HAT activity. A deacetylase is an enzyme that removes acetyl groups from proteins. Histone deacetyltransferase (HDAC) enzymes remove acetyl groups from histones; they may be associated with repressors of transcription. ...
Poster
... activites such as turning off genes, promoting the repair DNA, maintaining genome stability, and in cell metabolism. They have even been linked to increased lifespan. For example, scientists have discovered that restricting calories can extend the life of several research organisms. They noticed tha ...
... activites such as turning off genes, promoting the repair DNA, maintaining genome stability, and in cell metabolism. They have even been linked to increased lifespan. For example, scientists have discovered that restricting calories can extend the life of several research organisms. They noticed tha ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... Human mtDNA does NOT have introns. Introns are non-coding SEQUENCES of the double helix. The absence of INTRONS in human mtDNA means that mutations will have a greater impact because all of the information is needed for normal cell structure and function; there is no “fluff” What does human mtDNA co ...
... Human mtDNA does NOT have introns. Introns are non-coding SEQUENCES of the double helix. The absence of INTRONS in human mtDNA means that mutations will have a greater impact because all of the information is needed for normal cell structure and function; there is no “fluff” What does human mtDNA co ...
Chromatin Structure Is a Focus for Regulation 30.2
... • Histone acetylation is associated with activation of gene expression. • All the core histones can be acetylated, but the major targets for acetylation are lysines in the N-terminal tails of histones H3 and H4 ...
... • Histone acetylation is associated with activation of gene expression. • All the core histones can be acetylated, but the major targets for acetylation are lysines in the N-terminal tails of histones H3 and H4 ...
Nature Rev.Mol.Cell Biol
... The 4.6 kb Bam HI fragment is present when the b-globin gene is inactive and histones are deacetylated ...
... The 4.6 kb Bam HI fragment is present when the b-globin gene is inactive and histones are deacetylated ...
Answers-pg-294 - WordPress.com
... and demethylated to modulate structure and/or interactions of the core histone tails,isorthat to the small size ofsites the for circular chromosomes bacteria prevents replication from occurring serve as binding ancillary proteins orofenzymes. more than one spotSample simply answer: due to the lack o ...
... and demethylated to modulate structure and/or interactions of the core histone tails,isorthat to the small size ofsites the for circular chromosomes bacteria prevents replication from occurring serve as binding ancillary proteins orofenzymes. more than one spotSample simply answer: due to the lack o ...
Access Slides
... • Provide a marker for recognition by other proteins. For example, a conserved “bromo” domain found in SWI/SNF and other transcription factors recognizes this marker. ...
... • Provide a marker for recognition by other proteins. For example, a conserved “bromo” domain found in SWI/SNF and other transcription factors recognizes this marker. ...
Epigenetics – Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors
... Interestingly, inhibition of HDAC enzymes have proven to have potential in cancer treatment, and four compounds targeting HDACs have been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration thus far. In the Olsen group, we explore several avenues towards inhibition of HDAC enzymes with the ai ...
... Interestingly, inhibition of HDAC enzymes have proven to have potential in cancer treatment, and four compounds targeting HDACs have been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration thus far. In the Olsen group, we explore several avenues towards inhibition of HDAC enzymes with the ai ...
Histone Modifications
... Constitute a Code? • The authors believe that the answer is no because: • The total number of modifications does not contain more information than the sum of individual modification. • Problem: it has been shown to be combinatorial – bdf1 in vitro preference for tetra acetylated H4. ...
... Constitute a Code? • The authors believe that the answer is no because: • The total number of modifications does not contain more information than the sum of individual modification. • Problem: it has been shown to be combinatorial – bdf1 in vitro preference for tetra acetylated H4. ...
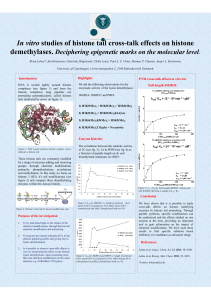
In vitro studies of histone tail cross
... We have shown that it is possible to study cross-talk effects on histone modifying enzymes by histone tail mimicking. Through peptide synthesis, specific combinations can be synthesized and the effects studied on one enzyme at the time, providing an important tool to gain information on the impact o ...
... We have shown that it is possible to study cross-talk effects on histone modifying enzymes by histone tail mimicking. Through peptide synthesis, specific combinations can be synthesized and the effects studied on one enzyme at the time, providing an important tool to gain information on the impact o ...
Chromatin Modifications
... following set of proteins, called histones: H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. 147 bp in each nucleosome. Heterochromatin is condensed chromatin, includes inactive genes and untranscribed regions (like the centromer). Euchromatin is non-condensed chromatin, includes active and repressed genes. ...
