MCB317 Topic 10, part 4, A Story of Txn Sp14
... Transform Reporter into each of our mutant strains: snf1-, snf2-, snf3-, snf4-, snf5-, snf6-, etc. Three key complementation groups identified: SNF2, SNF5 and GCN5 ...
... Transform Reporter into each of our mutant strains: snf1-, snf2-, snf3-, snf4-, snf5-, snf6-, etc. Three key complementation groups identified: SNF2, SNF5 and GCN5 ...
Gene Regulation Summary Slide Questions with
... Regions in chromosomes that are devoid of nucleosomes and allow for the binding of Tfs. About 100200 bp, within 100 bp upstream from the iniation site, but could be somewhere else (if DNA is folding over). These are tissue specific and can be used to figure out tumor origin, etc. 10. What is hemoglo ...
... Regions in chromosomes that are devoid of nucleosomes and allow for the binding of Tfs. About 100200 bp, within 100 bp upstream from the iniation site, but could be somewhere else (if DNA is folding over). These are tissue specific and can be used to figure out tumor origin, etc. 10. What is hemoglo ...
Activator Proteins
... • mark unwanted proteins with a label • 76 amino acid polypeptide, ubiquitin • labeled proteins are broken down rapidly in "waste ...
... • mark unwanted proteins with a label • 76 amino acid polypeptide, ubiquitin • labeled proteins are broken down rapidly in "waste ...
Chromosomes
... meiotically heritable changes in gene function that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence (Riggs et al. 1996) ...
... meiotically heritable changes in gene function that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence (Riggs et al. 1996) ...
Enhancer
... • Noncoding DNA segments with high regulatory potential • PRPs: Intersection of the High RP segments and the PReMods (clusters of conserved transcription factor binding site motifs) • Most constrained DNA segments, phastCons • DNase hypersensitive sites in CD4+ T cells • DNA segments occupied by CTC ...
... • Noncoding DNA segments with high regulatory potential • PRPs: Intersection of the High RP segments and the PReMods (clusters of conserved transcription factor binding site motifs) • Most constrained DNA segments, phastCons • DNase hypersensitive sites in CD4+ T cells • DNA segments occupied by CTC ...
Epigenetics-2015
... display reduced maternal care, even in the absence of stress The altered gene expression of target genes (GR in the hippocampus) is mediated by DNA methylation and histone modifications Expression patterns are inherited in future generations ...
... display reduced maternal care, even in the absence of stress The altered gene expression of target genes (GR in the hippocampus) is mediated by DNA methylation and histone modifications Expression patterns are inherited in future generations ...
Synthetic approaches to transcription factor
... • DNA-binding domain (DBD), which attach to specific sequences of DNA • Trans-activating domain (TAD), which contain binding sites for other proteins such as transcription coregulators. • Optional signal sensing domain (SSD) (e.g., a ligand binding domain), which senses external signals and in respo ...
... • DNA-binding domain (DBD), which attach to specific sequences of DNA • Trans-activating domain (TAD), which contain binding sites for other proteins such as transcription coregulators. • Optional signal sensing domain (SSD) (e.g., a ligand binding domain), which senses external signals and in respo ...
Human gene expression and genomic imprinting
... approx. 10 nm in diameter, are in turn coiled into a chromatin fiber ; the interphase chromosomes seems to consists of these chromatin fibers ...
... approx. 10 nm in diameter, are in turn coiled into a chromatin fiber ; the interphase chromosomes seems to consists of these chromatin fibers ...
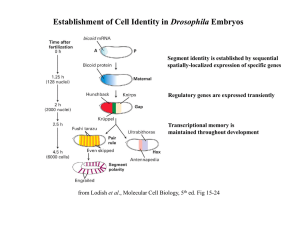
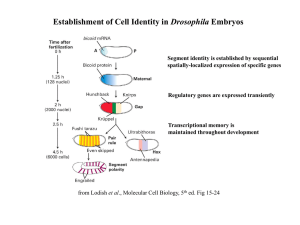
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... by de novo DNMTs at the blastocyst stage Primordial germ cells are demethylated through a TET-independent and a TET-mediated oxidative pathway ...
... by de novo DNMTs at the blastocyst stage Primordial germ cells are demethylated through a TET-independent and a TET-mediated oxidative pathway ...
struktur dan fungsi kromosom
... AUTOSOM : kromosom yang tidak ada hubungannya dengan penentuan jenis kelamin KROMOSOM KELAMIN (sex chromosome) : kromosom yang ada hubungannya dengan penentuan jenis kelamin ...
... AUTOSOM : kromosom yang tidak ada hubungannya dengan penentuan jenis kelamin KROMOSOM KELAMIN (sex chromosome) : kromosom yang ada hubungannya dengan penentuan jenis kelamin ...
1768-6475-2-RV
... Histone acetylation occurs by the enzymatic addition of an acetyl group (COCH3) from acetyl coenzyme A. The process of histone acetylation is tightly involved in the regulation of many cellular processes including chromatin dynamics and transcription, gene silencing, cell cycle progression, apoptosi ...
... Histone acetylation occurs by the enzymatic addition of an acetyl group (COCH3) from acetyl coenzyme A. The process of histone acetylation is tightly involved in the regulation of many cellular processes including chromatin dynamics and transcription, gene silencing, cell cycle progression, apoptosi ...