... following set of proteins, called histones: H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. 147 bp in each nucleosome. Heterochromatin is condensed chromatin, includes inactive genes and untranscribed regions (like the centromer). Euchromatin is non-condensed chromatin, includes active and repressed genes. ...
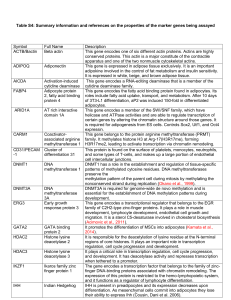
Table S4: Summary information and references on the properties of
... PCNA acts as a homotrimer and helps increase the processivity of leading strand synthesis during DNA replication. This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) subfamily of nuclear receptors. PPAR gamma is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation. N-terminal dom ...
... PCNA acts as a homotrimer and helps increase the processivity of leading strand synthesis during DNA replication. This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) subfamily of nuclear receptors. PPAR gamma is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation. N-terminal dom ...
Unpacking the Epigen..
... directly alter chromatin contacts, or they may indirectly remodel the structure.” ...
... directly alter chromatin contacts, or they may indirectly remodel the structure.” ...
The Code of Life: Topic 3
... DNA is negatively charged (phosphate groups) Histone proteins are positively charged This makes the DNA wrap around groups (8-9) of histones Each wrapped group is called a nucleosome The string then coils due to further charged-region interactions ...
... DNA is negatively charged (phosphate groups) Histone proteins are positively charged This makes the DNA wrap around groups (8-9) of histones Each wrapped group is called a nucleosome The string then coils due to further charged-region interactions ...
Chapter 19: Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... 8.) What are the steps for transcription initiation in eukaryotes? 9.) What is a transcriptional enhancer? How enhancers in the DNA work from such far distances? Lecture 26 “Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Part 2” PPT Review 1.) Is the final mature mRNA transcript composed of exons or intr ...
... 8.) What are the steps for transcription initiation in eukaryotes? 9.) What is a transcriptional enhancer? How enhancers in the DNA work from such far distances? Lecture 26 “Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Part 2” PPT Review 1.) Is the final mature mRNA transcript composed of exons or intr ...
Chapter 17 - Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... b. Regulatory transcription factors recognize regulatory elements that function as enhancers or silencers c. Regulatory transcription factors may exert their effects through TFIID and mediator d. The function of regulatory transcription factor proteins can be modulated in three ways e. Steroid hormo ...
... b. Regulatory transcription factors recognize regulatory elements that function as enhancers or silencers c. Regulatory transcription factors may exert their effects through TFIID and mediator d. The function of regulatory transcription factor proteins can be modulated in three ways e. Steroid hormo ...
Chromatin Structure and Gene Regulation
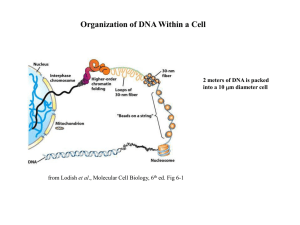
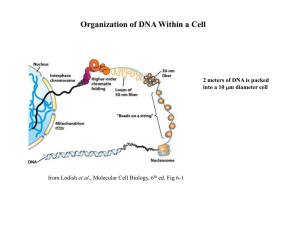
... • Chromatin – DNA/protein complex in eukaryotic cells • All the DNA in a cell, if spread out, would be thousands of times longer than the diameter of the cell – which is why chromatin folding is necessary ...
... • Chromatin – DNA/protein complex in eukaryotic cells • All the DNA in a cell, if spread out, would be thousands of times longer than the diameter of the cell – which is why chromatin folding is necessary ...
Dioxygen Binding in the Active Site of Histone Demethylase
... Now we have studied the first step of demethylation by JmjC proteins, highlighting the importance of non-local energy contributions from residues and substrate. Our next steps will involve understanding the structural basis for substrate selectivity within the active site, and the full reaction coor ...
... Now we have studied the first step of demethylation by JmjC proteins, highlighting the importance of non-local energy contributions from residues and substrate. Our next steps will involve understanding the structural basis for substrate selectivity within the active site, and the full reaction coor ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... Laemmli, Metaphase chromosome structure: Evidence of a radial loop model. Cell 17:856, ...
... Laemmli, Metaphase chromosome structure: Evidence of a radial loop model. Cell 17:856, ...
Histone acetyltransferase

Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.In general, histone acetylation is linked to transcriptional activation and associated with euchromatin. When it was first discovered, it was thought that acetylation of lysine neutralizes the positive charge normally present, thus reducing affinity between histone and (negatively charged) DNA, which renders DNA more accessible to transcription factors. Research has emerged, since, to show that lysine acetylation and other posttranslational modifications of histones generate binding sites for specific protein–protein interaction domains, such as the acetyllysine-binding bromodomain. Histone acetyltransferases can also acetylate non-histone proteins, such as nuclear receptors and other transcription factors to facilitate gene expression.