Kinetic proofreading of gene activation by chromatin remodeling
... be activated. While in our example we have distinguished between an acetylated versus a deacetylated state, other covalent modifications and their combinations [the “histone code,” (Strahl and Allis, 2000)] can clearly be included since their presence affects the off-rates kD, r−D, dD and t−D. For e ...
... be activated. While in our example we have distinguished between an acetylated versus a deacetylated state, other covalent modifications and their combinations [the “histone code,” (Strahl and Allis, 2000)] can clearly be included since their presence affects the off-rates kD, r−D, dD and t−D. For e ...
Supplementary Data
... immunoprecipitated by HDAC antibodies the cycle number was increased to 32 for all primer pairs. Input DNA was diluted to approximately 0.1 ng/µl and 5 µl used per PCR. As a result of the increased PCR cycle number, no statements can be made about the quantitative levels of HDACs associated with spe ...
... immunoprecipitated by HDAC antibodies the cycle number was increased to 32 for all primer pairs. Input DNA was diluted to approximately 0.1 ng/µl and 5 µl used per PCR. As a result of the increased PCR cycle number, no statements can be made about the quantitative levels of HDACs associated with spe ...
Epigenetics of Coeliac Disease
... Why this project? • Epigenetics is the first level of integration of genetic and environmental factors. • It may translate the effects of risk factors in terms of molecular events. • It is feasable with the recent development of micro arrays/Si RNA knowledge. • There is no data published to date on ...
... Why this project? • Epigenetics is the first level of integration of genetic and environmental factors. • It may translate the effects of risk factors in terms of molecular events. • It is feasable with the recent development of micro arrays/Si RNA knowledge. • There is no data published to date on ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... E : binding sites for the transcription factor MyoD; P : binding sites for the transcription factor PBX; M : binding sites for the transcription factor MEF2; T : the TATA box for Myog. In undifferentiated cells, several of these sites are inaccessible to the proteins that bind them due to the confor ...
... E : binding sites for the transcription factor MyoD; P : binding sites for the transcription factor PBX; M : binding sites for the transcription factor MEF2; T : the TATA box for Myog. In undifferentiated cells, several of these sites are inaccessible to the proteins that bind them due to the confor ...
... methylation is unlikely to be unique to C. elegans, since the relevant HMTs are quite conserved: MET-2 is the homolog of human SetDB1 or ESET, and catalytic domain of SET-25 strongly resembles the human HMT, G9a or hSUV3-9, and H3K9 methylation also correlates with lamin-associated domains in mouse ...
Gene7-21
... 6. HLH (helix-loop-helix) proteins have amphipathic helices that are responsible for dimerization, adjacent to basic regions that bind to DNA. 7. Many transcription factors function as dimers, and it is common for there to be multiple members of a family that form homodimers and heterodimers. 8. The ...
... 6. HLH (helix-loop-helix) proteins have amphipathic helices that are responsible for dimerization, adjacent to basic regions that bind to DNA. 7. Many transcription factors function as dimers, and it is common for there to be multiple members of a family that form homodimers and heterodimers. 8. The ...
DNA Packaging
... Histones are rich in the basic amino acids arginine and lysine, which together make up about 25% of the amino acid residues in any given histone protein. ...
... Histones are rich in the basic amino acids arginine and lysine, which together make up about 25% of the amino acid residues in any given histone protein. ...
NUCLEUS
... Gene activity depends on: the stage of ontogenetic period, type of cell, environment. It also depends on the level of DNA condensation. Transcription is associated with nucleosomal level only. Transcriptionally active chromatin regions have core histones undergoing high rates of acetylation and deac ...
... Gene activity depends on: the stage of ontogenetic period, type of cell, environment. It also depends on the level of DNA condensation. Transcription is associated with nucleosomal level only. Transcriptionally active chromatin regions have core histones undergoing high rates of acetylation and deac ...
Chromosomes and DNA Packaging
... Very thin (2.0 nm), extremely fragile Diameter of nucleus = 5-10 mm DNA must be packaged to protect it, but must still be accessible to allow gene expression and cellular responsiveness ...
... Very thin (2.0 nm), extremely fragile Diameter of nucleus = 5-10 mm DNA must be packaged to protect it, but must still be accessible to allow gene expression and cellular responsiveness ...
Class 11
... These complexes affect the interaction of DNA with the nucleosomes – opening the DNA for access by other factors ...
... These complexes affect the interaction of DNA with the nucleosomes – opening the DNA for access by other factors ...
Ch_ 19_2
... expression can occur at any step in the pathway from gene to functional protein 1. packing/unpacking DNA 2. transcription 3. mRNA processing 4. mRNA transport 5. translation 6. protein processing 7. protein degradation ...
... expression can occur at any step in the pathway from gene to functional protein 1. packing/unpacking DNA 2. transcription 3. mRNA processing 4. mRNA transport 5. translation 6. protein processing 7. protein degradation ...
Histone acetyltransferase

Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.In general, histone acetylation is linked to transcriptional activation and associated with euchromatin. When it was first discovered, it was thought that acetylation of lysine neutralizes the positive charge normally present, thus reducing affinity between histone and (negatively charged) DNA, which renders DNA more accessible to transcription factors. Research has emerged, since, to show that lysine acetylation and other posttranslational modifications of histones generate binding sites for specific protein–protein interaction domains, such as the acetyllysine-binding bromodomain. Histone acetyltransferases can also acetylate non-histone proteins, such as nuclear receptors and other transcription factors to facilitate gene expression.